Wilfred Hugh Miller Kirk was perhaps Richmond Chess Club’s strongest player between 1925 and 1937, as well as playing an important administrative role in the club.
Wilfred was born in Culmstock, Devon on 18 May 1877, where Teddington novelist, market gardener and chess player RD Blackmore also lived for a time. His family were originally from London, but his father was working in Devon as a Schools Inspector at the time of his birth. The family later returned to London, where young Wilfred joined the Civil Service on leaving school. He would remain there for his entire working life.
In 1899 he married 20 year old Mabel Ellen Gannaway. Wilfred and Mabel had four children, Talbot (1902), Beatrice (1903), Evelyn (1907) and Ruby (1908).
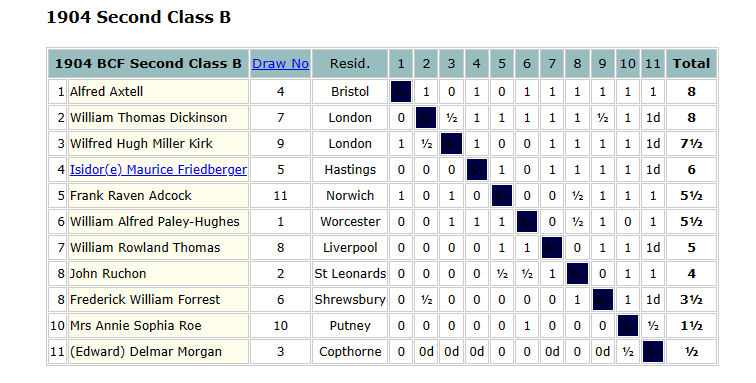
We hear of him as a chess player for the first time only in 1904, at the age of 27, when he took part in the Second Class B section of the inaugural British Championships at Hastings. He did pretty well for a newcomer to competitive chess, finishing in third place, just half a point behind the joint winners.
The following year he took part in the Kent Open Amateur 2nd Class A tournament, held that year at Crystal Palace, where he shared first place with his old rival WT Dickinson.
Shortly afterwards, leaving his wife and two young children at home, he crossed the channel to Ostend, where a mammoth tournament was taking place. The master event had no less than 36 entrants, with a complex group structure, and, below that, there were two amateur sections which attracted a number of British participants. Wilfred played in the Amateur B section, scoring a very respectable 11/17.
He didn’t take part in another tournament until 1908, when he again played in the Kent congress, that year held in Sevenoaks. This time Wilfred was promoted to the 1st Class Open Section 2. He found 1st class competition a lot tougher than the 2nd class, scoring only 1½/6, The leading scores in this section were Harold Godfrey Cole (5), Kate Belinda Finn and Percy Rawle Gibbs (4½). Miss Finn wasn’t the only (fishy) lady in the section: Mrs Frances Dunn Herring brought up the rear on 1/6.
Although he wasn’t very active in tournament play at the time, he was very much involved in Civil Service chess. He may well have been playing for the Local Government Board before his first tournament, and, when the Civil Service Chess League was founded in 1904 he was appointed to the post of Secretary.
When the British Championships were held in Richmond in 1912 he returned to the fray. This time he was in the 1st Class Amateurs B section, and, from the result, it was clear that he was a lot stronger now than a few years earlier.
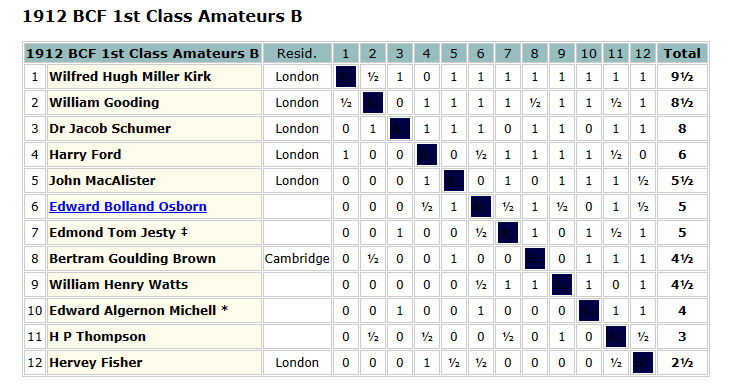
The British Chess Magazine (October 1912) remarked that Mr. W. H. M. Kirk (Putney) is a well-known fine player in the Civil Service League, but does not play much otherwise. With work and family commitments, it was understandable that he wouldn’t have had much time for tournament play.
Unfortunately the only game of his from this event that appears to be extant was his only defeat. For all games in this article, click on any move for a pop-up window.
Kirk took part in the Surrey Championship that year, where he finished in first place with a score of 4½/5. This time we do have one of his wins, which his opponent, a dentist usually known as Frank St J Steadman, generously submitted to the British Chess Magazine. It was published in their December 1912 issue.
Wilfred entered the 1st Class Open in the 1913 Kent & Sussex Congress but had to withdraw before the start of the tournament. However, he did play in the Major Open section of the 1913 British Championship, making a respectable showing in a strong tournament.
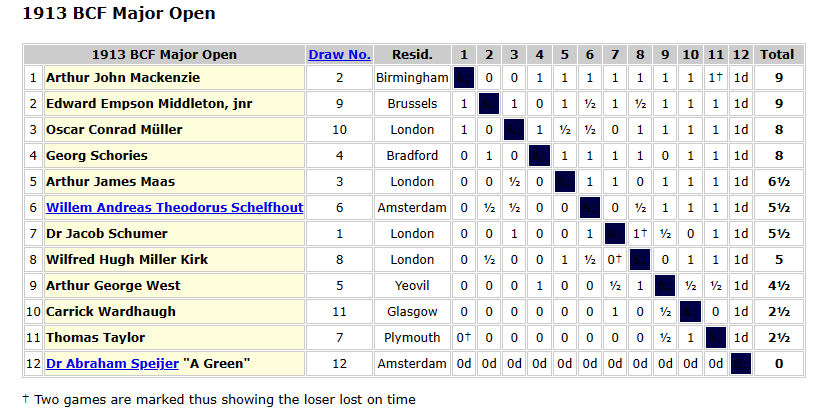
Here’s a loss against the German born but English resident Georg Schories, a regular Major Open competitor whose nationality precluded his participation in the championship.
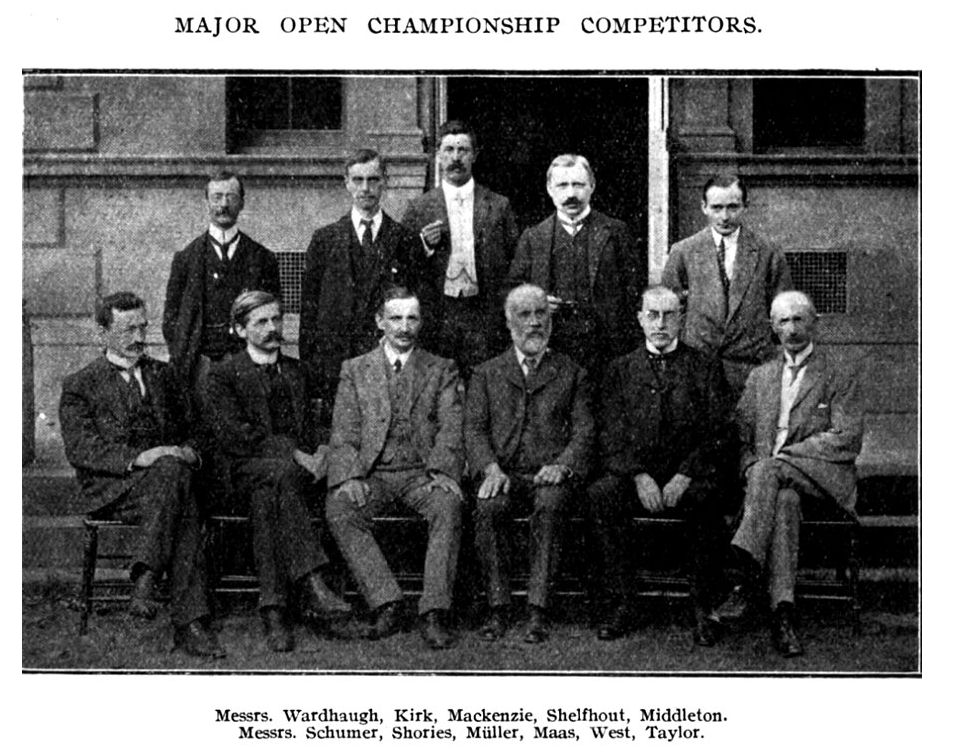
In this photograph of the competitors in this section, Kirk is the good looking youngish man (he was now 35) standing second on the left. He doesn’t look very happy, does he? But then they rarely did in those days.

And then World War 1 intervened. The Civil Service Chess League continued in 1915, but then stopped for the duration, only resuming in 1919.
The British Championships were also suspended, again resuming with a Victory Congress at Hastings in August that year. The British title itself wasn’t awarded, the top section being a semi-international event with visiting stars Capablanca and Kostic taking the first two places, well ahead of Sir George Thomas and Yates. The Major Open went to Edward Guthlac Sergeant, and, below that were three parallel First Class sections. Kirk was in the C section, finishing in first place, beating, amongst others, future World Champion Max Euwe. The enforced break had done nothing to dull his chess strength.
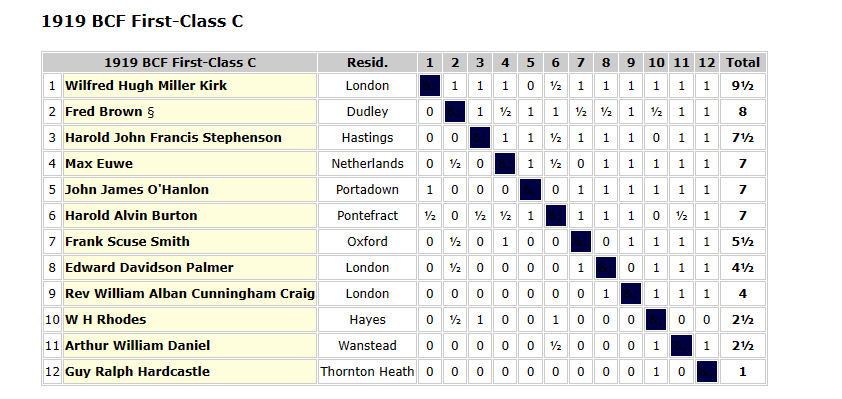
Again, his only loss, against Irish champion John James O’Hanlon, is the only one of his games from this event I’ve been able to locate.
In 1919 he also entered the City of London Chess Club Championship: the only time he took part in this prestigious event. He finished in 6th place with 6/11 behind Sir George Thomas, a clear winner on 9½, Michell, Walker, EG Sergeant and Blake, whom he beat in this game: a notable scalp.
Throughout much of his life, Wilfred Kirk seemed to move house every two or three years. He had previously lived in Putney and Wimbledon, but by this time had moved to North London, playing for Hampstead Chess Club and winning the Middlesex Championship in 1920. He had also moved departments in the Civil Service, from the Local Government Board to the Ministry of Health.
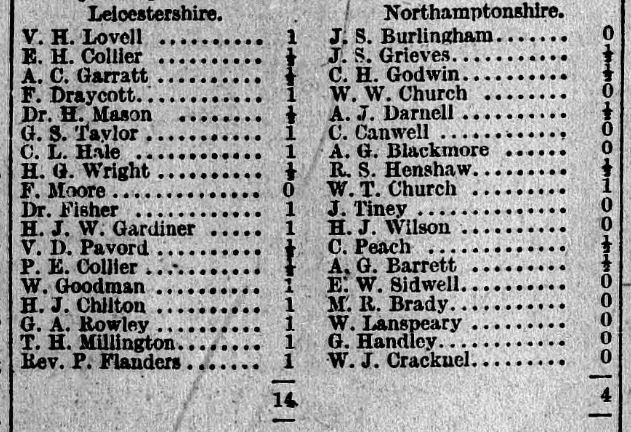
Then, in Autumn 1925, he moved to Richmond, living in several addresses in Richmond and Twickenham in the following 12 years or so. He wasted no time in joining Richmond Chess Club, but, in his first match, was only playing on Board 3.
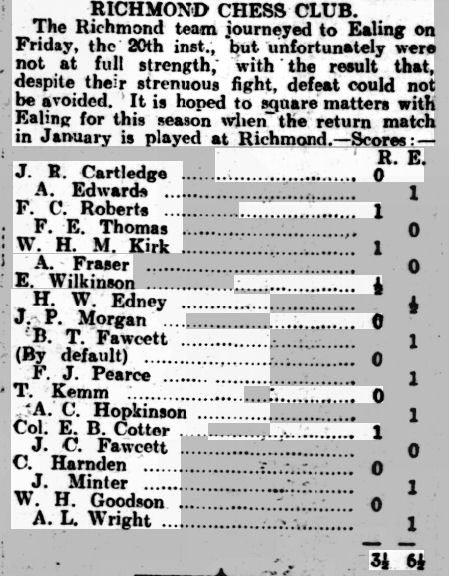
He also entered the Surrey Championship, in 1926 regaining the title he had previously won 14 years earlier.
As an able administrator he was soon appointed secretary of his new club, as reported here, where, on top board, he was successful against our old friend George Archer Hooke.
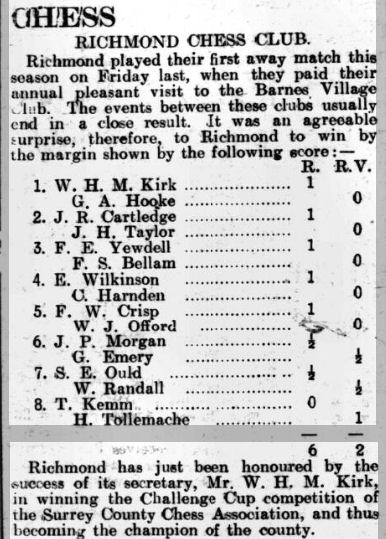
His addresses at this point included 17 The Barons, St Margarets in 1927 and 27 Richmond Hill in 1928.
In the 1928-29 season Kirk swept the board, winning not just the club championship (you’ll see PGL Fothergill in 3rd place: he only seemed to play in internal competitions rather than club matches), but the handicap tournament (one wonders how the scores were calculated) and the prize for the best percentage score in matches.

That summer he took part in a Living Chess game against Reginald Pryce Michell at Asgill House in Richmond to raise money for the local hospital.

Wilfred was very much involved in charitable endeavours of all sorts, promoting chess at the Star and Garter Home for disabled ex-Servicemen, donating money to a fund for distressed miners, and, later in life. helping at a local home for the blind.
That summer, by then in his 50s, he unexpectedly received an invitation to take part in the British Championship, held that year in Ramsgate.
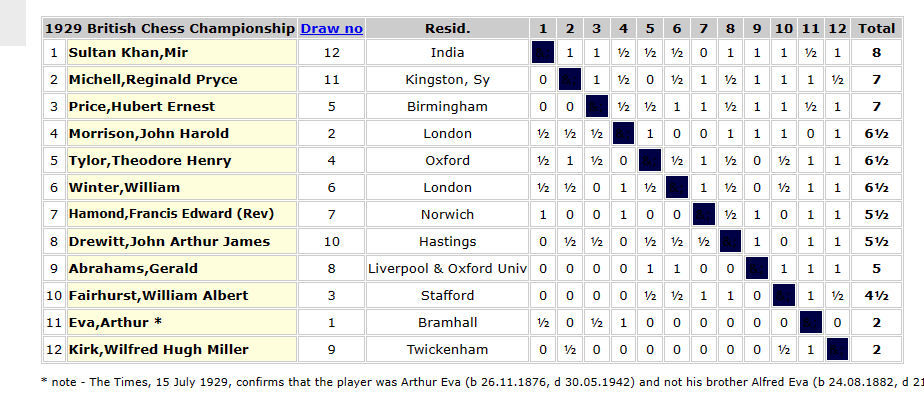
Wilfred was a very effective player top level club opposition, but here, against mostly master standard opponents, he was rather out of his depth.
He lost in 19 moves to Gerald Abrahams: a game which attracted some attention at the time. Abrahams, rather typically, played a speculative sacrifice which Kirk should have accepted, but instead declined it and resigned the next move.
Here’s his draw against future Scottish champion and bridge designer William Albert Fairhurst.

In this group photograph, Kirk is standing on the left next to the permanently disheveled William Winter.
That year there was a merger between Richmond and Kew chess clubs, who, however, continued to meet at both venues on different days of the week. Kirk now had a serious rival in Kew star Ronald George Armstrong, about whom more in a future Minor Piece.
Meanwhile, in 1933, Kirk’s service to chess in the Civil Service was marked by a presentation.

This 1934 match must have been a surprise result.
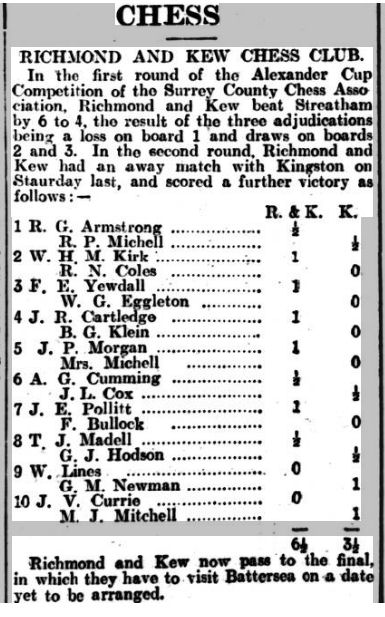
Richmond & Kew were a second division team, playing in the Beaumont Cup, while Kingston, who had won the Surrey Trophy two years earlier, were a genuine first division team. Unfortunately, they lost to Battersea in the final of the Alexander Cup.
Armstrong must have been very pleased with his draw against Michell, while Kirk also shared the point with (Richard) Nevil Coles, who later became a celebrated chess author and who beat me in a Richmond v Guildford Surrey Trophy match in 1972.

In the 1934-35 season Kirk won the club championship while Armstrong took the handicap shield: they gave a tandem simul at the end of season prizegiving.

It was the same story in 1937, with Kirk taking the club championship for the sixth time with a 100% score, and Armstrong again preferring the handicap shield. Wilfred was now entitled to hold the cup in perpetuity, but generously returned it for future years. I wonder what happened to it.
At this point, though, Wilfred Kirk retired from the Civil Service, spending some time travelling round Europe playing chess before moving, like many retired chess players of the time, to Hastings.
However, he competed in the 1938 British Championships in Brighton, now down in the First Class B section, where he shared first place on 7/11, winning this miniature.
He was soon involved in administration again, both at Hastings Chess Club, and with their annual tournament. He also found time to compete in the 1938-39 event, sharing second place in the Premier Reserves C section.
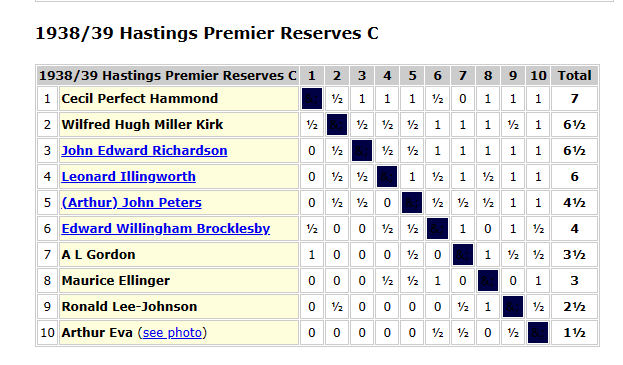
He also threw himself into county chess, here losing to another former Civil Service player Bernard Henry Newman Stronach.
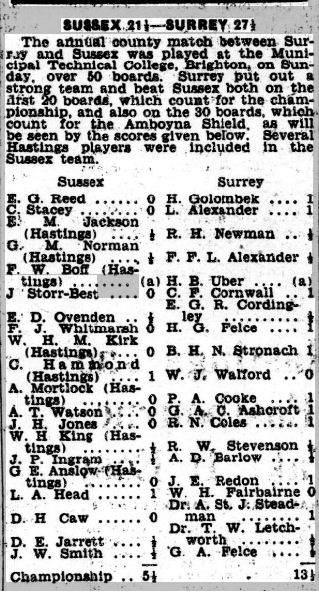
By now the world was at war again, but Hastings managed to arrange their annual tournament that winter, with Kirk taking part in the Premier.
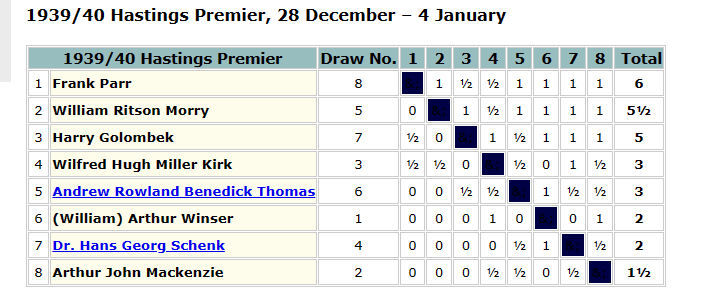
In this game he held the tournament winner Frank Parr to a draw, sacrificing a knight for a perpetual check.
Although it was no longer possible to run formal competitions, Hastings Chess Club remained active during the war, with friendly matches against local rivals Eastbourne and Bexhill.
His opponent in this game, George Edward Anslow, a Gas Company clerk, was a member of both Eastbourne and Hastings Chess Clubs for many years. He beat me in a 1974 friendly match between Hastings and Richmond & Twickenham Chess Clubs.
Frederick William (Fred) Boff, whom he defeated in this game, seems to have been an interesting character both on and off the chessboard.
He was still very active locally as the war finally came to an end, and was involved in the administration of the 1945-46 Hastings Congress as Treasurer and Assistant Secretary. In June that year, still playing regularly in club events, he was taken ill with appendicitis. The operation, sadly, proved unsuccessful.


There’s more information in this pen picture from Kevin Thurlow’s book on chess in the English Civil Service.

Wilfred Hugh Miller Kirk, then, was a strong player (2261 at his peak according to EdoChess) and a highly efficient administrator. He seems to have been well respected at work and was also devoted to various charitable causes.
His family life, though, wasn’t happy.
In the 1901 census we see Wilfred and Mabel, only recently married, and living in Pimlico.
They soon moved south of the river, the births of their first three children being registered in Wandsworth, and the youngest in Balham.
By 1911 the family had split up. Wilfred was living on his own in Streatham, a Second Division Clerk in the Civil Service. Mabel didn’t appear to be around. Talbot, Beatrice and Evelyn (aged 9, 7 and only 4) were boarding at a school in Wimbledon, while 2-year-old Ruby was living with Wilfred’s mother in Battersea.
Then, in 1914, Mabel filed a petition for judicial separation. She was represented by her solicitor, PR Gibbs, who, I’d imagine, was the same Percy Rawle Gibbs who had played Wilfred at Sevenoaks in 1908.
Mabel’s petition, citing eight addresses, mostly in the Wandsworth area, at which they lived during their marriage, listed dates and places, from 1906 onwards, when and where Wilfred had assaulted her, and treated her with coldness and neglect. He had punched her on her body and head, thrown her against the furniture and onto the floor, grabbed her by the collar and dragged her upstairs. Wilfred denied the charges of cruelty, claiming that Mabel had become mentally deranged and assaulted him violently, and he was only acting in self-defence. On other occasions she had become hysterical and behaved in an ill tempered and unreasonable manner, causing him to lose his temper.
It was also revealed that, from late 1910, she had been a patient at St Luke’s Hospital: she was probably still there at the time of the 1911 census.
The separation was granted, with Mabel having custody of the two older children and Wilfred the two younger children. Would a man who had assaulted his wife, even with provocation, be given custody of two young girls today?
Was he a violent and abusive wife beater whose behaviour had driven his wife to the lunatic asylum, or a good man who found it difficult to cope with his wife’s mental health problems? I don’t know: I wasn’t there and it’s far from me to pass judgement.
The ramifications continued for a decade (the papers are available online at ancestry.co.uk).
The 1921 census found Wilfred now living in Islington with Evelyn and Ruby, who were both at school. Mabel and Beatrice, now an art student, were the other side of London, in South Norwood. Meanwhile, Talbot had emigrated to the USA, where he married in 1927 and had two sons, Fred (1928-76) and Jack (1929-67).
His marriage didn’t last and he returned to England. The 1933 Electoral Roll shows Mabel, Talbot and Beatrice sharing a house right by Hampstead Heath.
Then, in 1934, Wilfred sued Mabel for divorce on the grounds of adultery.

Well, I don’t know. In September that year he married Olive Emily Holmes. Was he committing adultery as well? Again, I wasn’t there.
What happened to the rest of his family? Talbot remarried in 1941 in Brentford, at some point moving to Yorkshire, where he died in 2006 at the extraordinary age of 104.
Beatrice never married: by 1939 she was working as a typist in the Ministry of Food, and died in Hastings at the age of 78.
Evelyn married young, in 1926, to a man almost twice her age, George Arthur Tomlinson, who seems to have been a mechanical engineer working at the National Physical Laboratory in Teddington. They lived with Wilfred for a time after the marriage before moving to North London where two sons, Brian (1928) and Robin (1930) were born. George died in 1944, but Evelyn, like her brother, lived a long life, dying in Bath at the age of 96.
Ruby married in 1939, like Evelyn to a much older man: a divorcee with the impressive name Bernard de Lerisson Cazenove. She had no children and, again like Evelyn, lived into her 90s: she was 91 when she died in Warwickshire.
The report of Wilfred’s cremation leaves some questions unanswered. You might have wondered why the local paper mentioned that he left a son, but failed to note his daughters.

At the cremation, Talbot, Evelyn and Ruby were there, but there was no mention of Beatrice as a chief mourner. Did the paper forget her? Or had they become estranged?
Talbot, Dolly and Sylvia sent flowers, but who were Dolly and Sylvia? There were also flowers from Eric, Brian and Robin. Brian and Robin were his grandsons, but who was Eric? And why wasn’t Evelyn included? Her second marriage, in 1948, would be to Ernest (Vokes), not to Eric. Or was ‘Eric’ a misreading of ‘Evelyn’?
There’s one further family tragedy to report.

This is Wilfred and Mabel’s grandson Robin taking his own life in 1950, at the age of 19.
Had he inherited mental health problems from his mother? Impossible to tell, of course.
Although Wilfred Hugh Miller Kirk was a formidable club player and respected administrator, it seems that his family life was unsettled (moving house every couple of years) and unhappy. I can only hope that the game of chess brought him some comfort.
Sources:
ancestry.co.uk
findmypast.co.uk
British Newspaper Library
Wikipedia
BritBase (John Saunders)
EdoChess (Kirk’s page here)
chessgames.com (Kirk’s page here)
British Chess Magazine 1912
A History of Chess in the English Civil Service (Kevin Thurlow: Conrad Press)
The City of London Chess Club Championship (Roger Leslie Paige: Publish & be Damned)
Hastings & St Leonards Chess Club website (Brian Denman article here)