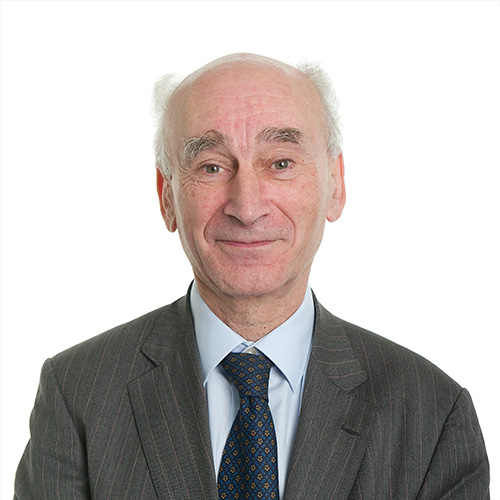
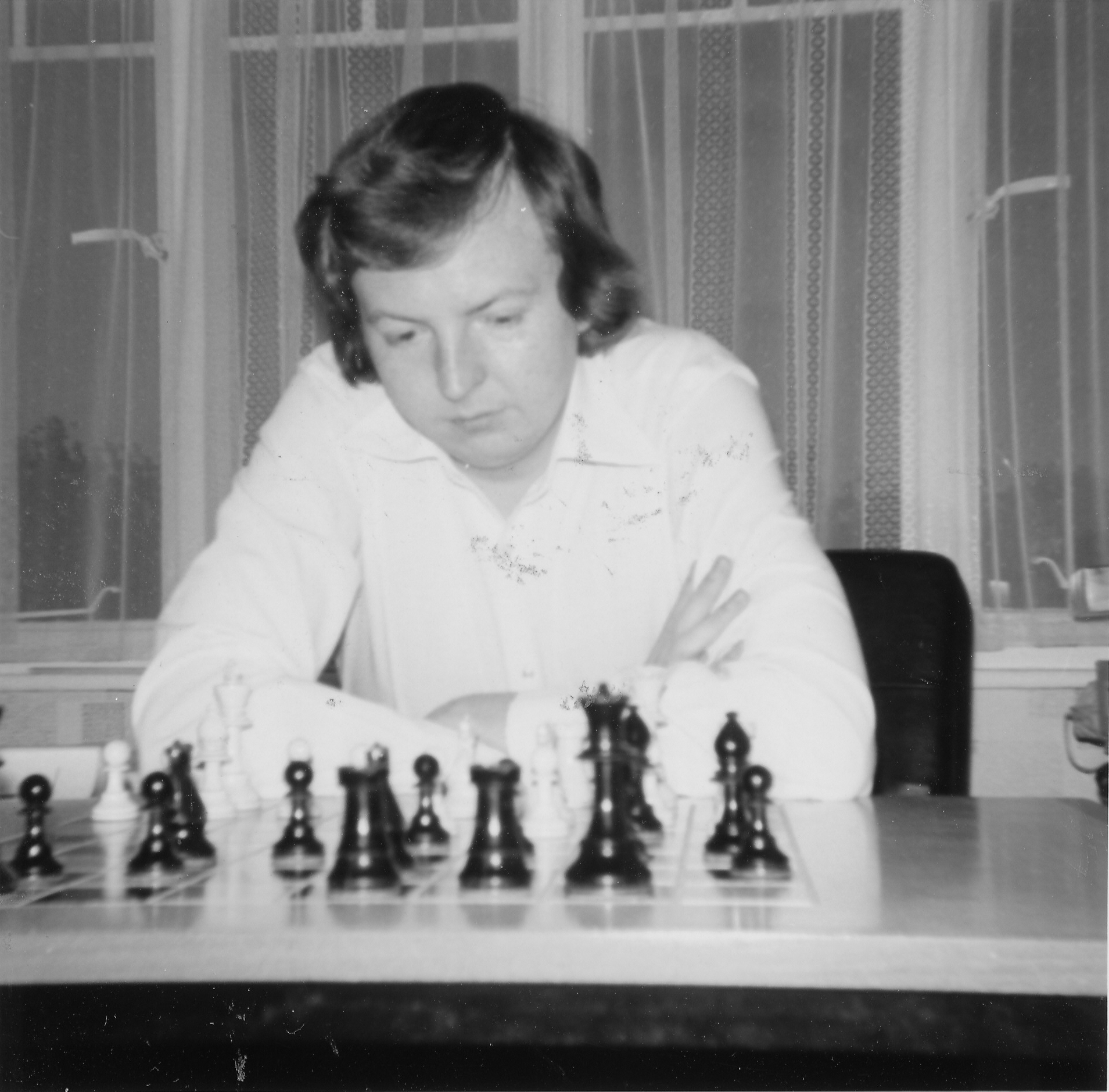
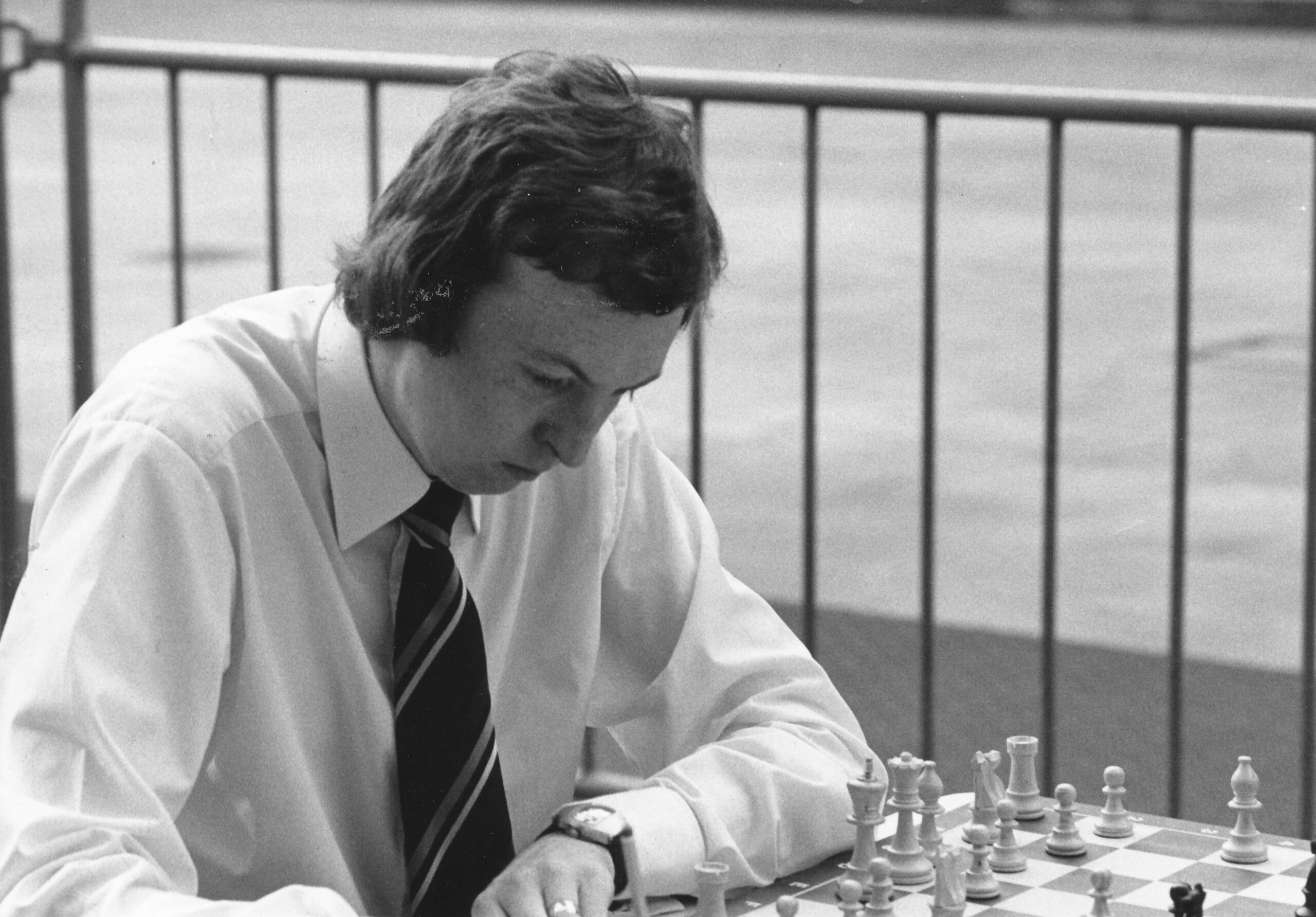
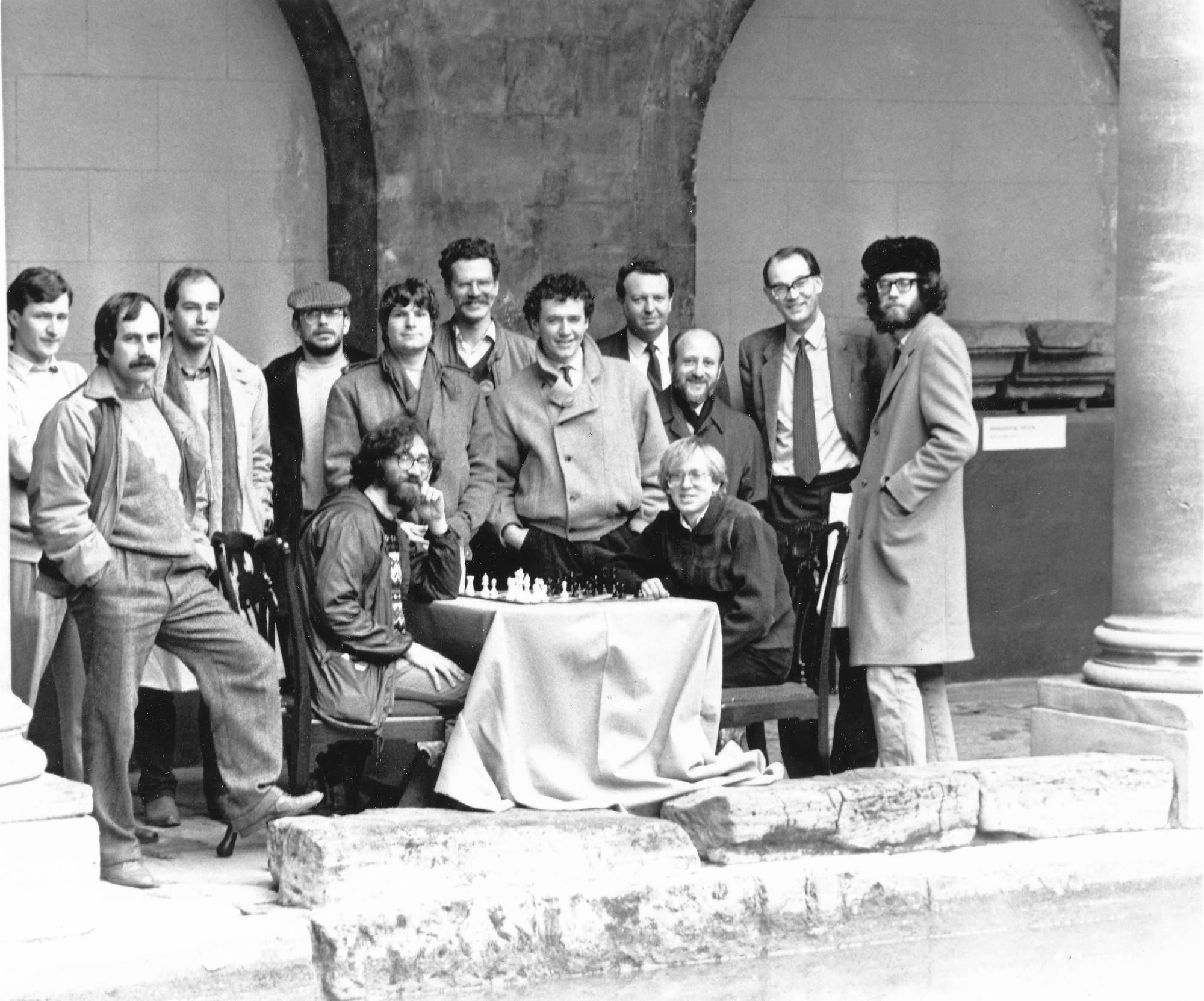
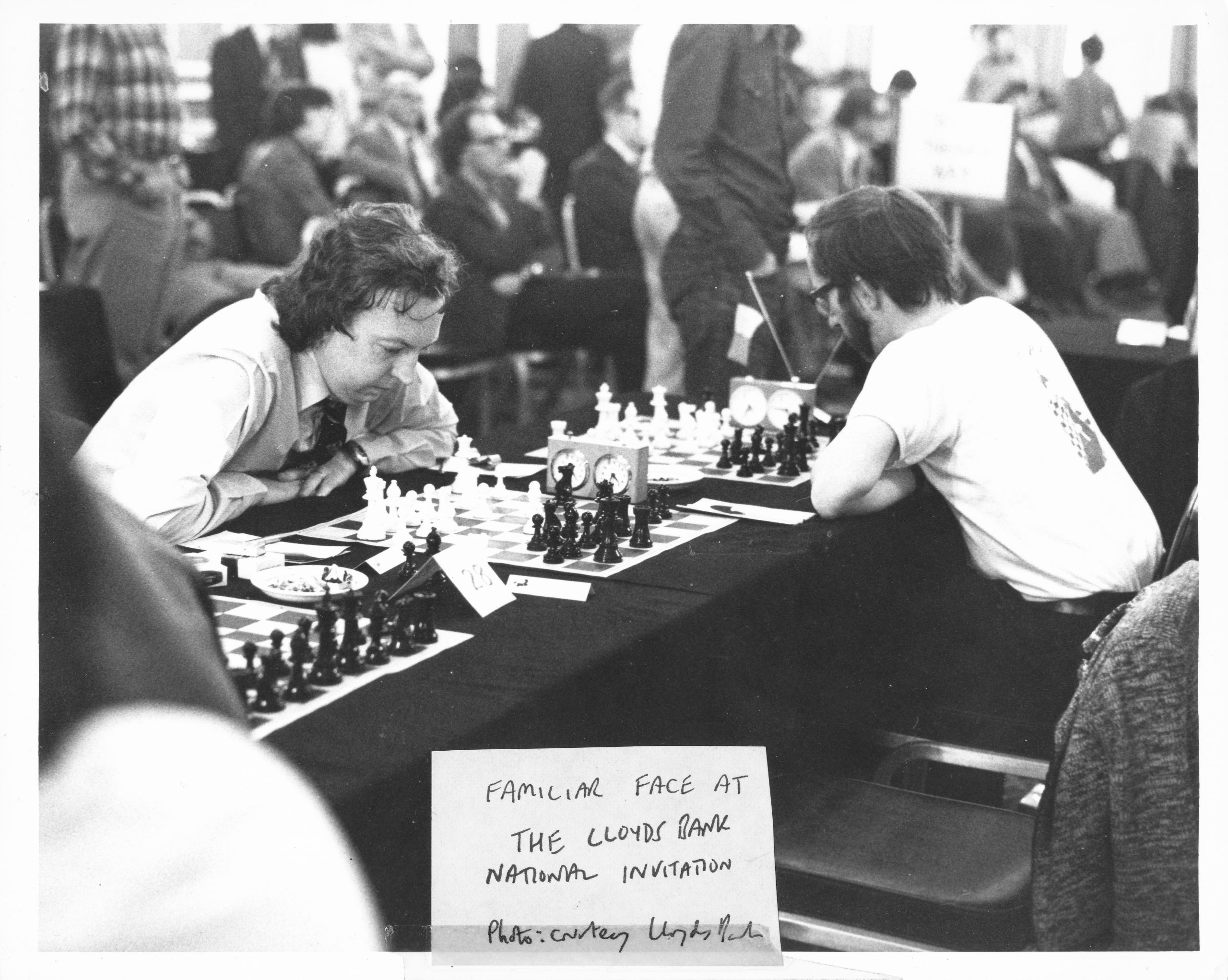
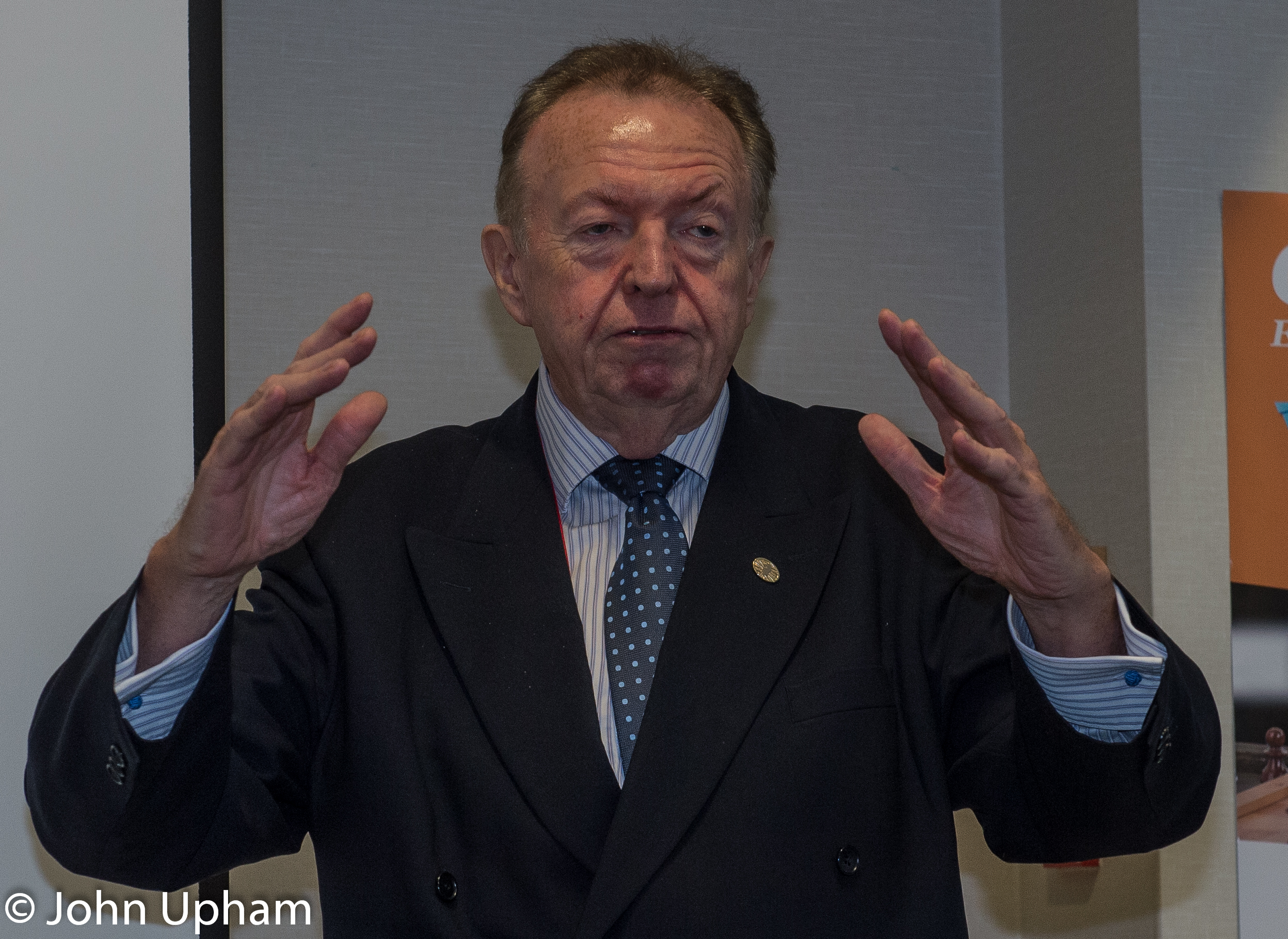
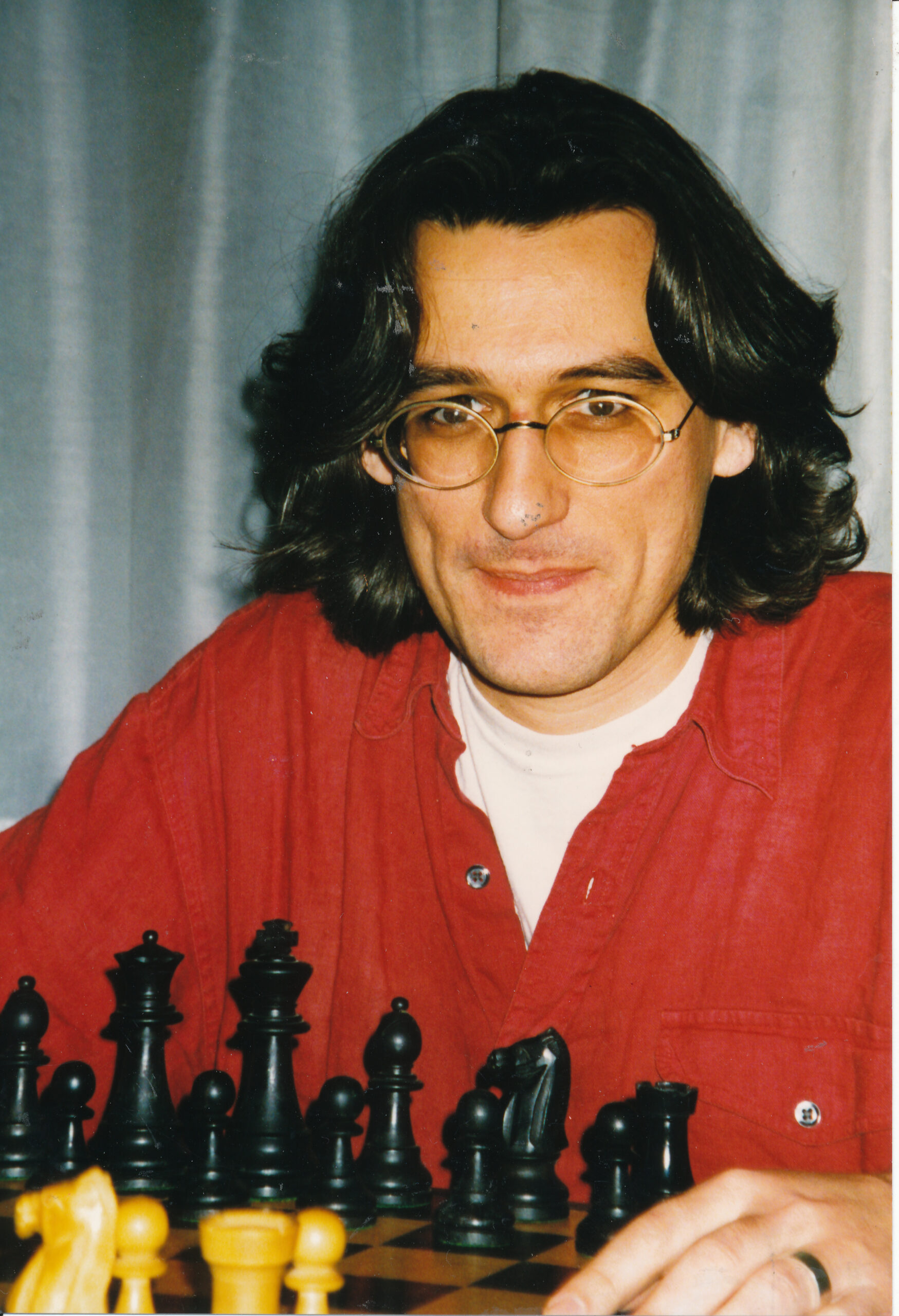
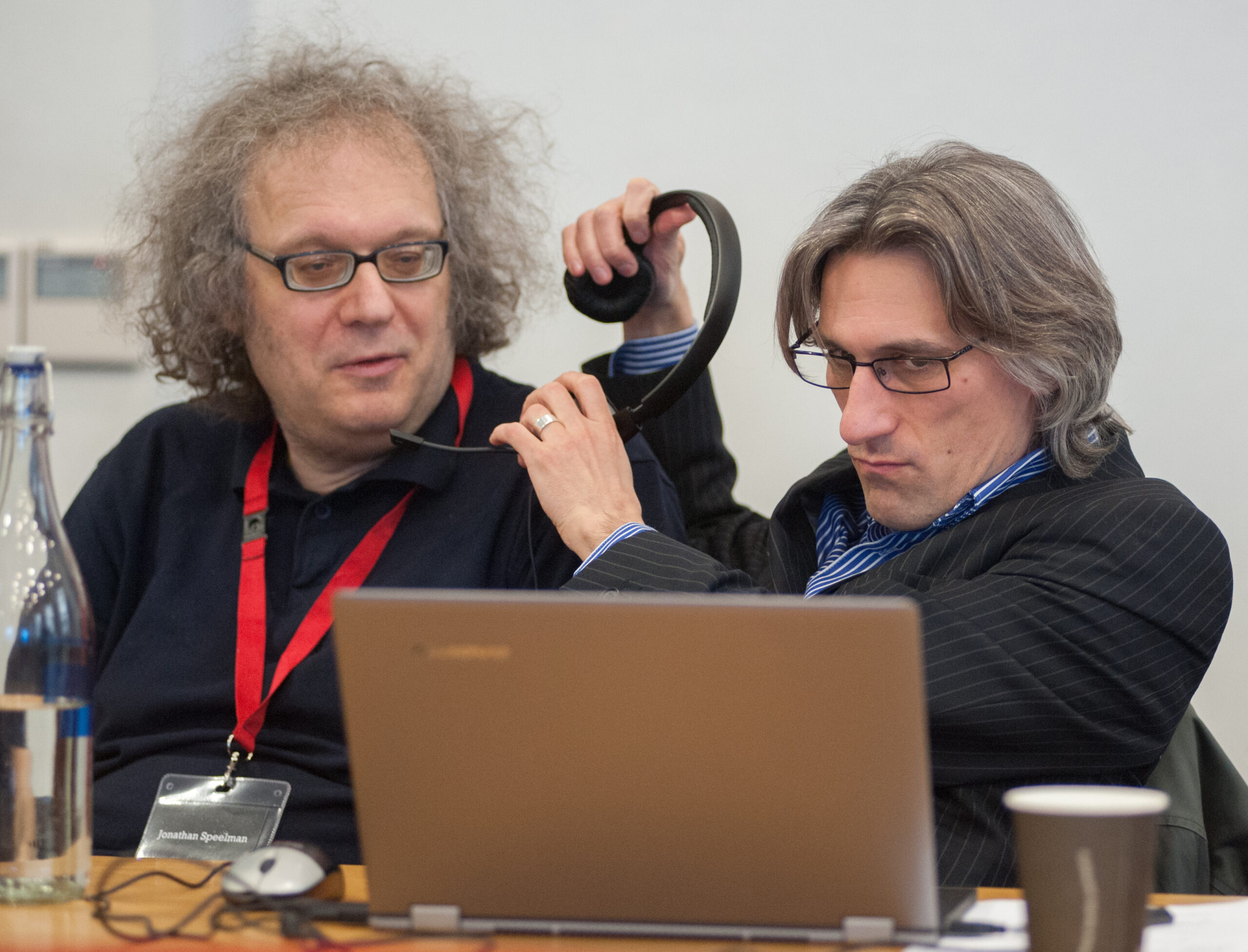
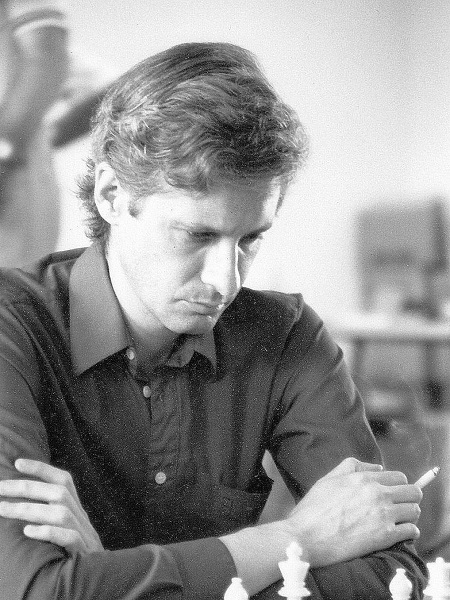
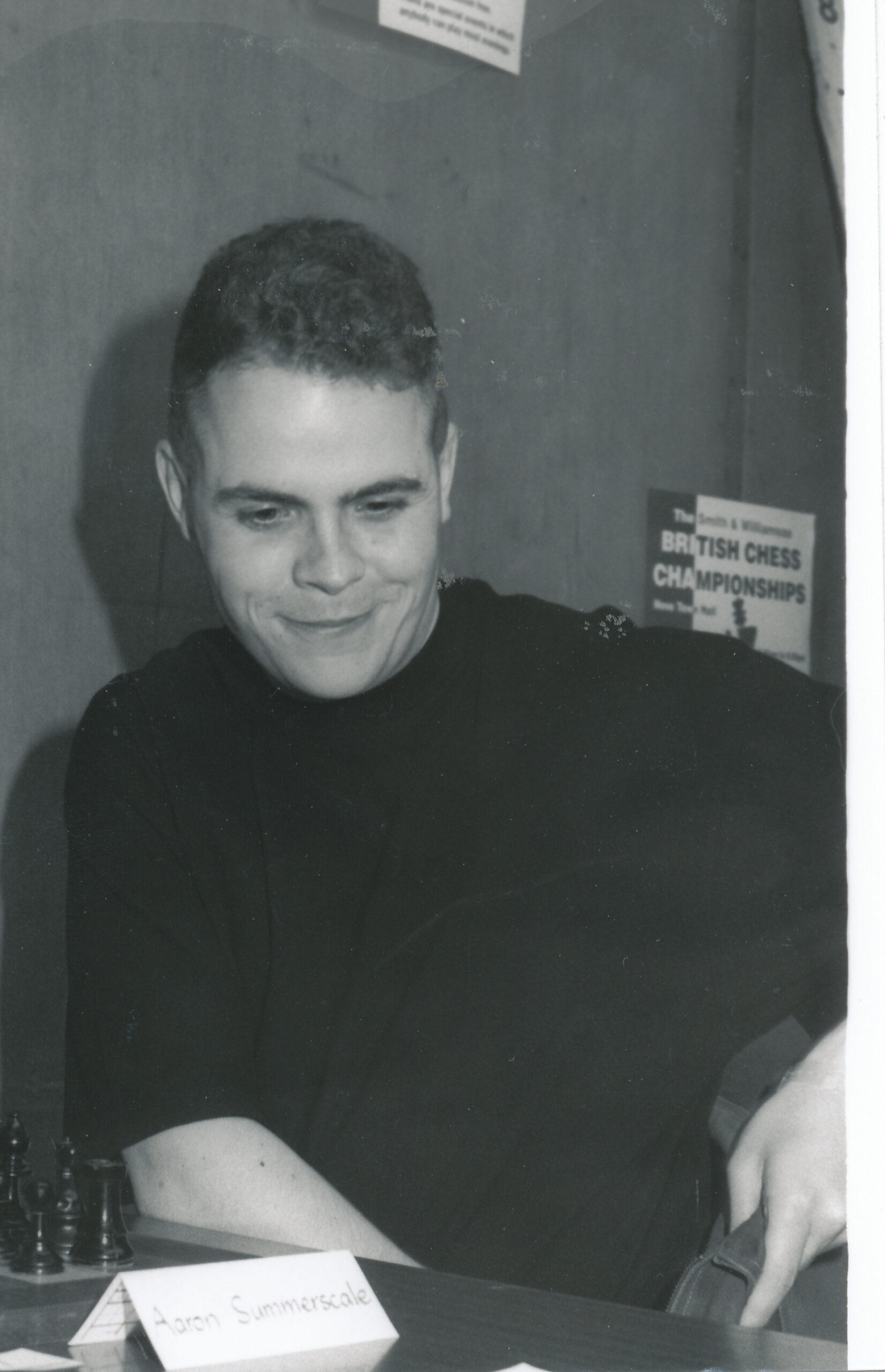
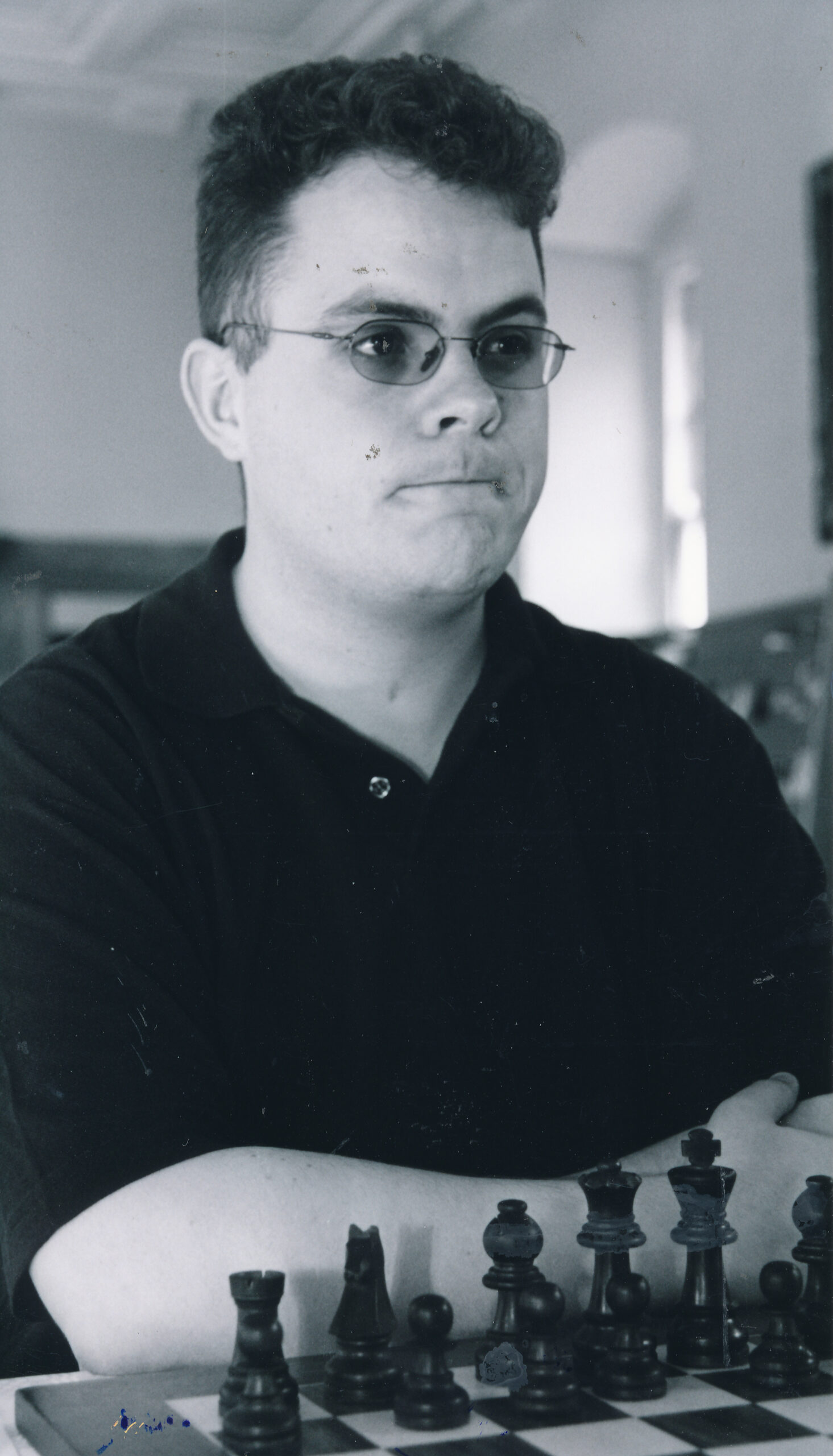
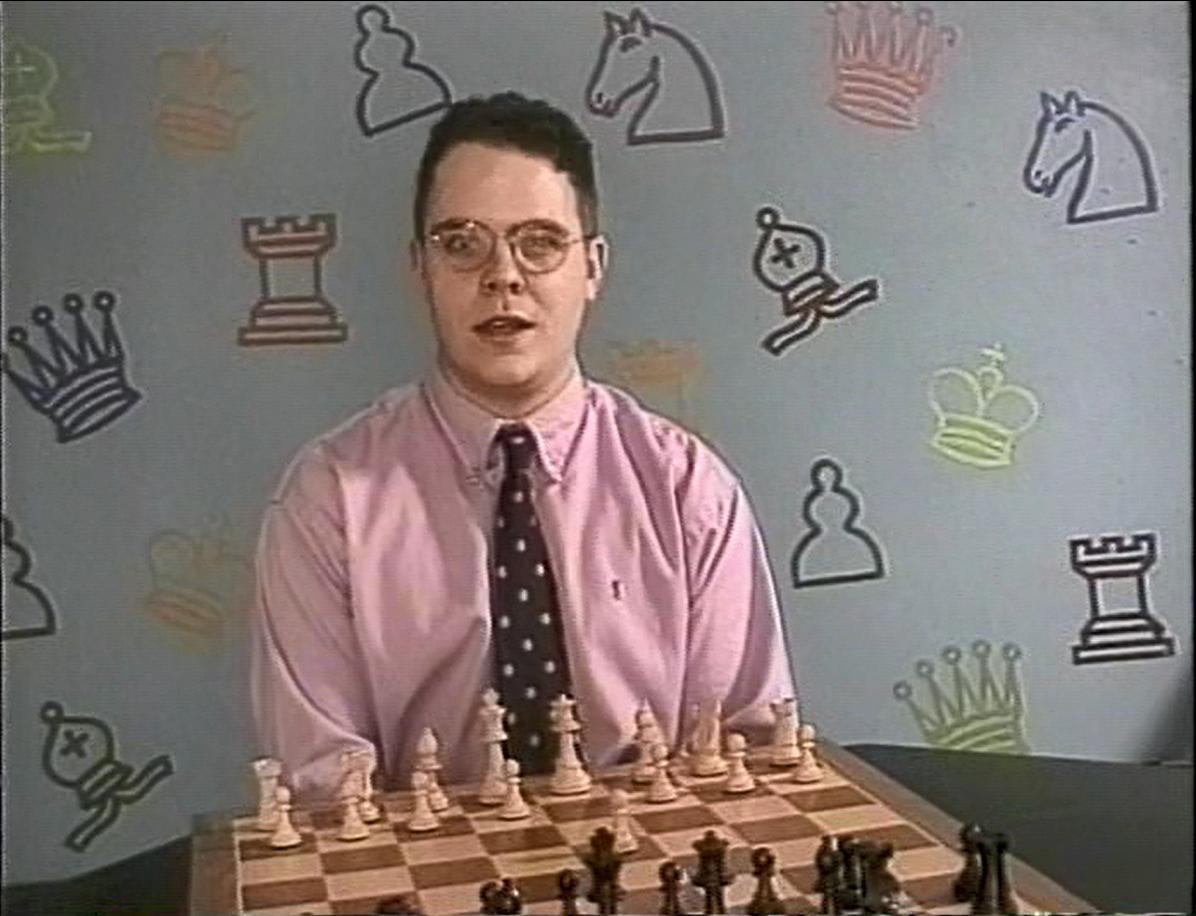
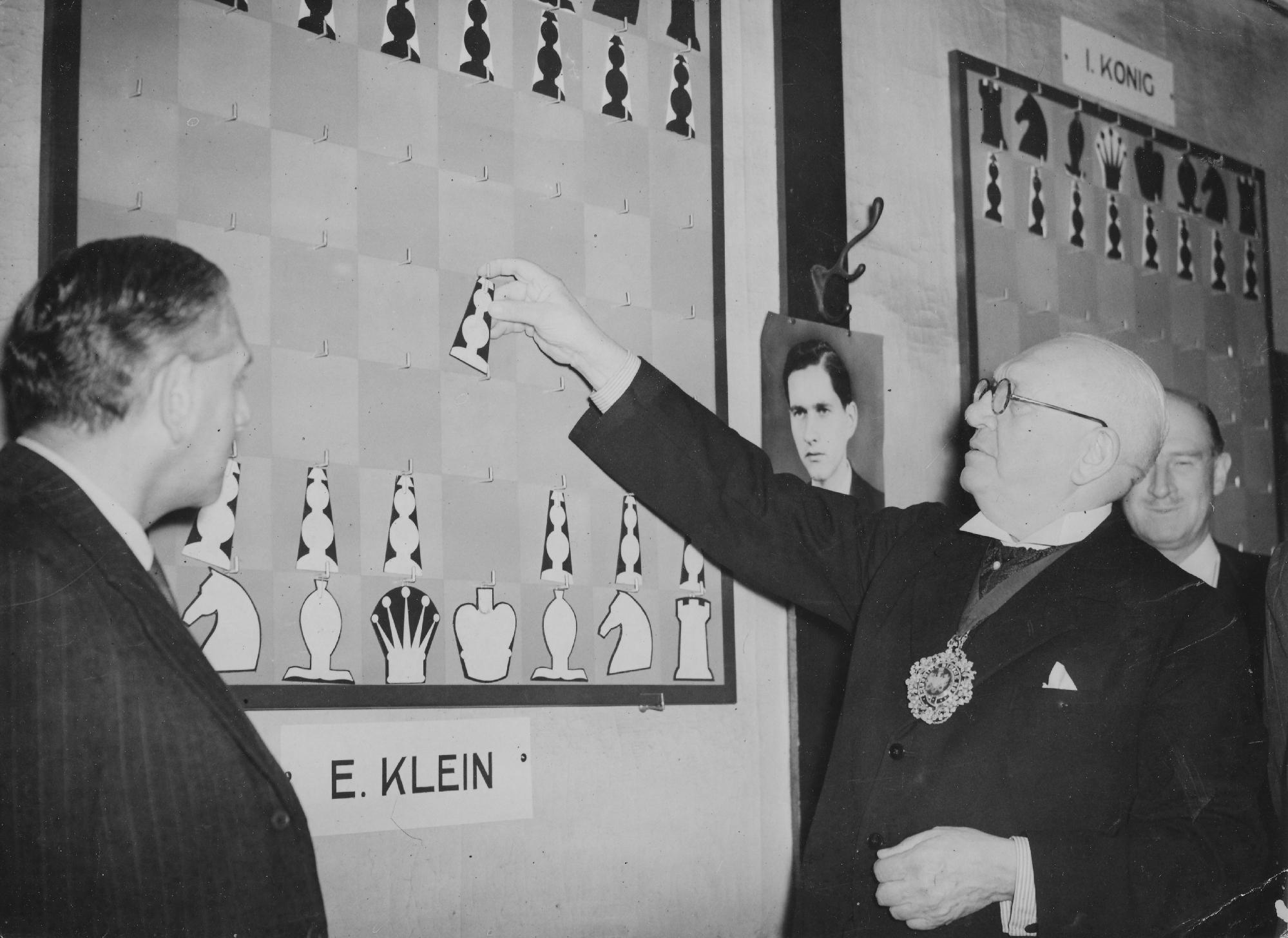
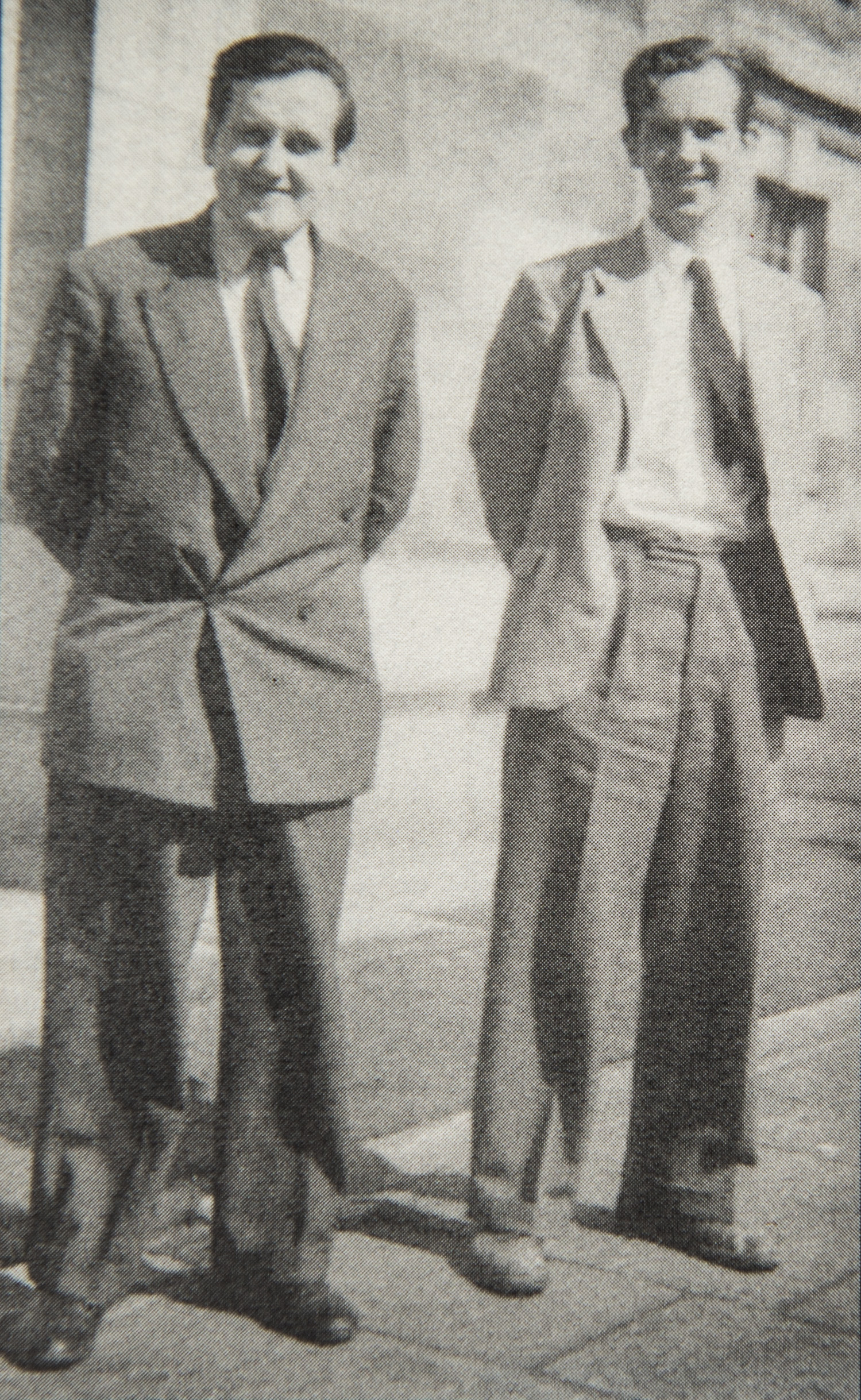
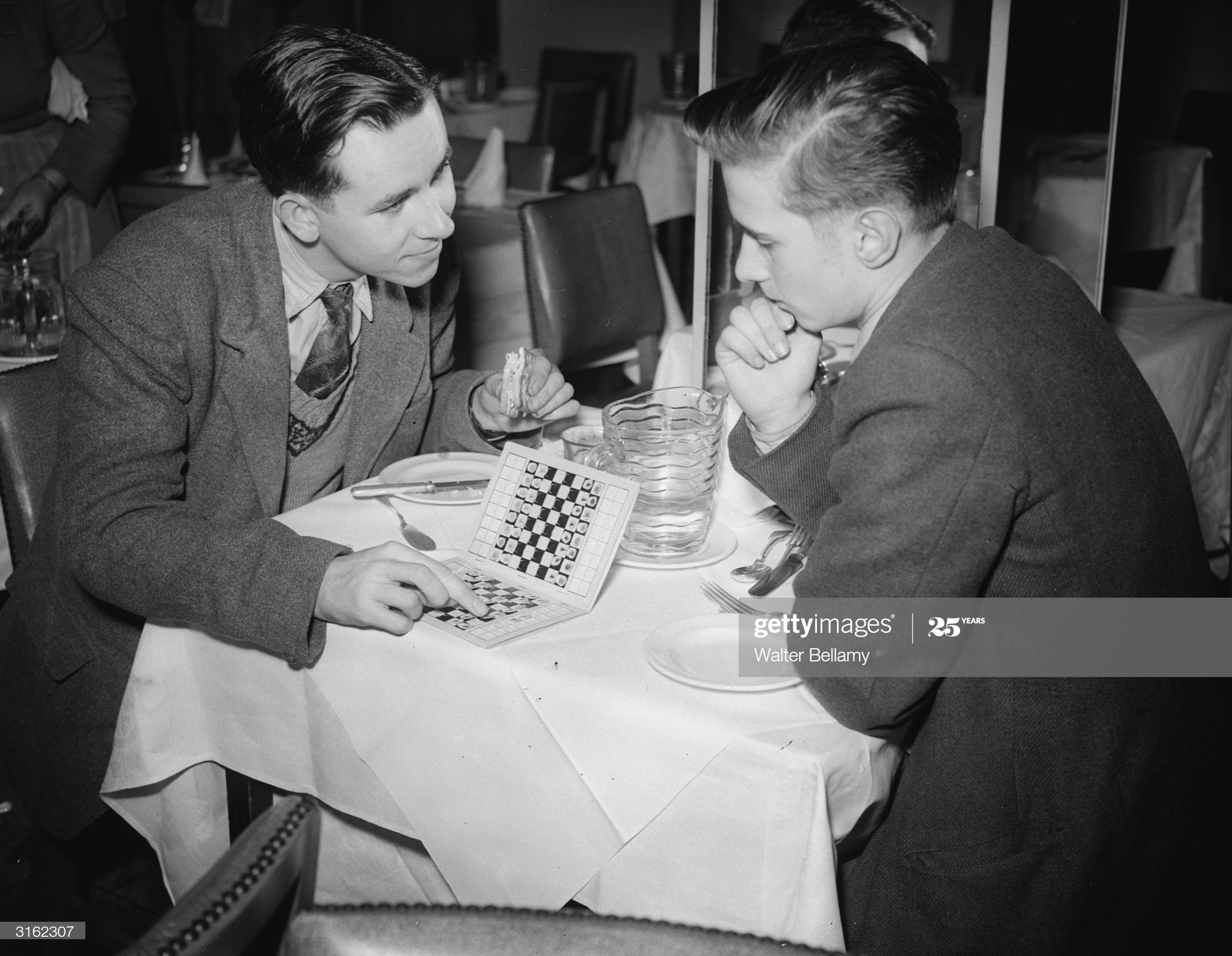
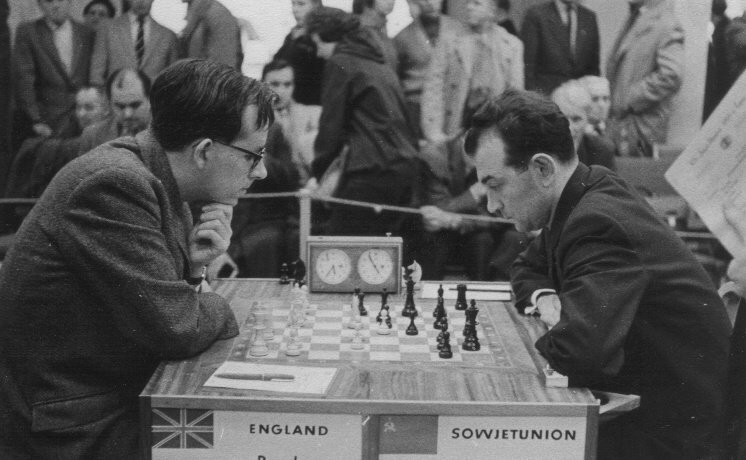
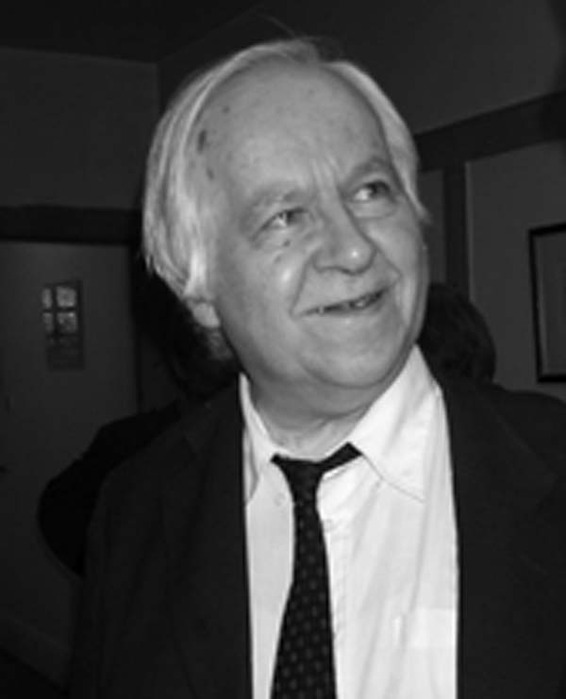
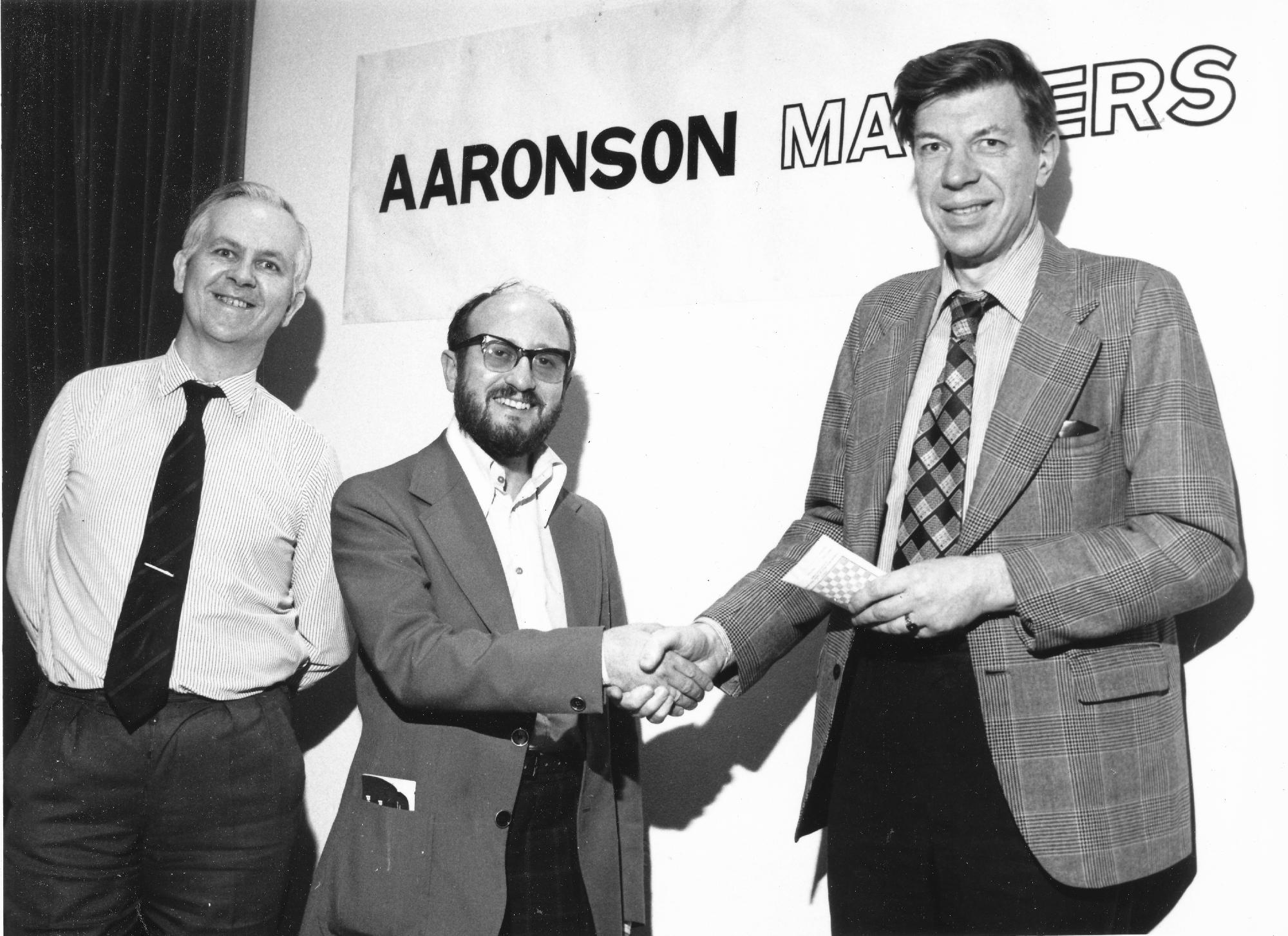
We send best wishes to GM Michael Stean on his 71st birthday,
Michael Francis Stean was born Michael Francis (some say Frank) Stein on Friday, September 4th, 1953 in Pancras, London. His mother’s maiden name is / was Jean Feldman. Michael has a brother, Howard.
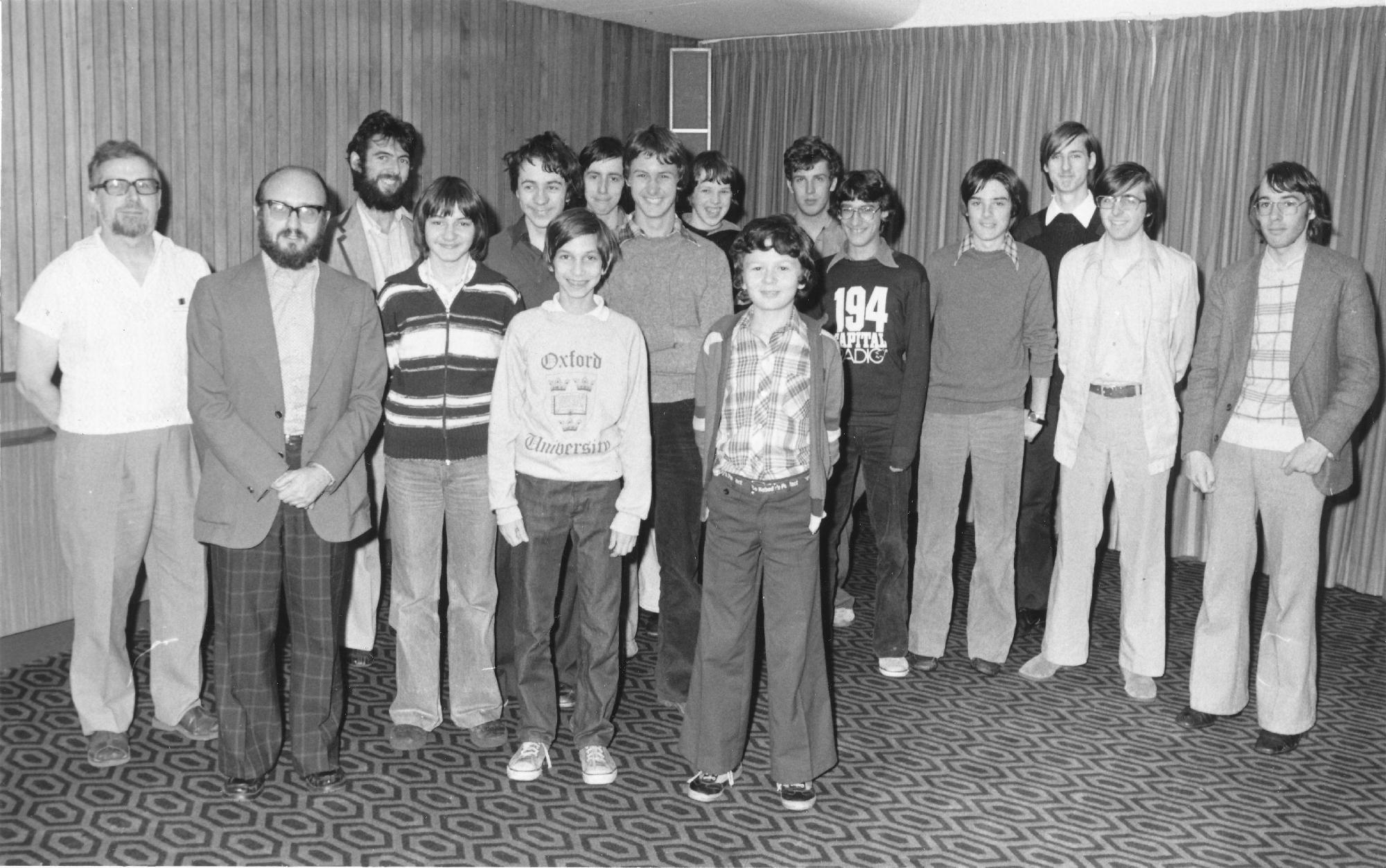
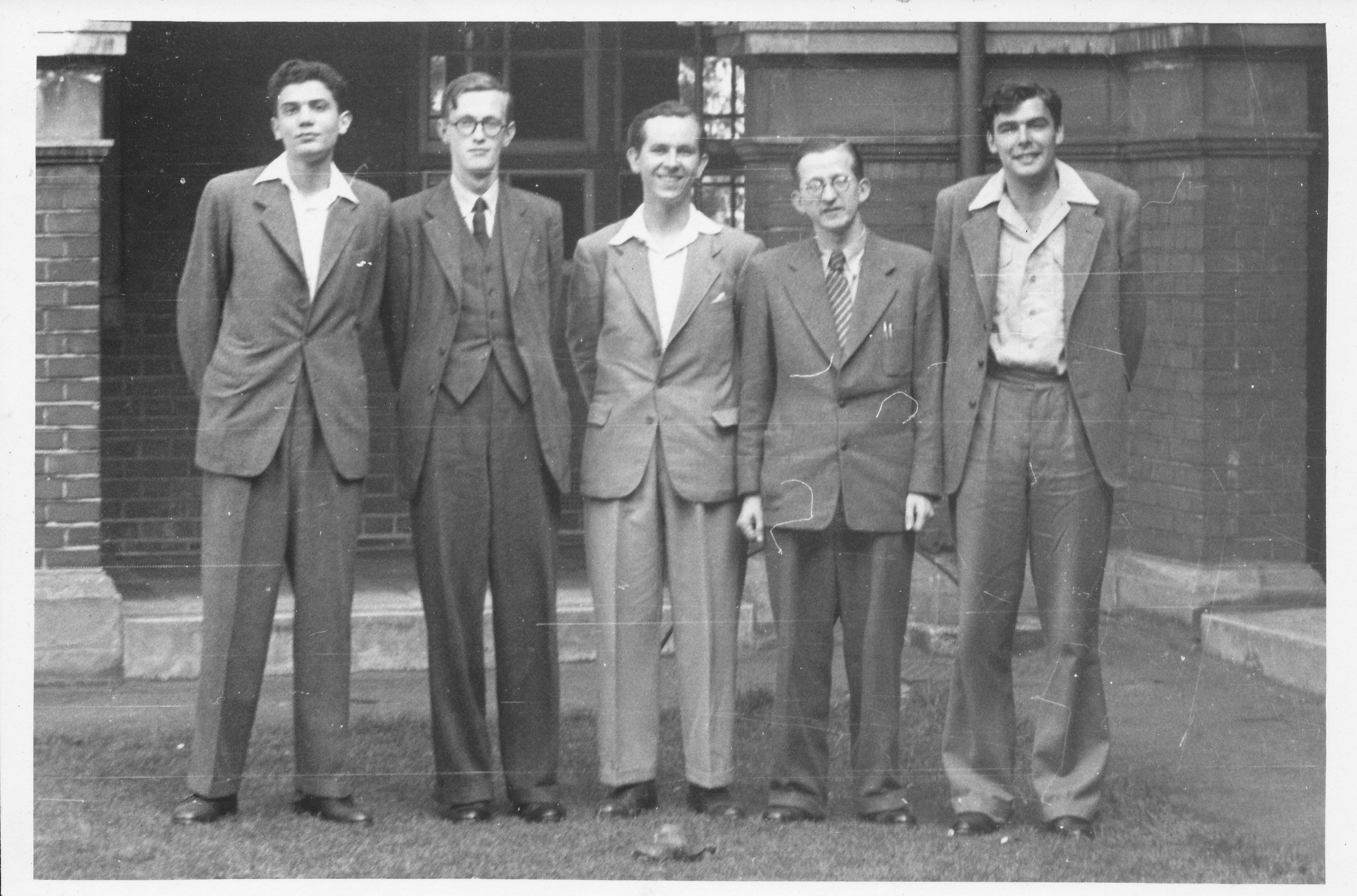
He attended Latymer Upper School and Cambridge University and his early chess days were spent at Richmond and Twickenham Chess Club.
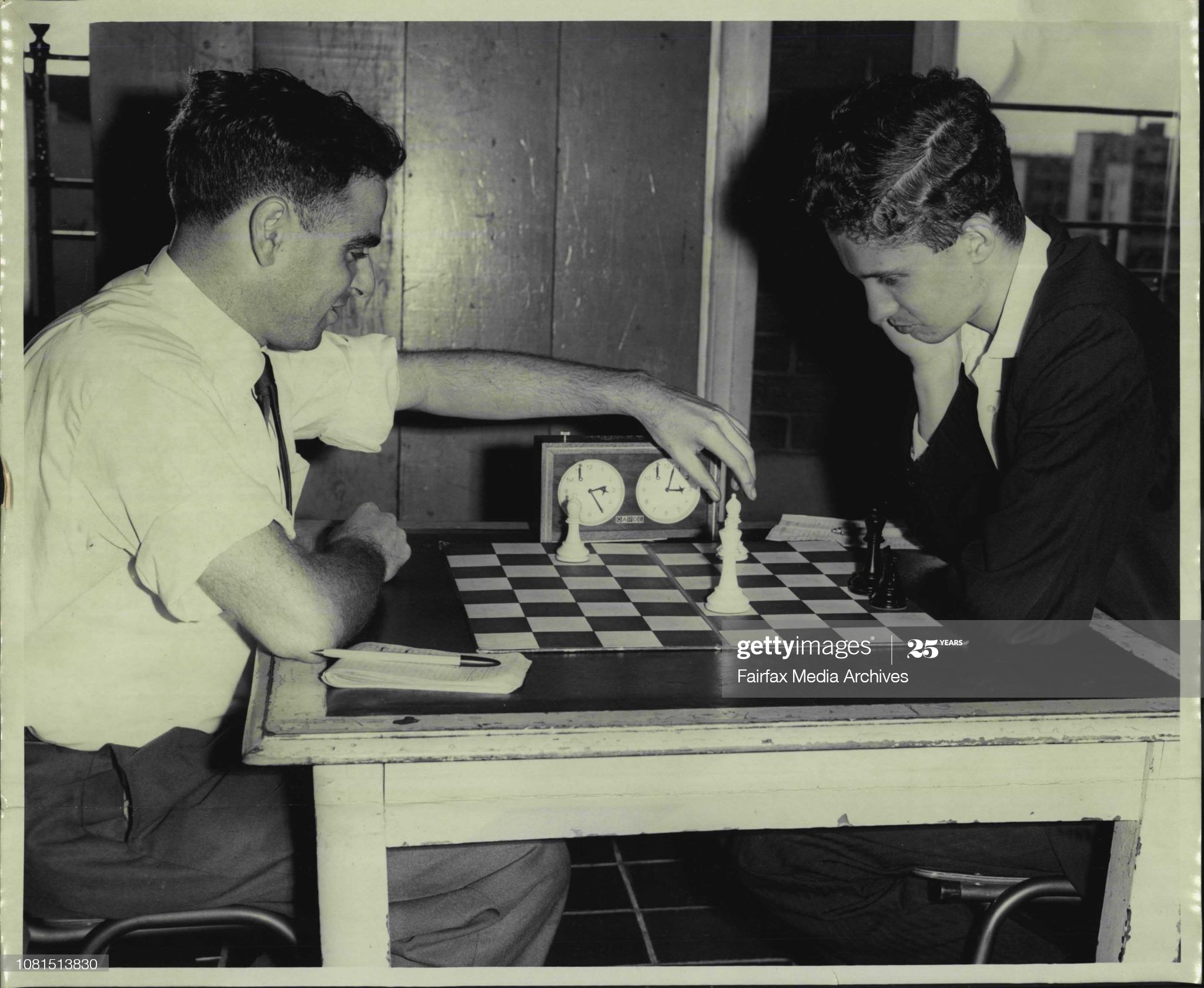
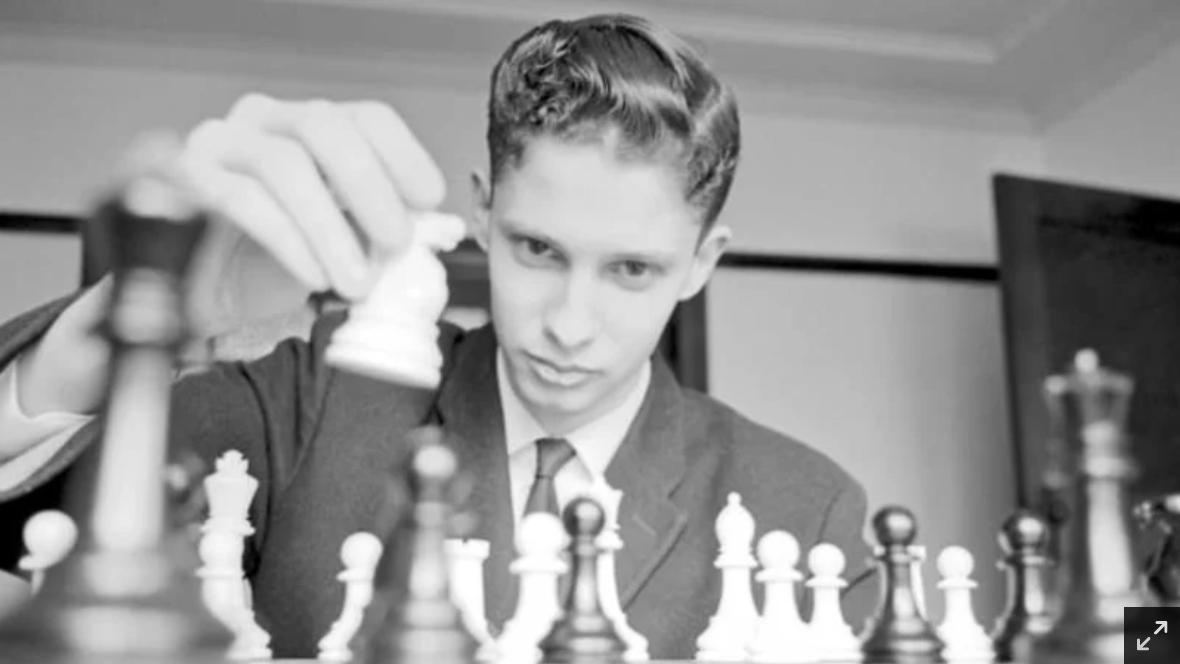
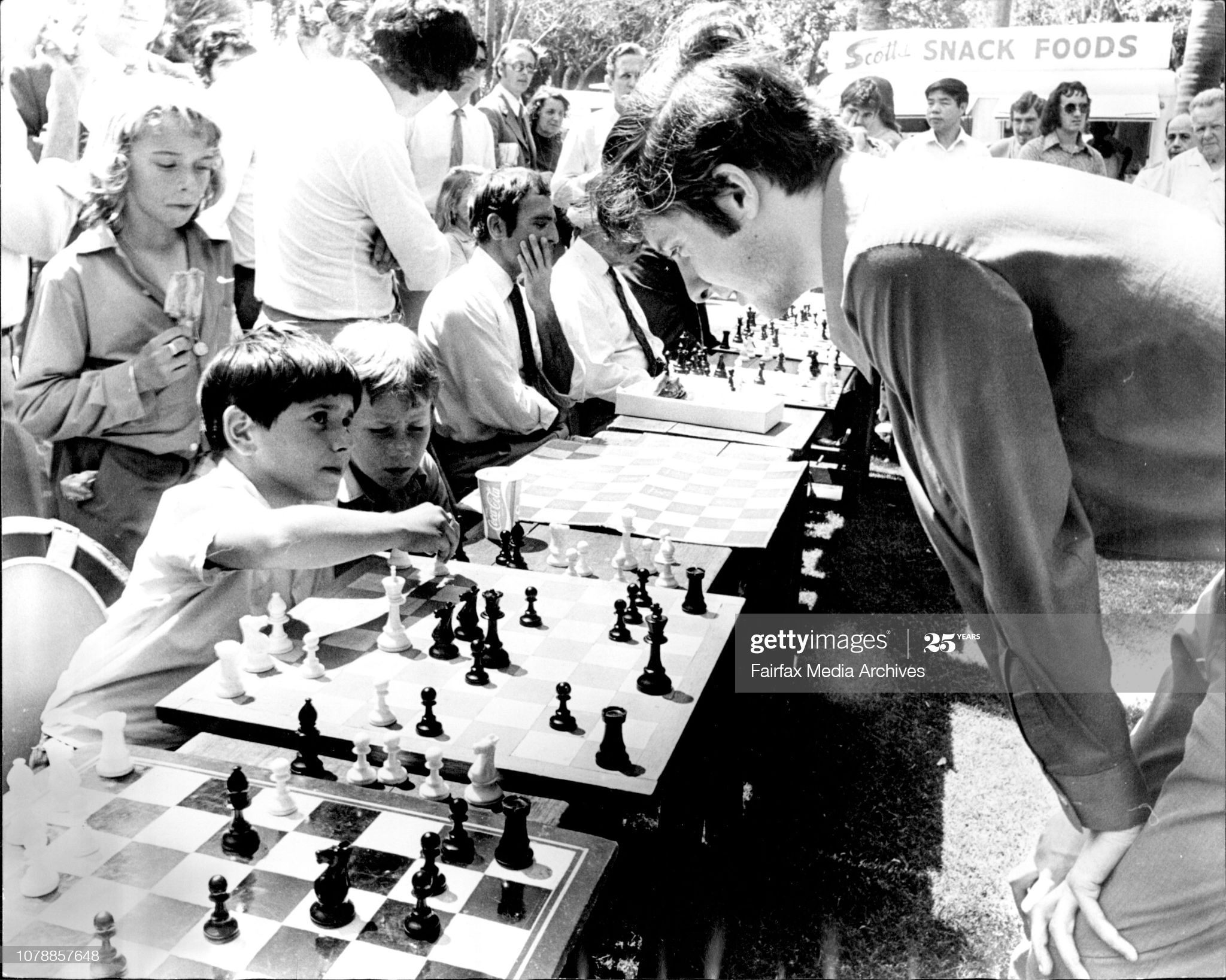
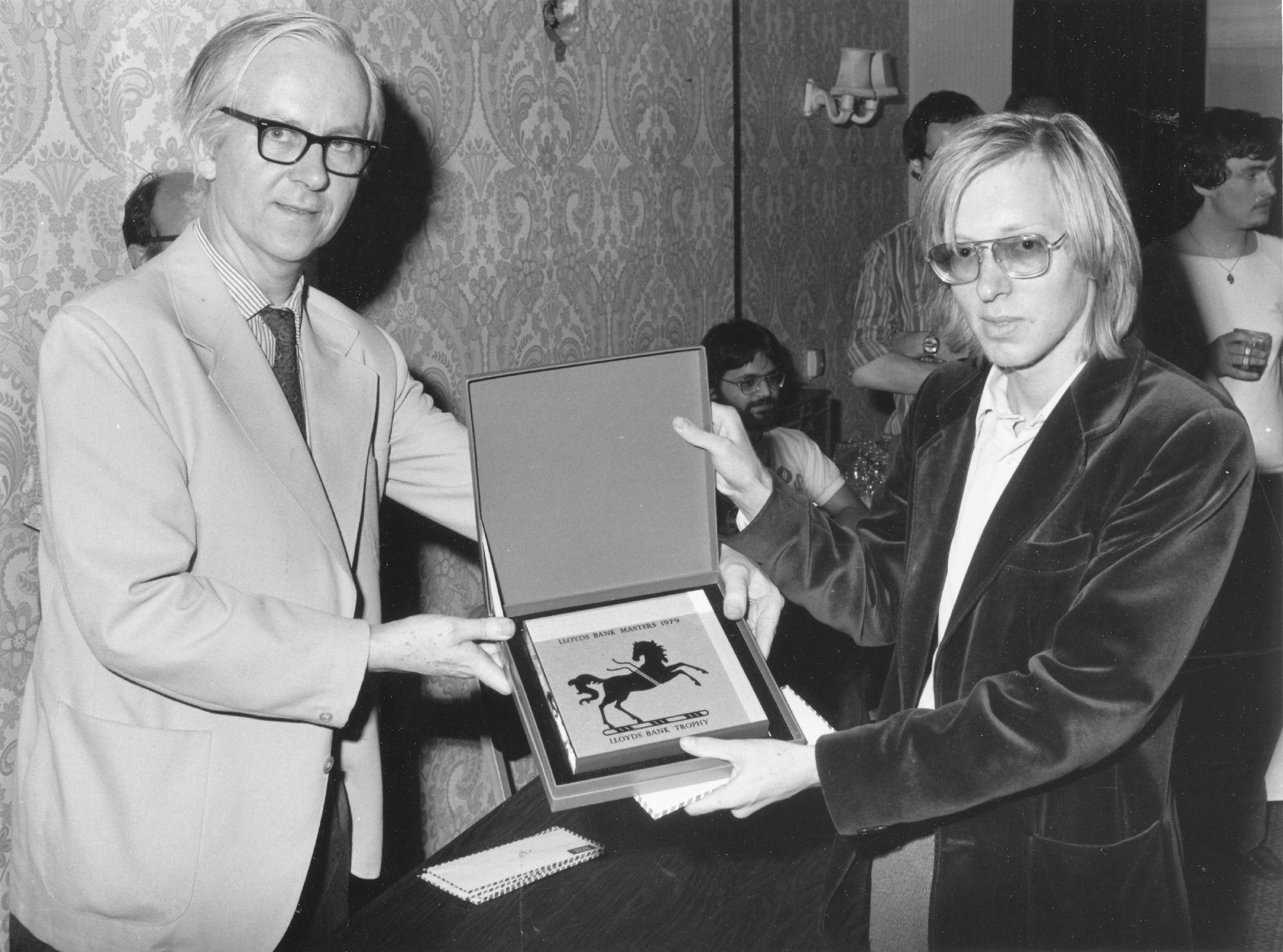
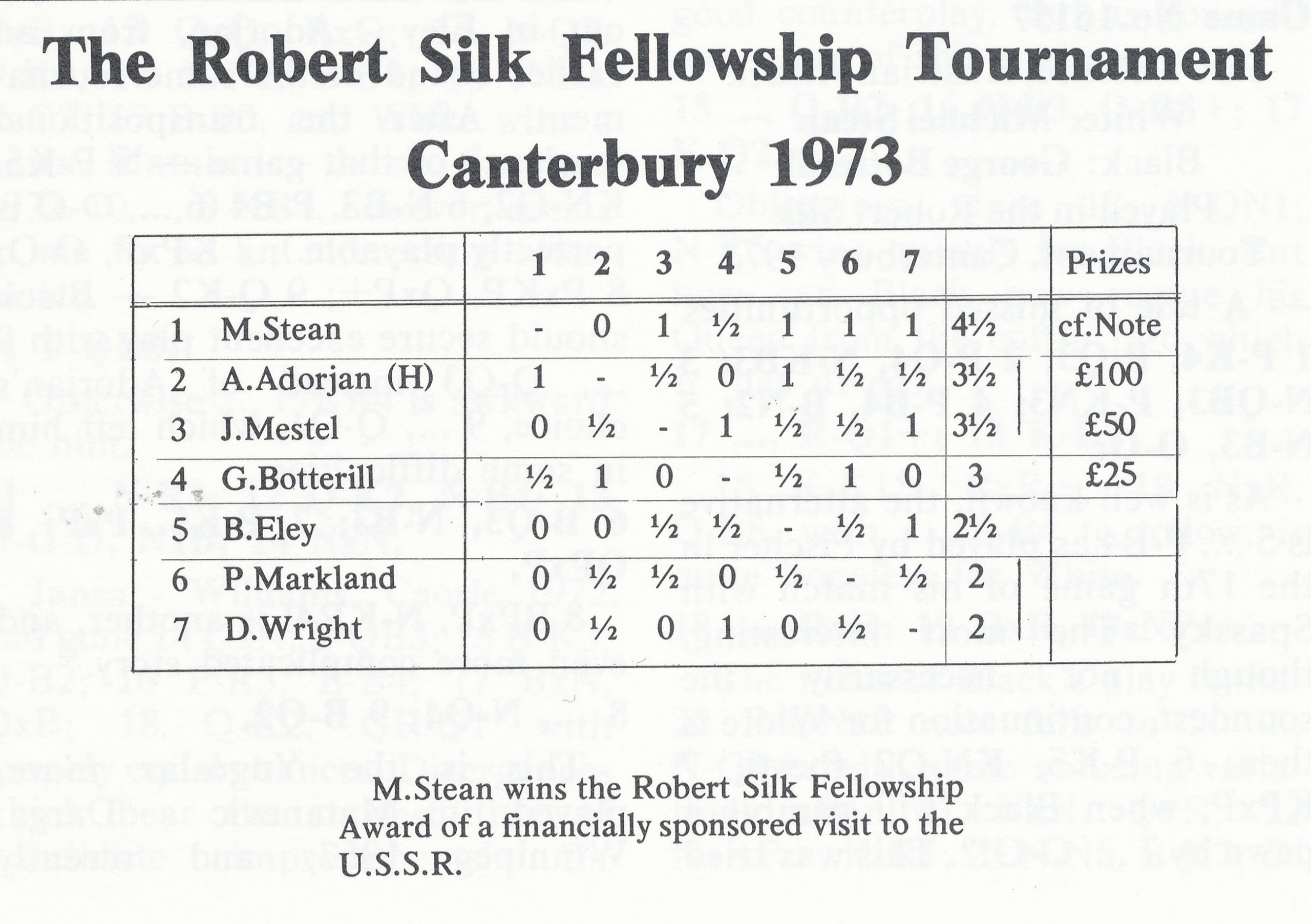
He became an International Master in 1975 and England’s third (OTB) Grandmaster in 1977 winning £2,500 from the Jim Slater Foundation.
He was the chess correspondent of The Observer.
Some notable opponents that he has a plus score against include:
John Nunn: 3.5/5
Jonathan Speelman: 2.5/4
Gert Ligterink: 2.5/3
Robert Bellin: 2.5/3
Brian Eley: 2.5/3
Vladimir Liberzon: 2/3
and others.
With the white pieces Michael played 1.e4, 1.c4 and 1.Nf3 but rarely 1.d4 preferring the Ruy Lopez, Exchange Variation.
With the black pieces he played the Sicilian Najdorf (and was a leading expert), the Nimzo-Indian and the Queen’s Indian defences.
He has the dubious honour of being the first Grandmaster to lose a blitz game to a computer (Chess 4.6) in London, 1977. Stean exclaimed, “This computer is a genius!”
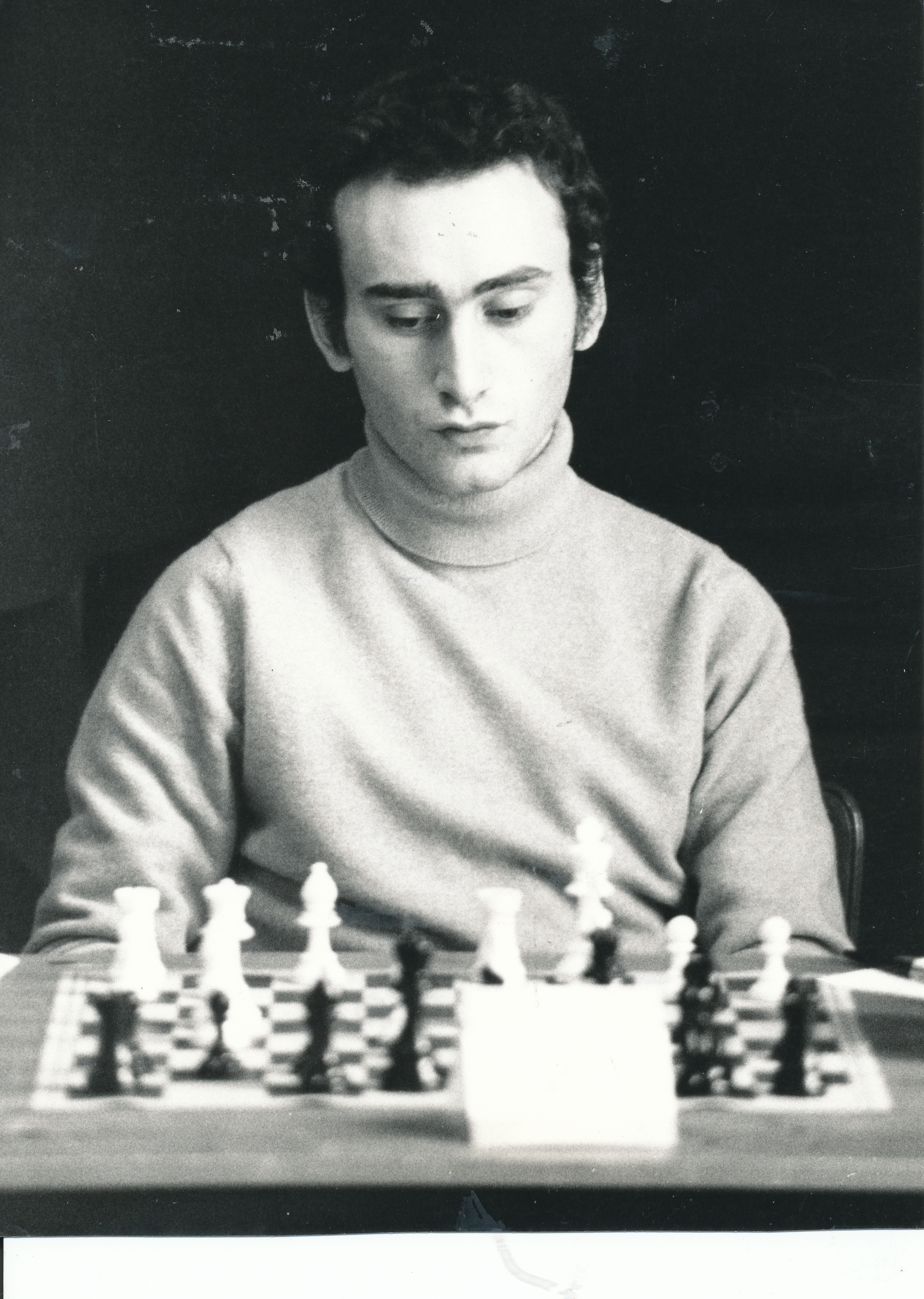

His peak FIDE rating was 2540 in January 1979.
His mother (Jean) presented a trophy to the Marlow Congress (now the Berks and Bucks Congress) which became the Mrs. Jean Stean Cup.

According to British Chess (Pergamon, 1983) by Botterill, Levy, Rice and Richardson :
“Stean was educated at Cambridge University, He was equal first in the British Championship, Clacton, 1974, although only 4th in the playoff. He has been an important member of Korchnoi’s team for the last 5 years, and this perhaps has been responsible more than anything for the rounding out and maturing of his style from the sharp tactical play of the early 1970s to the solid positional GM (especially with the White pieces) of today.

Stean is a fine author; Simple Chess and the Sicilian Najdorf are both excellent books.
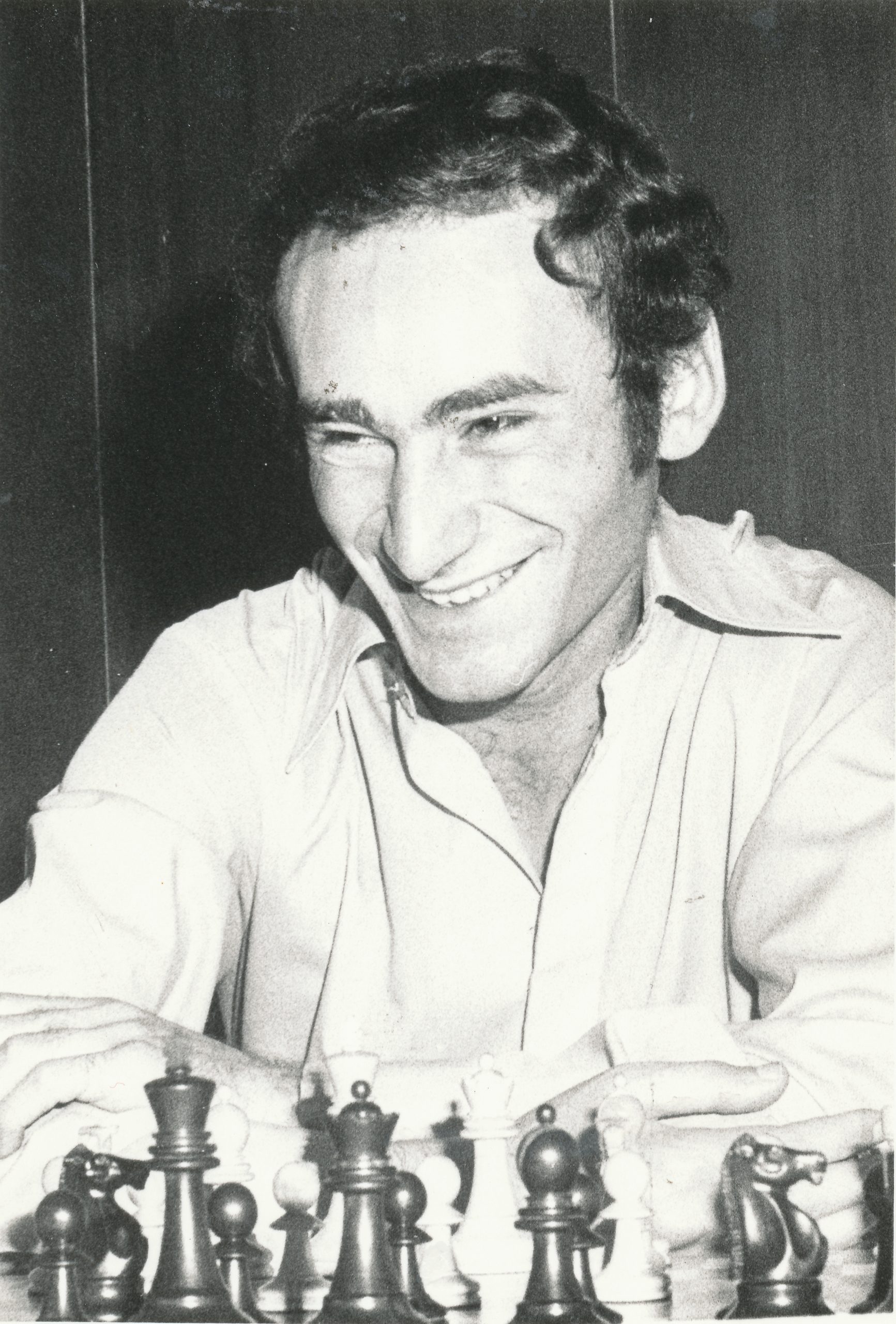

Temperamentally he is generally pleasant, good humoured and self confident, although he suffers from intermittent poor health which might help to explain his at times erratic results.”
According to Chessgames.com :
“Michael Francis Stean was born on the 4th of September 1953 in London, England. He finished 3rd at the 1973 World Junior Chess Championships behind Alexander Beliavsky and Tony Miles. Awarded the IM title in 1975 and the GM title in 1977 (The third Englishman to attain the title after Miles and Keene).
He finished 1st= in the 1974 British Championship but lost the play-off. He played on 5 English Olympiad teams from 1974 – 1983 and has won 1st prizes at Vrsac 1979, Smederevska Palanka 1980 and Beer Sheba 1982.
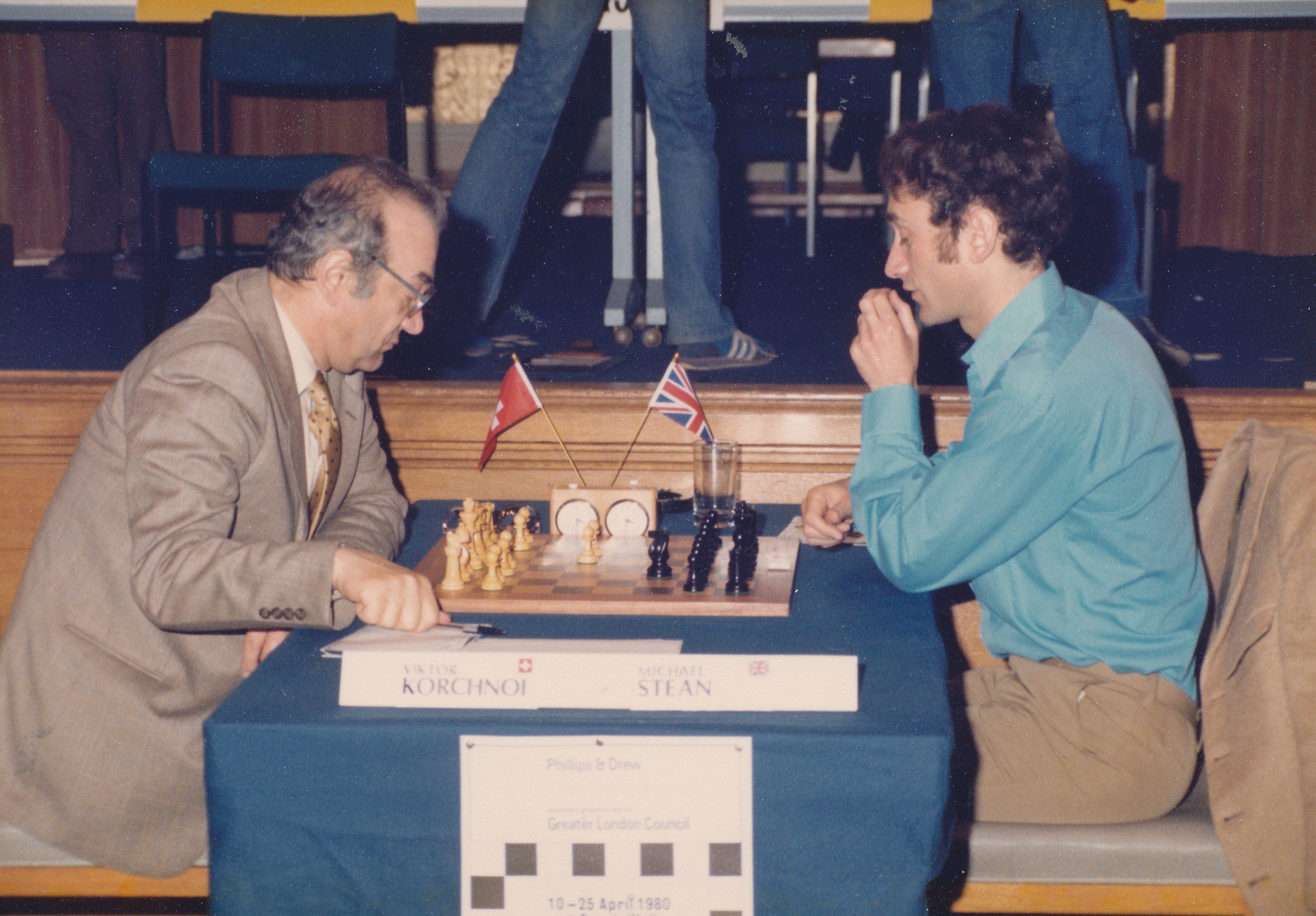
A specialist in Opening Theory he served as one of Viktor Korchnoi’s seconds in the 1977 – 1981 period. He is the author of Simple Chess, an introduction to chess strategy.”

Harry Golombek wrote this about Michael in a 1980 Dataday chess diary :
“The fact that he has sprung up into second place among English players as regards Elo ratings demonstrates the considerable advance Michael Stean has made in the course of a year.

In the 1978 diary I wrote that it would not be long before he gained the grandmaster title since he already possessed one norm of the title. The forecast proved to be correct as he duly acquired the title a few months after I wrote the prophecy.

He had though to take two more bites at the cherry before he managed to gain the required norms since the tournaments in which he played were not long events. They were Montilla in August 1977 where he came third below Gligoric and Kavalek and the Lord John Cup Tournament in London in September 1977 where he was equal 2nd with Quinteros and Mestel, first place being occupied by the Czechoslovak grandmaster, Hort.
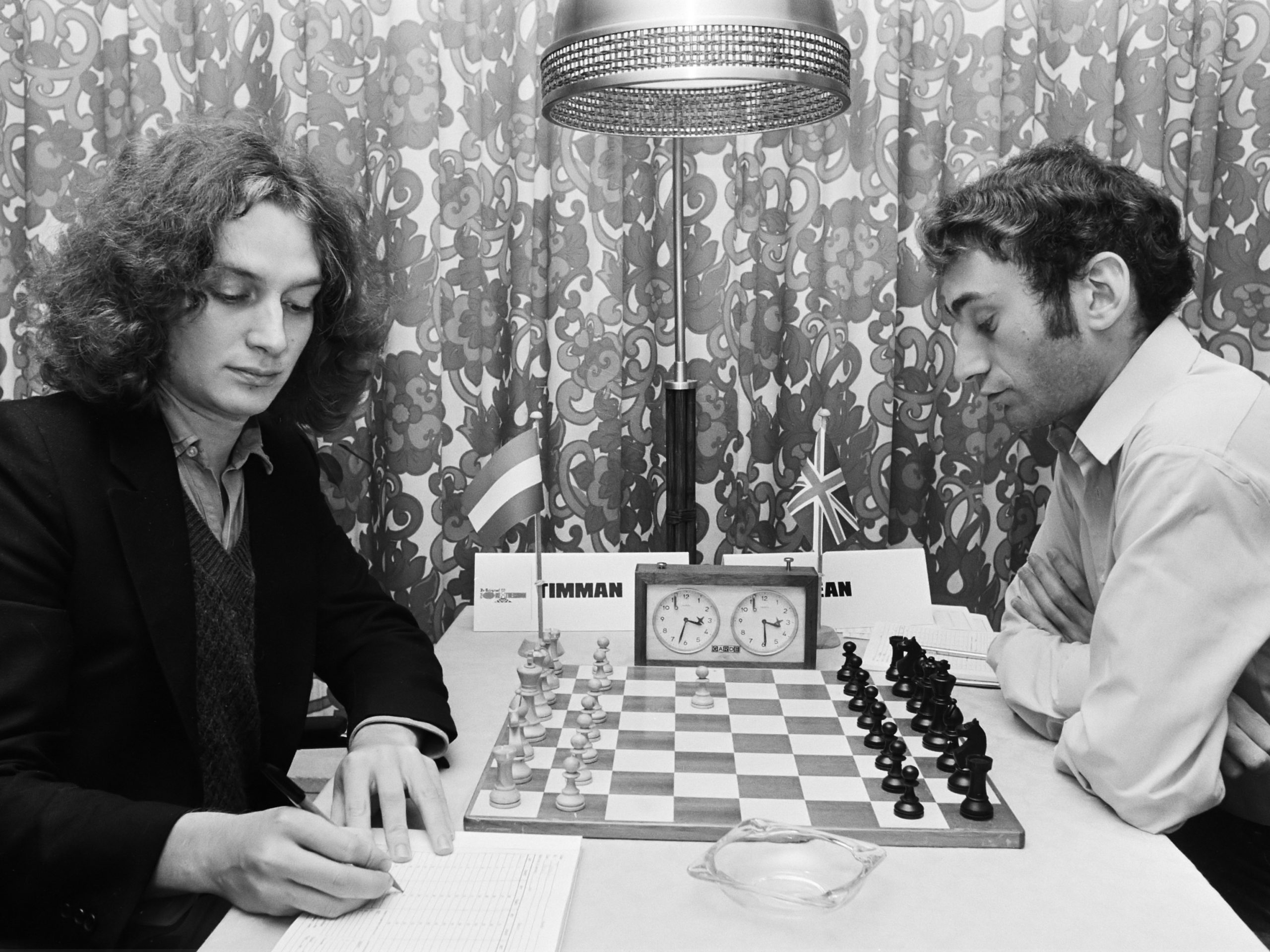

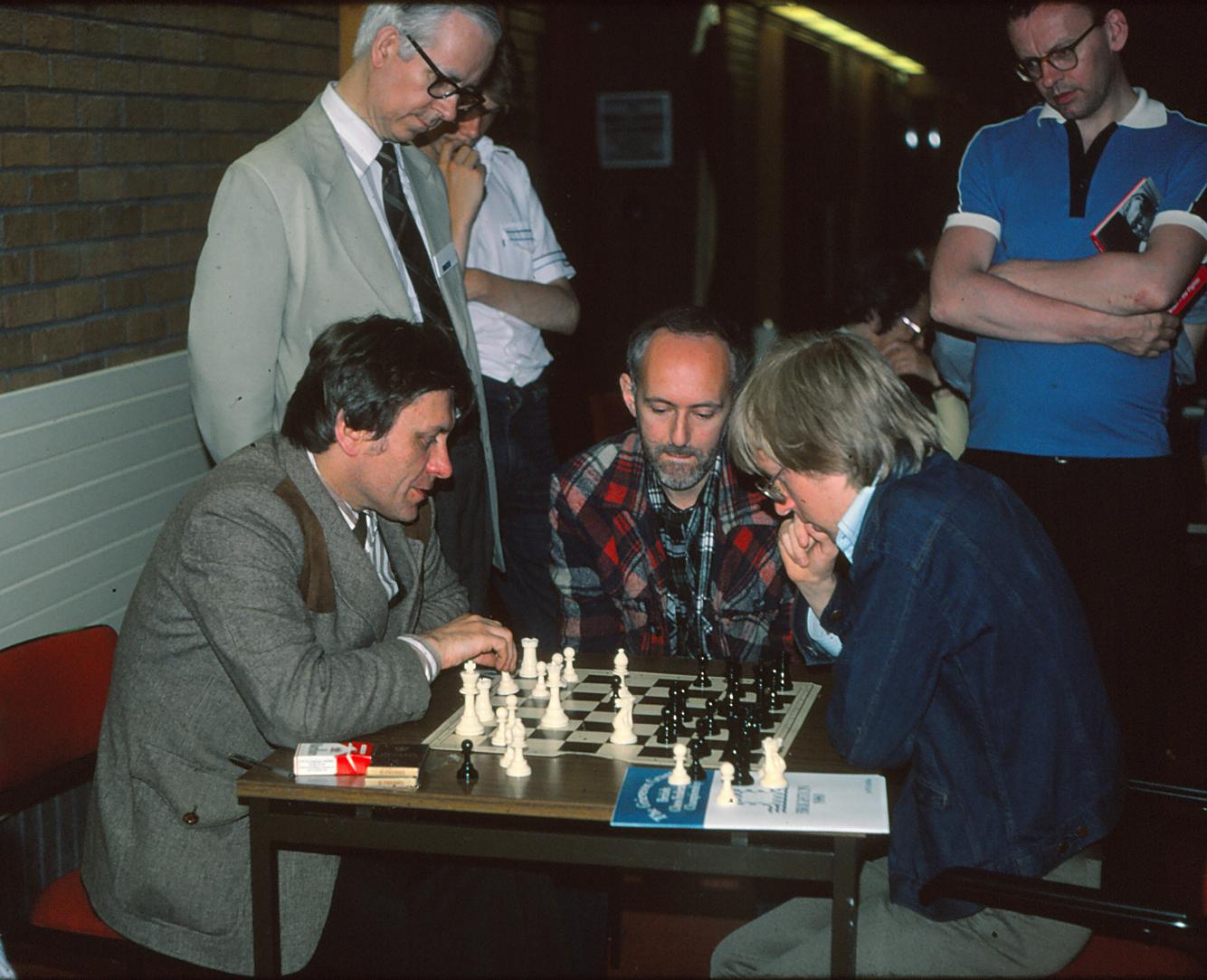
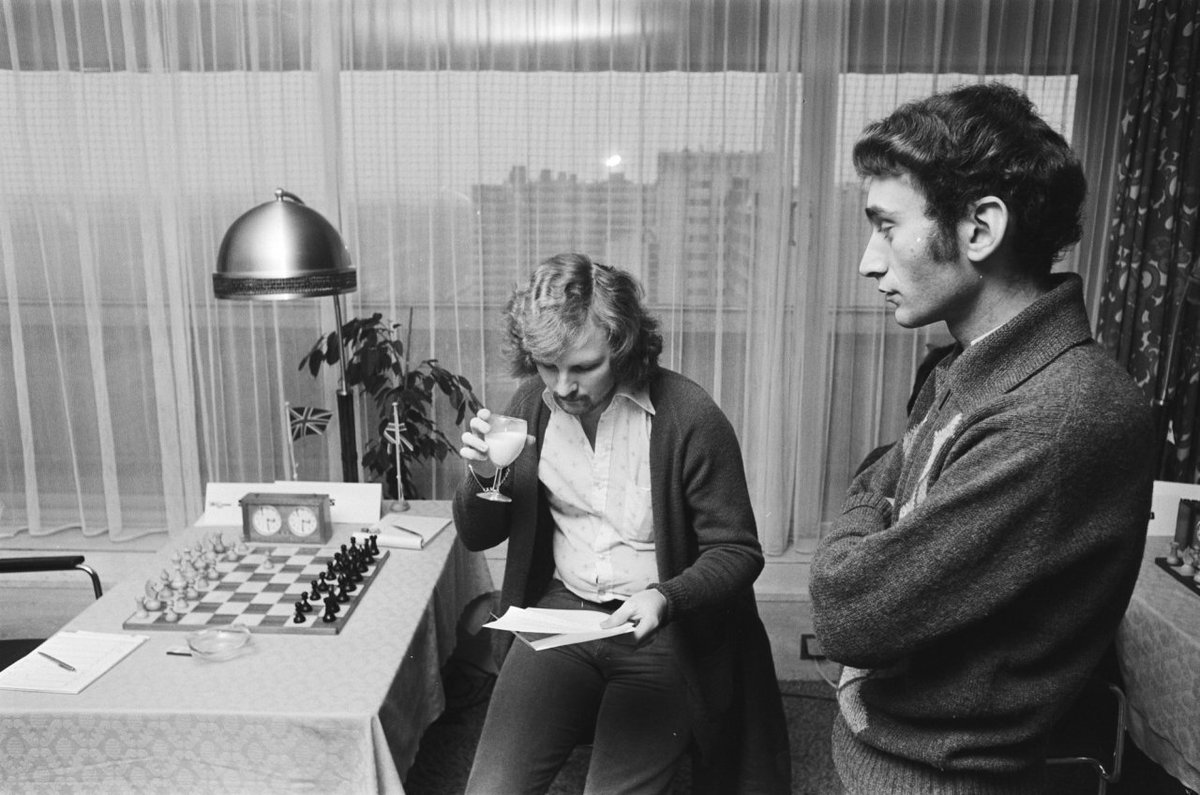
Before that he had assisted Keene in seconding Korchnoi in his candidates match versus Polugayevsky and had done this to such effect that Korchnoi asked him and Keene to act as his seconds at his final match in the Candidates at Belgrade and later on still at the World Championship match against Karpov in the Philippines.
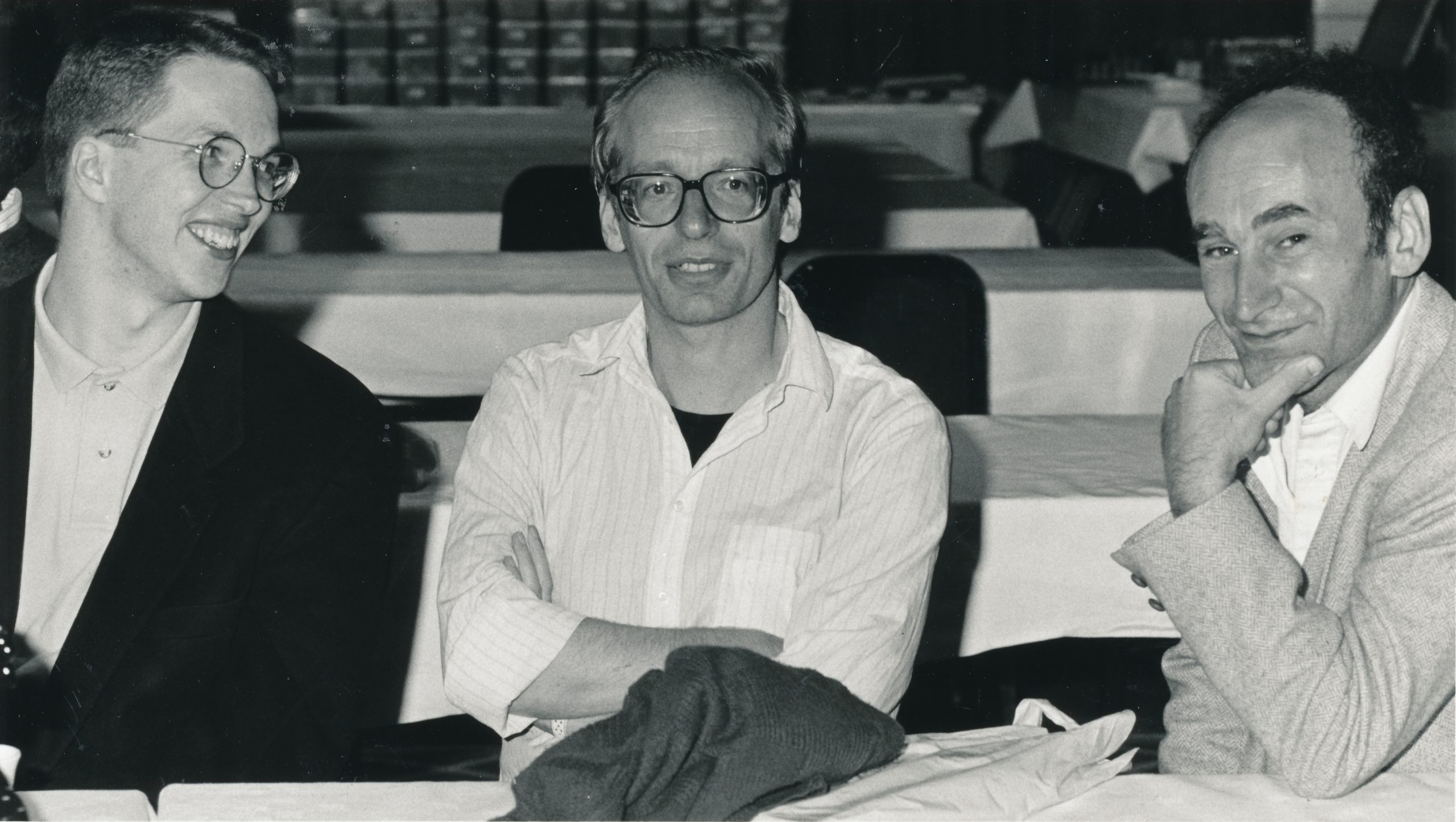

He also played successfully in Yugoslavia in 1977 (equal 2nd at Virovitica and equal 2nd at Bar). In 1978 he was 3rd at Beersheba below Korchnoi but head of Keene. Five points out of nine at the very strong Swiss System tournament at Lone Pine was followed by an excellent equal 4th with Miles at the tournament at Las Palmas. He has shown that he not only possesses the title of grandmaster but also plays like one.
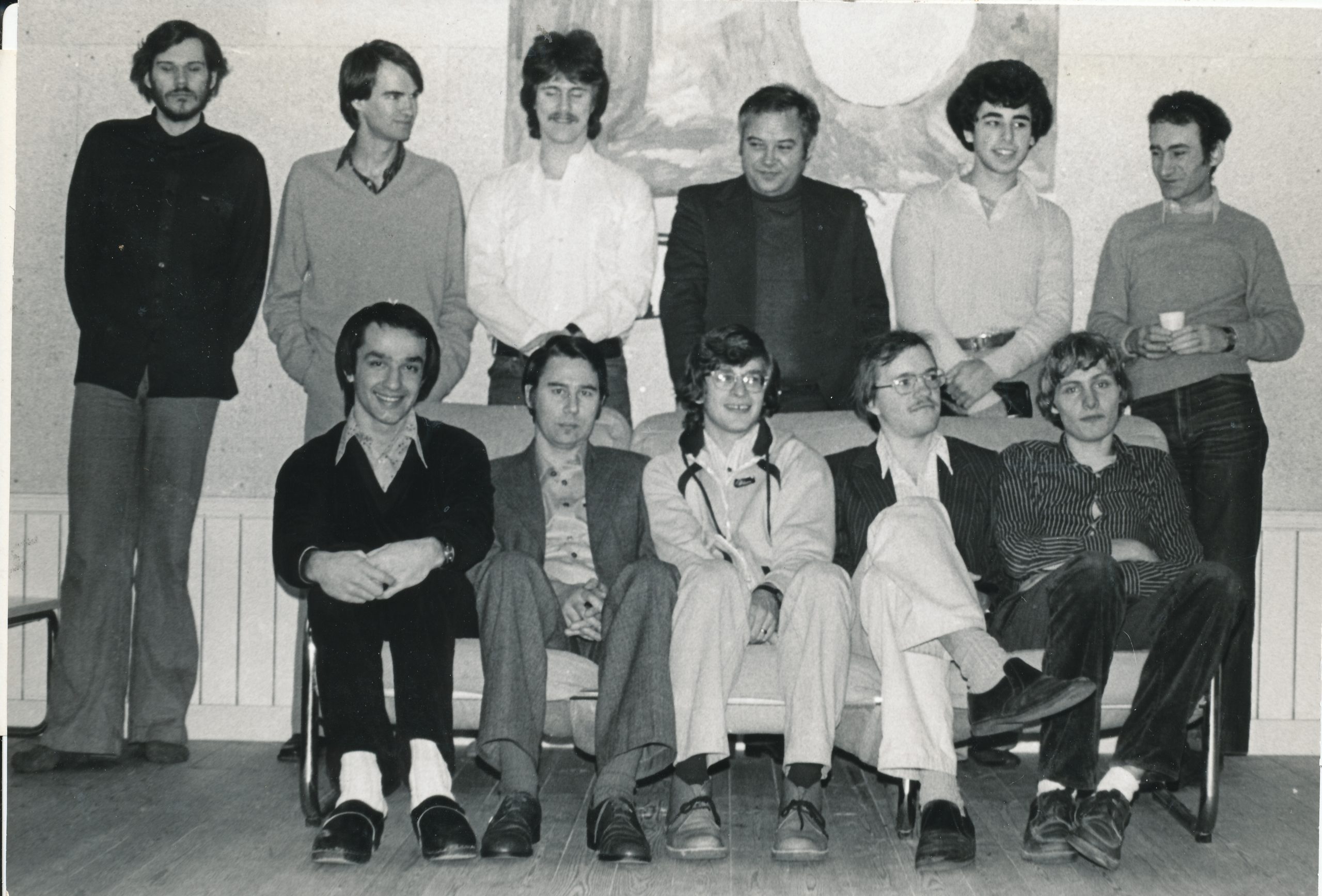

A good example in the following game (Stean-Sax) against one of the joint first prize winners at the Las Palmas event. It was awarded the prize for the best game :”
From The Oxford Companion to Chess (OUP, 1984) by Hooper & Whyld :
“English player, International Grandmaster (1977). At Nice 1974, in the first of his several Olympiads, he won the brilliancy prize for his game against Browne.
Since then he has had several good results: Montilia 1976, equal second with Kavalek and Ricardo Calvo (1943— ) after Karpov; Montilia 1977, third (-1-3 = 6)after Gligoric and Kavalek ahead of R. Byrne, Taimanov, and Andersson; London 1977. second (+4=4—1) equal with Mestel and Quinteros after Hort ; Vrsac 1979, first (+ 8=5—1); Smederevska Palanka 1980, first (+7-6); Beersheba 1982, first, Stean was one of Korchnoi’s seconds in the world championship cycles of 1977-8 and 1980-1, and the two became close friends.
In particular Stean provided help with the openings, a subject on which he specialises. He published a book on the Najdorf variation of the Sicilian defence in 1976, and Simple Chess, a guide to the understanding of positional ideas, in 1978.”

From Wikipedia :
“Michael Francis Stean (born 4 September 1953) is an English chess grandmaster, an author of chess books and a tax accountant.

The game below (Stean-Browne) was the first winner of the World Brilliancy Prize established in 1974 by Isador Samuel Turover. The value of the prize was $1,000.”
See Michael Stean’s Wikipedia entry for more
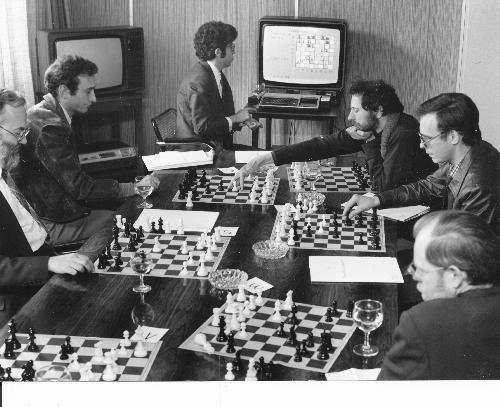


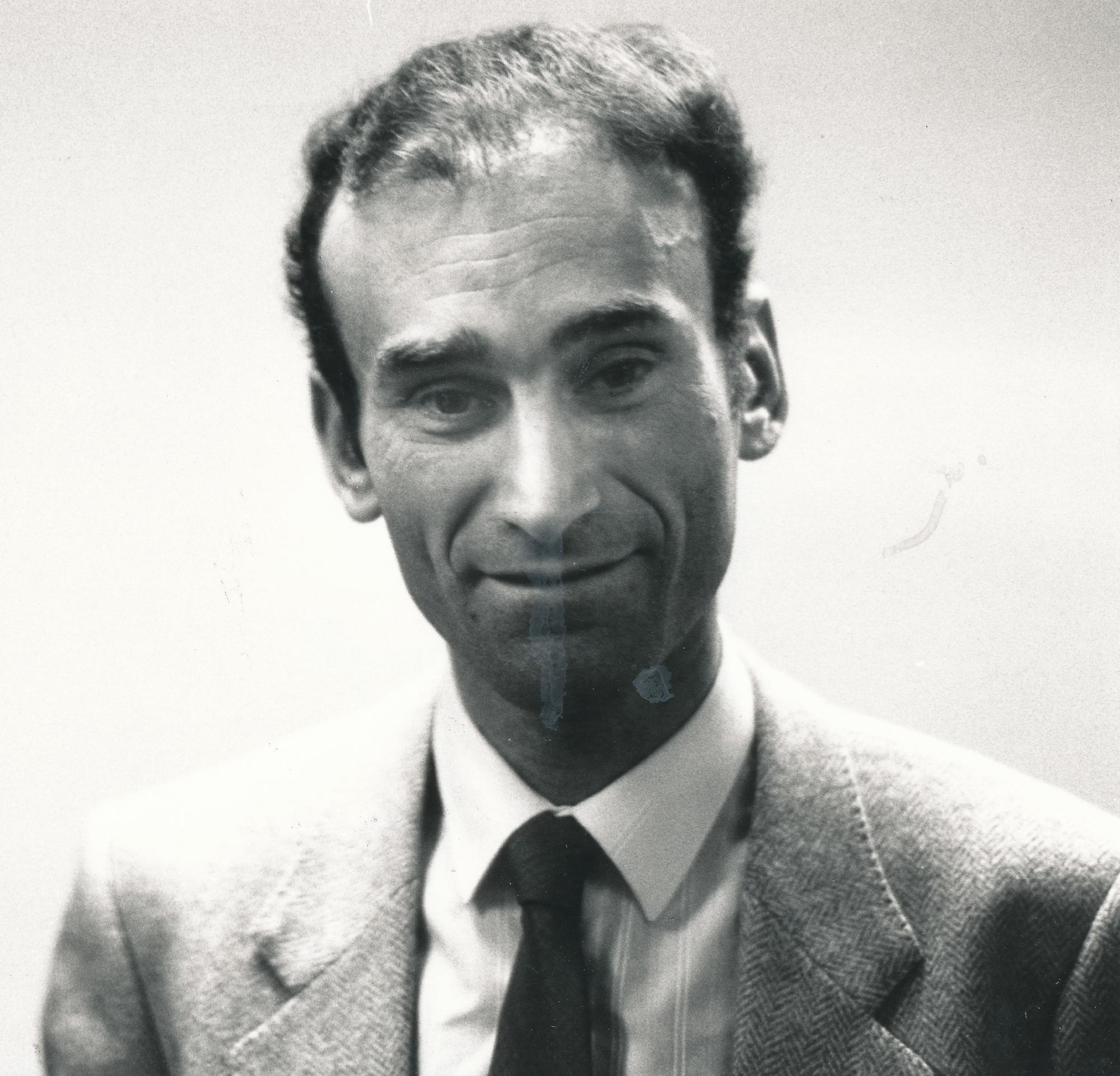
In 1983 at the height of his powers Michael left the chess work and became a tax accountant. He is now a senior partner at RSM UK.
Apparently :
“A cross disciplinary tax partner, Michael’s experience spans both corporate and non-corporate taxation for clients spanning a wide range of companies (listed and private) as well as high net worth individuals. Areas of activity include advice on transactions and structures, dealing with enquiries conducted by the tax authorities and forensic tax services in tax disputes.
As a member of the large business and international tax sub-committee of the tax faculty of the Institute of ICAEW, Michael was an active contributor to the consultation and development of the so-called ‘GAAR’ (general anti-abuse rule) law enacted in 2013.
Formerly a professional chess grandmaster, Michael brings an analytical approach to the field of tax.”