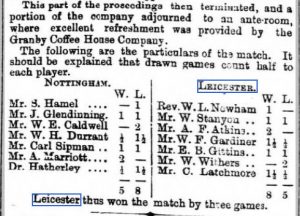
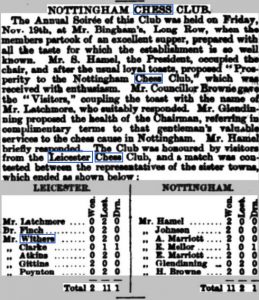
There are a few chess players who, while not being outstanding exponents themselves, achieved immortality through a flash of inspiration. Saavedra is one example, and another is the subject of this article: Oliver Harcourt Labone.

You might have seen something like this before, either this position or a similar position published by Lasker ten years later. I’m sure you don’t need me to tell you the answer. (Spoiler: it involves an underpromotion.)
Problemist Steven Dowd posted this on the BCN Facebook page, asking for more information about Labone.
There’s a lot to tell about a man who lived an eventful life, so do come along for the ride. It’s a rather extraordinary story.
Let’s take you back to the Central Criminal Court on 20 August 1861. A solicitor named Richard Austwick Westbrook was accused of manslaughter. He was a divorcee boarding with a lady named Jane Janette Cathrey, whose husband was had emigrated to Australia: both Richard and Jane, who were probably having an affair, had a reputation for being hot-headed and violent. During an argument Richard threw a knife across the table, hitting Jane in the abdomen and causing her death. A hearing in a magistrates’ court earlier in the month had found him guilty of manslaughter, but now the prosecution offered no evidence, believing it was an accident, and Richard walked free. Sounds like a combination of toxic masculinity and male privilege to me. Perhaps it affected his business, though, as he was declared bankrupt two years later.
Richard Austwick Westbrook had been born in Reading in 1815. In 1841 he married Hannah Grant Stiles. They had four children, but she died in 1852, and in 1855 he married Anne Topley at St Paul’s Church, Hammersmith. In 1857, a son, Rowland Martin Westbrook, was born, followed in 1858 by Oliver Harcourt Westbrook. It seems they split up shortly after Ollie’s birth and he went to live with Jane Cathrey. His petition for divorce was granted in 1860, naming a man called Demetrio as co-respondent. In 1862 he married a third time and had two more children.
Meanwhile, there was a Clement Leslie Dalba born in Brentford in 1860 (mother’s maiden name Mesina). There’s no other record of him, or of anyone else in the area with any of those names, so my best guess is he was the Clement Claude Leslie Labone we’ll meet later. The name Demetrio, along with Dalba and Mesina, suggests an Italian connection, so I suspect he was the son of Nicholas Demetrio and Anne Topley, and his birth had been registered using false names.
At some point in late 1860 or early 1861, Nick, Anne and the three boys moved to Glasgow, happy to escape Richard’s hot temper, and, to avoid detection, changed their name to Labone. Rowland’s middle name was also changed, from Martin to MacDonald: you can’t get much more Scottish than that. She also seems to have changed her maiden name from Topley to Copley, and sometimes added Mary in front of Anne.
In the 1861 Scottish census he’s Nicholas Labone, aged 28, living in a boarding house in Glasgow, but described as a Landed Proprietor. In 1862, a daughter, Flora Adelina, was born to Nick and Anne. Nick set up in business as a Professor of Languages, teaching French, German and Italian, but, just like Richard, ran into financial problems and, in 1863, was declared bankrupt. In 1865, a son, Gregory, was born, but sadly died the same year. In 1866 Nick’s publishers were trying desperately to unload 155 copies of his book A French Verbary.
In 1871 Ollie is away at school, but we find Nick, a Professor of Languages, living with his wife Annie M Labone, and two other sons, Rowland M (15) and Leslie C (12). Flora doesn’t seem to be around. Flora would later marry and have a family. Rowland died in his 40s, never apparently marrying or having a job, which suggests some sort of health problem. All I can find out about him is that in 1876 he was looking for a job as a lay evangelist. We’ll return to Clem/Les later.
Nicholas Labone/Demetrio, when he wasn’t teaching languages and writing books, was, it turns out, a chess player. He was very much involved with the Glasgow Chess Club in the early 1870s, both as a player and an administrator. He must have taught the game to Ollie and Clem. Nick and Anne’s marriage doesn’t seem to last. They both move down to Lancashire. Nick, now known as Nicholas Demetrio again, remarried in Barrow-in-Furness in 1882. There’s also a Demetrio who played in chess matches between Manchester and Liverpool in the early 1880s, who, I assume, was Nick. According to a rate book from 1890, he was still in Manchester, living in poverty. In 1891, Annie, claiming to be a widow born in Derby, was living with Rowland in Liverpool.
For the moment, though, we need to follow Ollie. We next pick him up in 1879, now living in Liverpool, where a public notice informs us that he’s no longer working for John Gibbs & Son, Ironfounders and Export Agents. At some point after Nick’s death the family seems to have moved from Glasgow to Liverpool. By 1881, he’s in Manchester, where he married Emily Etchells, the daughter of a Methodist preacher, and at the time of the census the young couple have just set up home together in Salford. Ollie is now described as a Commercial Traveller.
In 1883 he first makes his mark in the chess world, submitting a problem to the Illustrated London News. In 1884 he’s playing for Manchester, and, the following year in Stourbridge, Worcestershire. Over the next few years he’s active in Birmingham and Liverpool, along with half-brother Clem. In 1886 the position that would send his name around the world was published: quite an achievement for the young man.
Here’s a game from 1886.
And Problem 1, a mate in 3 from The Field 1 Jan 1887:
(Solutions to problems are at the end of the article)
Two games from 1888:
I can find no adult male with a name anything like L E Whitby anywhere near Liverpool in 1888 or anywhere else any other time, yet he is often mentioned in chess columns. Can anyone help?
The 1891 census tells us that, now a commission agent, he’s moved to Wolverhampton, along with Emily and their children Walter, Leonard and Marie. Another son, Oliver Martyn, had died at the age of only 4 months the previous year.

But in 1893 the family’s world was turned upside down. Ollie was up before the law, accused of embezzlement from his business partner, one Enoch Howard, found guilty and sentenced to a month’s hard labour. Naughty Ollie!
Undaunted, though, the following year he took up a new hobby: giving simultaneous displays against weaker clubs. Over the next 20 years or so he travelled the country, possibly connected with his job as a travelling salesman in machine oils, giving simuls wherever he went and gaining a national reputation as an expert simul giver. In 1894 it was Northampton, in 1896 it was Norwich.
He spent much of 1896 playing a match for the Staffordshire Championship with the Reverend John H Robison of Walsall, which he won easily, winning 10 games and drawing 2. In 1898 he faced a more formidable opponent for the county title: Charles William Draycott. Ollie only managed one draw from the first three games, but eventually scored 10 wins and 3 draws to his opponent’s 7 wins.
Here’s the final game of the match:
Against Lasker (it’s not clear at the moment whether this was a casual game or a simul, and exactly where it took place), he played an unambitious opening and a passive middlegame.
In 1901, still a commission agent, but working on his own account, he was living at Ivy Side, Rookery Road, Handsworth, West Bromwich with Emily, Len and Marie, Walt having left home. He was playing a lot of chess, but not playing Happy Families. There were clearly domestic problems of some sort, and, just a few months later, Emily and Marie set sail for New Zealand, as far away as possible from poor Ollie. Marie, would die a few years later, but Walt and Len would later join her with their families. She later married again, perhaps to a younger man she met on board ship, but there’s no evidence that she and Ollie were divorced.
Meanwhile, Ollie had found himself another woman, in fact another Emily, Emily Yates. (Every one was an Emily, ‘e wouldn’t ‘ave a Lily or a Pam.) She had been born in 1877 in Heywood, Lancashire, so perhaps they’d met on one of his visits to Manchester or Liverpool. Perhaps Emily Mark 1 had had enough of his constant travelling, or of his chess addiction. Or perhaps it’s just one of the oldest stories around: a middle-aged man is attracted to a younger woman. A son, Cyril, was born in Norwich in 1903, and another son, Douglas, in Leicester in 1905.
Here’s Problem 2: Mate in 3 from the Illustrated London News 15 Dec 1906.
A game from this period:
Yes, we seem to have found ourselves back in Leicester again, and, of course, Ollie soon threw himself into the chess life of the city, playing in matches and giving simuls, but also visiting Liverpool in 1909 to take part in a blindfold simul against Blackburne. In 1911 they’re in New Bridge Street, not very far from what was then Filbert Street but is now the King Power Stadium. He’s a Commercial Traveller in Oils, while Emily Yates is a Housekeeper. (This was a common euphemism in census returns, but sometimes employers did have affairs with their housekeepers. Ten years later, for example, South Warwickshire farmer Thomas Woolley had an affair with his housekeeper while his wife was in the lunatic asylum. Pretty despicable, you might think, but if he hadn’t done so, you wouldn’t be reading this article today.)
Here’s the Blackburne game, which doesn’t make a very good impression. He misplayed the opening and never stood a chance. You get the impression he was a strong attacking player, but when facing top level opposition he curled up into a ball and defended weakly. As it happens, one of his relations was a much better defender.
A game from his time in Leicester:
It wasn’t long before he was on the move again. By 1913 he was in Blackpool, where his sons would be baptised the following year.
Problem 3, another mate in 3, was published in the Illustrated London News on 9 October 1915.
While his family settled down by the Lancashire coast, he was back on the road, spending some time in Devon and Cornwall, and, of course, giving simuls. He was back in Exeter in 1918, where he played Plymouth champion Thomas Taylor.
In February 1920 he was writing to the Illustrated London News from Belfast, and, a few moths later, he was in Barrow-in-Furness.
Problem 4, mate in 3 Illustrated London News 17 Sep 1921:
At that point it seems he settled down in Blackpool, now running an advertising agency of sorts. In 1925 he was still submitting problems and games for publication in the Illustrated London News.
Problem 5, mate in 3 Illustrated London News 9 May 1925
Perhaps he just had time to see this game in print before, beset by financial problems, he decided to take his own life.

His son Cyril would also have an unhappy life, and by 1939 was in a mental hospital, described as a pianist. He died in 1947 at the age of 43.
So that was the sad end of Oliver Harcourt Labone, chess addict, player, problemist and simul giver, indefatigable writer to chess columnists. He must have been a troubled man throughout his life. Did his passion for chess help him through his darkest days, or was it one of the causes of his problems, not leaving him enough time for his work and family? It seems like several members of his family were beset by mental health probems, so my guess would be the former.
Oliver Harcourt (Westbrook) Labone, this was your life.
But it’s not the end of our story. Let’s return to Ollie’s probable half-brother Clement Claude Leslie/Clement Leslie/Leslie Clement, who, as we’ve seen, was also a chess player, but at a lower level. He had a much less eventful life, in spite of job changes. He was a schoolmaster in 1891, a book-keeper in 1901 and a mercantile clerk (which might, I suppose, involve book-keeping) in 1911. He was active as a club player between 1885 and 1894, annotating a consultation game in 1891. After that, I suppose, family life and work took over. He remained in Liverpool all his life, living in West Derby in 1891 and 1901, and in Everton in 1911. If you were following football in the 1960s the names Labone and Everton will be inextricably linked. Any connection?
Clem married Fanny Price and had four children, the oldest of whom, born in 1887, was also named Clement Claude Leslie Labone, and, by 1939, had become a Dining Room Proprietor. He married Edith Birch and had three sons, the middle one of whom was named Arthur Leslie Labone. Arthur, in 1939 a Lead Merchant’s Travelling Agent (sounding not unlike great uncle Ollie) married an Irish girl named Bridget (Patricia) Rice. Their son was indeed Brian Leslie Labone (1940-2006), the Everton and England footballer, who, unlike his great great uncle, excelled at defending. He wasn’t the only footballer in the family: his uncle Harold played as a centre forward for Aston Villa.
There’s more yet. When I posted about the connection between Ollie and Brian on Twitter, my good friend John Foley replied that he was also related to Brian Labone (verified by DNA), whose mother’s maiden name was Foley. So Brian Labone, assuming Clem senior and Ollie were indeed blood relations, was related to chess players on both sides of his family.
It’s a small world, as you’ll find out when we return to Twickenham for future Minor Pieces.
Solutions to problems:
Problem 1:
1. Qh4 Kc5 (1… Ng3 2. d4 c5 3. Qd8#) (1… Kxe5 2. d4+ Kd6 3. Qd8#) ( 1… d4 2. Nxc6 d3 (2… e5 3. Qe7#) (2… Kc5 3. Qxd4#) 3. Qd4#) 2. Qb4+ Kxb4 3. d4#
Problem 2:
1. Nd6 Kxd6 (1… Bxc7 2. Qe3+ Kxd6 3. Qe5#) (1… Kd4 2. Qf2+ Kc3 3.
Qb2#) (1… Kb6 2. Qa5+ Kxa5 3. Nc4#) 2. Qa5 Bxc7 (2… c5 3. Qb6#) 3. Qe5#
Problem 3:
1. Nb5 (1. Rhe6 Bd7) 1… Kxe4 (1… Bxb5 2. Rhe6 Bc6 3. R4e5#) (1…
Rxb5 2. Rhe6 Rb1 3. R4e5#) (1… Bxc2 2. Rhe6 Bxe4 3. Nc7#) (1… Bb3 2. Rhe6 Bxc2 3. R4e5#) (1… axb5 2. Rhe6 b4 3. R4e5#) 2. Re6+ Kf3 3. Nd4# 1-0
Problem 4:
1. Rh6 Bc6 (1… b5 2. c8=Q b4 (2… Nc6 3. Qg8#) 3. Qc4#) (1… Nc6 2.
c8=Q Ne5 (2… Nd4 3. Qc4#) (2… b5 3. Qg8#) 3. Rd4#) (1… Rc5 2. Rd4+ Ke5 (2… Kc6 3. c8=R#) 3. Nf7#) (1… Rb5 2. Rd4+ Kc5 3. Ne4#) (1… Bb5 2. Rd4+ Kc5 3. Ne4#) 2. c8=N Bxb7 3. Ne7# 1-0
Problem 5:
1. Qh5 {Threats: 2. Ne5 and 3. Qf3#, 2. Ne3+ dxe3 3. Nb6#} Kxc4 (1…
Bxc4 2. Nf6+ gxf6 (2… Kc6 3. Qf3+) 3. Qf3#) (1… Ke4 2. Ne5 g2 (2… Kf4 3. Qg4#) 3. Qf3#) (1… g2 2. Ne3+ (2. Rc5+ Ke4 3. Nf2#) 2… dxe3 3. Nb6#) (1… e5 2. Qf7+ (2. Nxe5 g2 3. Qf3#) 2… Ke4 3. Nc5#) 2. Ne5+ Kb5 (2… Kb3 3. Qd1#) (2… Kd5 3. Qf3#) 3. Qe8# 1-0