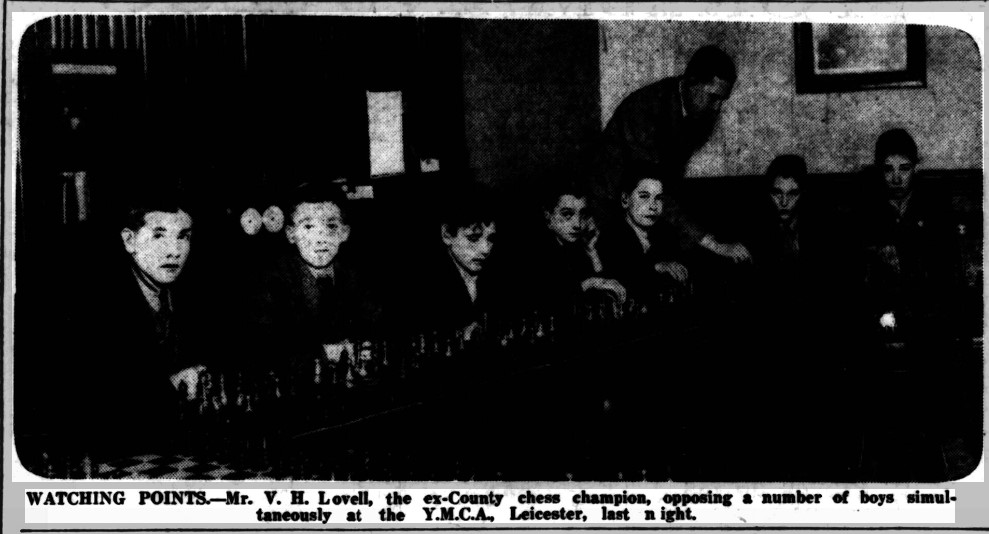
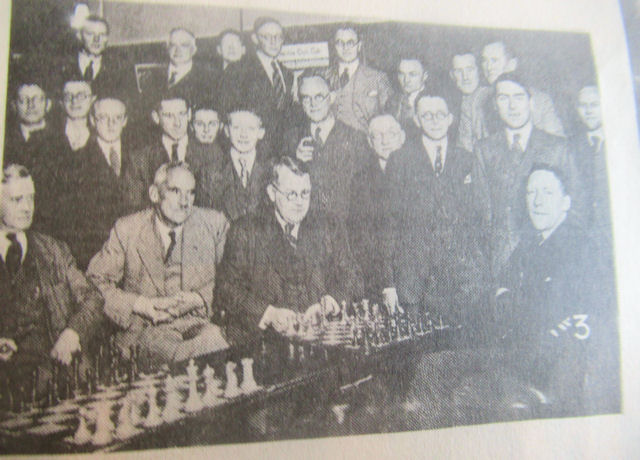
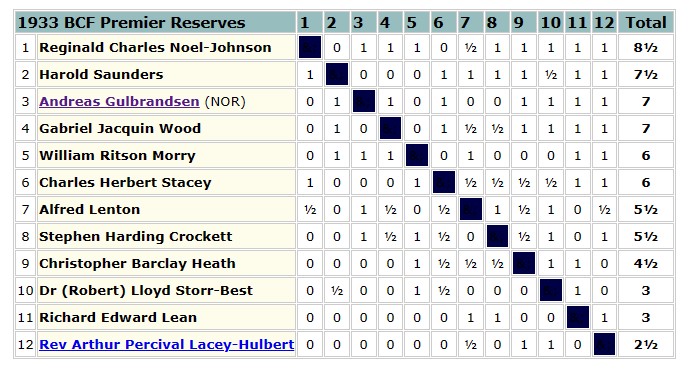
We left Reginald Charles Noel-Johnson last time, having just married Jane Ann Richards and joined the RAF on war service.
Before I move on, my thanks to Brian Denman, who has sent me a whole pile of Noel-Johnson’s games. I’ll add a few earlier scores here: as always, click on any move for a pop-up window.
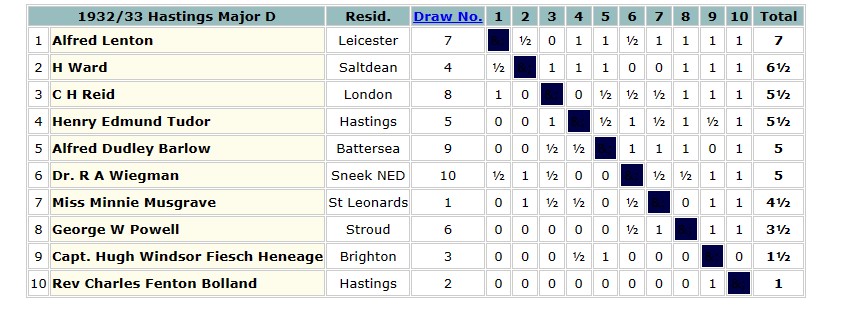
Even in 1924, as an inexperienced 20-year-old, he was capable of playing strong positional chess, being particularly severe here against his opponent’s Dutch Defence, and not being distracted by the magnificent view from the roof of Australia House. William Henry Watts was, apart from being a civil servant, a prominent chess journalist and author.
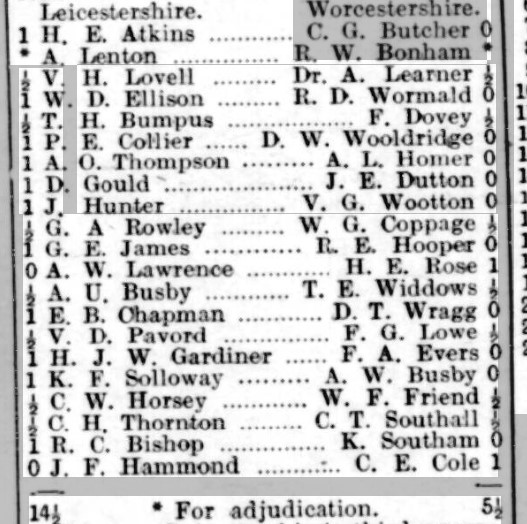
In this county match game from 1936 he won quickly against his Essex opponent’s rather unsophisticated opening.
In another county match game he took a notable scalp when one of England’s finest amateurs, perhaps in time trouble, lost the plot.
Finally, for the moment, another game against Yeeles, which might, as Brian suggests, have been played in a club match, but also fits in with the 1937 county championship final. He was lucky here, as Yeeles stood better before giving up the exchange for no obvious reason: perhaps again a time trouble blunder.
Returning to his life story, Reginald and Jane had two children, Patricia, born in Chester in 1942, and Christopher (who sadly died in 2010), born in Surrey in 1946. During this period his work for the RAF took him to India, and it was only in 1947 that he was able to resume his chess career.
He wasted no time in picking up where he left off.

His final game was a textbook example of strong positional play, his pressure on his opponent’s backward c-pawn eventually leading to material gain. Click on any move of any game in this article for a pop-up window.
Although he’d been living in central London since at least 1929, he maintained his loyalty to Kent, playing in county matches as well as the county championships.
This game from a match between West/Mid Kent and Metropolitan Kent had a curious conclusion. White thought he had no defence to Black’s threats, but in fact he had a slight advantage.
In 1949 he won the Kent Championship for the eighth time. In this game from the first round he again demonstrated strong positional play, winning material, but returning it for two far advanced connected passed pawns in the centre.
In this county match game he missed a tactical opportunity, but his more active pieces still made life difficult for his Sussex opponent.
Noel-Johnson also remained loyal to Lewisham. In this National Club Championship game his international opponent blundered, allowing a smart finish.
Facing another international opponent in a London League match, he gave a textbook example of how to play against the Dutch Stonewall, taking advantage of Black’s weak dark squares and undeveloped queen’s bishop to set up a decisive pin.
This game bears testimony to Reginald’s considerable endgame skills.
1951 marked the centenary of the Great Exhibition in London, which included the world’s first international chess tournament, and it was only right that the 1951 Festival of Britain should also include some chess. Reginald Noel-Johnson, by now a respected organiser and populariser of chess as well as a very strong player, was involved, and television cameras were present.


In case you’re unfamiliar with some of the personalities involved: David Farrar CEM Joad Eamonn Andrews Sir Ronald Storrs
(Sir Ronald founded the first chess club in Palestine in 1918, hoping to unite Arabs, Jews and Christians stationed in Jerusalem, and to help promote peace and understanding. It didn’t work out: it closed within a year due to tensions between Arabs and Jews.)
In 1951 Noel-Johnson organised a London Transport team who travelled to Hastings Chess Club.

The home team won 21½-8½, but König and Noel-Johnson, on the top two boards, against Winser and Waterman.
(Chess was a very big thing amongst London Busmen at the time, a story I should perhaps investigate further.)
In October 1952 the National Chess Centre re-opened, just across the road in Oxford Street from the previous centre which had been burnt down during the war. Noel-Johnson was very much involved in its re-establishment. He was also honoured by being appointed President of the Southern Counties Chess Union in 1952-53.
Here’s another game, this one from the 1952 county championship, resulting in a minor piece ending.
This game was played on top board in a county match at the National Chess Centre. It looks like White miscalculated or misjudged the position round about move 20.
The 1953 National Chess Centre Championship gave Reginald another chance to demonstrate his positional mastery.
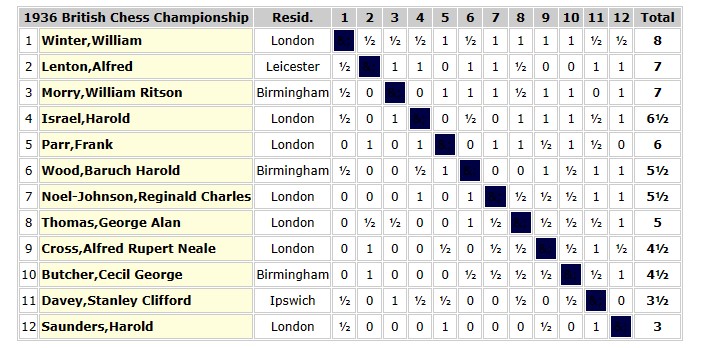
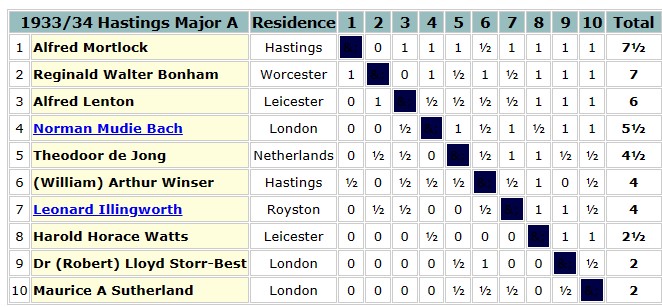
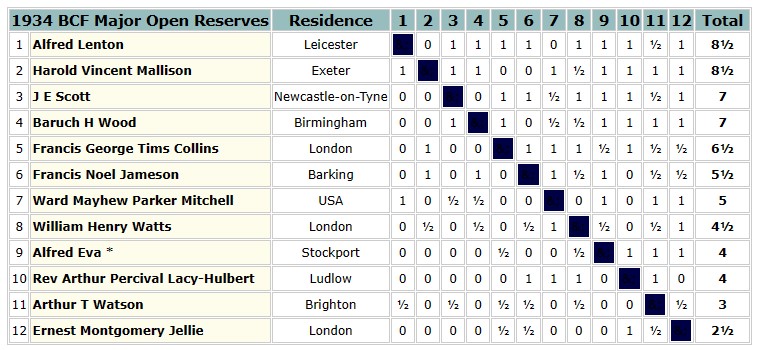
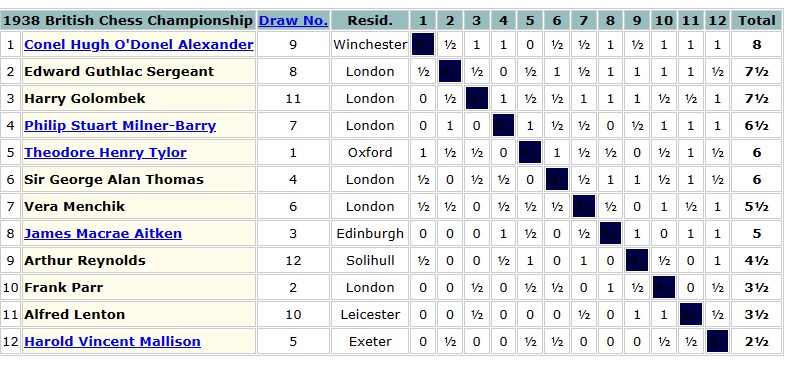
In 1954 the British Chess Federation published its second (and first full) grading list. Reginald Noel-Johnson was there on 3a (209-216, or about 2300 Elo), along with Alfred Lenton, and several of his other erstwhile opponents. At the age of 50, he seemed to be playing as well as ever.
But at that point he became a lot less active. By the 1955 grading list he’d slipped to 4a (193-200, approaching 2200 Elo).
One reason might have been that he was now becoming active in the musical world as a composer. I’d imagine that his work at Ricordi’s (he’d moved from Chappell’s) involved, on occasion, being commissioned to write incidental music.
Back in 1933 he’d been writing songs in the style of his father, his setting of Weep you no more, sad fountains, an anonymous Elizabethan verse set by everyone from John Dowland to Roger Quilter, being admired for its combination of freshness and charm. “The harmonic scheme in the accompaniment is never dull and the melody has a quiet flow and a beautiful ending, suitable for soprano or tenor”, according to the West Middlesex Gazette (27 May 1933).
Unfortunately, I can’t find a recording of this or any of his other music, but I recently heard Ivor Gurney’s setting in a recital. I rather suspect Noel-Johnson’s setting was closer to that of Quilter.
Judge for yourself here.
In 1952 Noel-Johnson had composed the music for Enid Blyton’s Noddy Song Book, and these were used for a children’s play produced over the Christmas holidays in December 1954. No, I wasn’t in the audience.
It was repeated the following year, when the cast list included ‘Ronald’ Corbett as Mr Whiskers and Jinky, while older children could watch the Famous Five in the evening.
In 1953 an ice pantomime, Sinbad the Sailor (pantomimes on ice were very big in those days) included a ballet based on Morphy’s Opera House Game, with music by Noel-Johnson.
There was a new job for him in 1958, when he was appointed general manager of Ascherberg, Hopwood and Crew.
You might have expected that Reginald’s chess career had come to an end, but in 1974 he unexpectedly turned up playing for King’s Lynn, in Norfolk. He was rapidly appointed match captain, and was involved in a ‘chess happening’ forming part of the King’s Lynn Festival.

In 1975 he reappeared on the grading list at 190, seemingly having retained his strength into his 70s, despite a 20 year long absence from the board.
He didn’t appear in the next two grading lists, but returned in 1978, now living in Worthing, on the south coast. That year he was down to 181, but by 1982 he was up to 194, and, after a decline the following year, back to 192 in 1984. This would be about 2150 – pretty impressive for someone in his late seventies.
In this game he renewed acquaintance with an old Kent rival, now promoted to the rank of Canon within the Church of England, who left it far too late to develop his queen’s knight.
Here, he faced a Cannon rather than a Canon. John Cannon was a strong Sussex player who, I believe, claimed to hold a record for the number of county matches he played.
Noel-Johnson also started playing in tournaments again, favouring those in Devon, often playing in Paignton and occasionally in Torquay. In 1981, despite a last round defeat, he shared first place in the top section at Paignton.

In one of the key games from this event he scored the full point against one of the other joint winners, who went wrong on his sealed move.
In 1981 he changed his allegiance from Worthing to Rustington: I wonder if this was under the influence of his old friend Eric Smith. Perhaps it was he who had enticed him to the delights of Sussex in the first place.
In this club championship game from 1981 he switched from his usual 1… e5 to the Sicilian, scoring a quick victory. He clearly knew his opponent well.
Brian Denman tells me that in 1982 Noel-Johnson reached the Sussex final, and, if he had won, he would have been the oldest champion. However, he lost both games against Feliks Kwiatkowski. Here are a few more victories from Brian’s files.
The last game I have is a loss, from 1987.

Reginald Charles Noel-Johnson died on 27 December 2000 at the great age of 96, his death being registered in Windsor and Maidenhead.
Two of his brothers also had interesting stories to tell. Dennis, who, you may recall, changed his surname to Cullum, achieved fame as an athletics coach, specialising in hammer throwing. You can read more about him here.
Reginald’s youngest brother, George Douglas, had been a member of the Territorial Army (Artists’ Rifles) in 1937, but in 1939, with war imminent, joined the RAF, flying Hurricanes in Greece and eventually rising to the rank of Squadron Leader. He retired from the services in 1956.
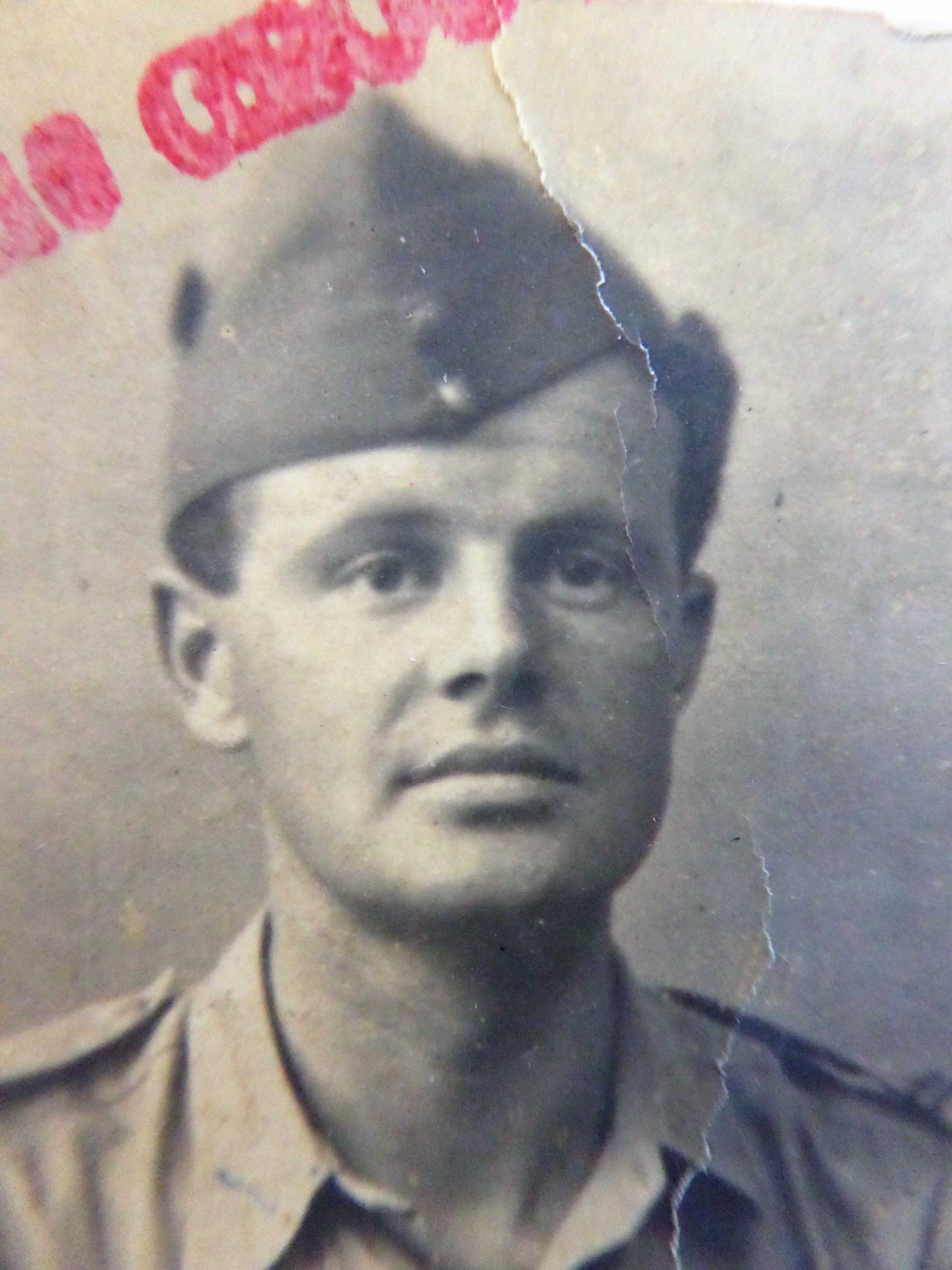

War often brings people from very different backgrounds together, and so it was with George Douglas Noel Noel-Johnson, who, in Heliopolis in 1945, married a secretary in the WAAF named Catherine Lucy Gunn (she was now spelling her name Katharine Lucille).

They would have three children, Clive, Mark and Sally, and, while her husband died relatively young in 1972, she would live on until 2018, reaching the age of 98. I must show my appreciation here to Clive and Sally for generously sharing so much family information through their online trees.
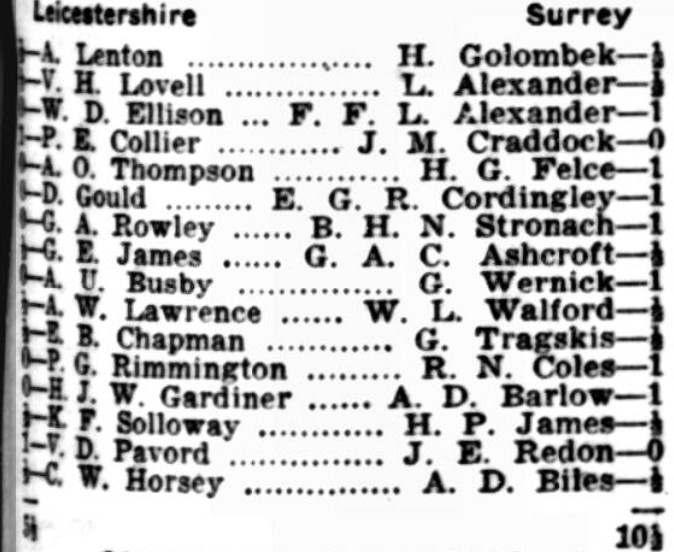
Her parents had met while working in a mental health hospital, and Catherine, the youngest of four children, lost her father to pneumonia when she was only 2. Her mother, Edith Mary White, was the daughter of a groom, and the granddaughter of an agricultural labourer from near Warwick. Her grandfather, Thomas White, had a cousin, Sarah, who married Robert Padbury. Robert had many granddaughters, one of whom, Florence, was, in 1921, working as a housekeeper to a farmer whose wife was in Hatton Lunatic Asylum. She was no doubt unaware that her third cousin Edith had been working there ten years earlier. Florence had an affair with her employer: their daughter was my mother. This makes Reginald Charles Noel-Johnson, if my tree is correct, the brother-in-law of my 4th cousin once removed. And, you might recall from the first article, he played on two occasions against my father’s kinsman Alfred Lenton.
Noel-Johnson and Lenton, despite their very different backgrounds, had a lot in common. They were both mainly positional players, Noel-Johnson playing in classical style, as opposed to Lenton’s hypermodern approach. Lenton was slightly stronger in the 1930s, playing for England on several occasions, but Noel-Johnson retained much more of his strength into old age. Both took a break in middle age, returning to chess in their retirement, and both remaining active in the chess world into their tenth decade.
We should certainly thank Reginald Charles Noel-Johnson for his services to chess, both as a player and an administrator, over more than 70 years. I believe it’s important for the whole chess community to keep the memory of players such as him alive.
Sources & Acknowledgements:
ancestry.co.uk (family trees of Clive Noel-Johnson and Sally (Noel-Johnson) Giddings)
findmypast.co.uk/British Newspaper Library
Wikipedia
BritBase (John Saunders – thanks also for his RCNJ games collection)
ChessBase/Stockfish 16
Brian Denman (thanks for his RCNJ games collection)
Guy Holloway
YouTube



 Again, from two years later:
Again, from two years later:  Here we have a successful composer of music mostly for home consumption: songs, short pieces for cello and piano and so on. Music which, perhaps sadly, has now gone out of fashion: I haven’t been able to find any recordings of these songs, but a later work, comprising three short piano pieces, has been recorded for YouTube by Phillip Sear, a specialist in this type of repertoire.
Here we have a successful composer of music mostly for home consumption: songs, short pieces for cello and piano and so on. Music which, perhaps sadly, has now gone out of fashion: I haven’t been able to find any recordings of these songs, but a later work, comprising three short piano pieces, has been recorded for YouTube by Phillip Sear, a specialist in this type of repertoire. But the family’s idyllic seaside life was shattered in January 1916 when William Noel Johnson, now living near Southend, died suddenly of pneumonia, leaving Rosie a widow with six young children.
But the family’s idyllic seaside life was shattered in January 1916 when William Noel Johnson, now living near Southend, died suddenly of pneumonia, leaving Rosie a widow with six young children.
















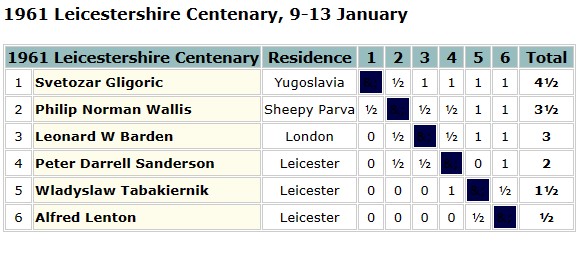 Tournament report
Tournament report 
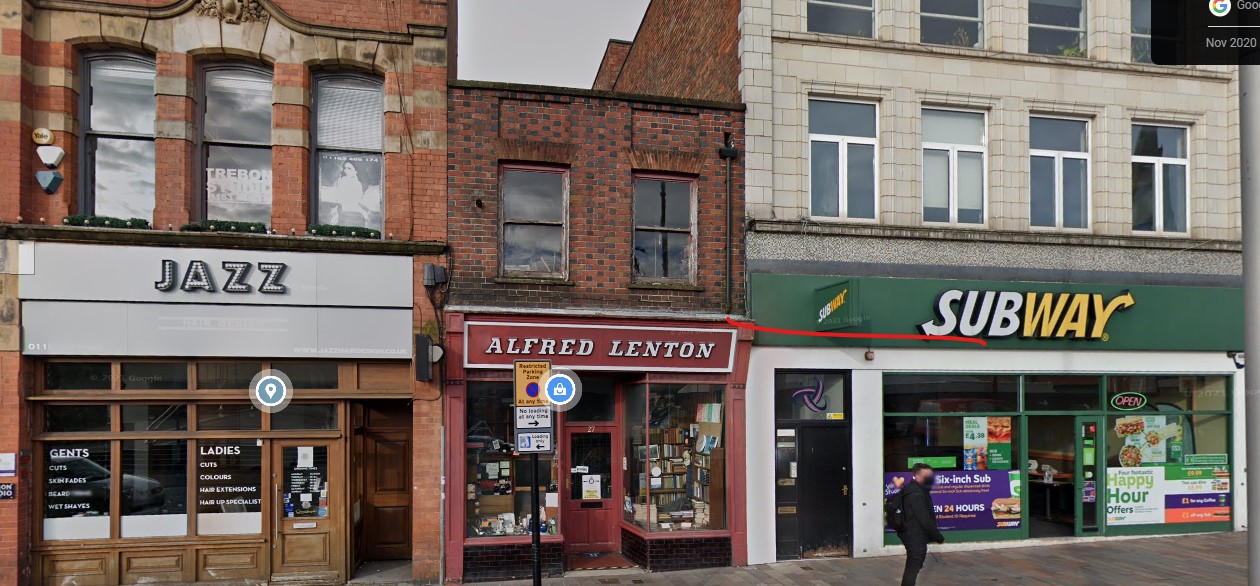





 In 1910 this Thomas married Ethel Wood, born in 1888. Ethel was perhaps slightly higher up the social scale: her father, John, was a School Attendance Officer, although his background was also very much working class. Here he is, on the right. John and his wife Sarah had five daughters (Ethel was the fourth), the oldest of whom married into a branch of the Gimson family, followed by a son.
In 1910 this Thomas married Ethel Wood, born in 1888. Ethel was perhaps slightly higher up the social scale: her father, John, was a School Attendance Officer, although his background was also very much working class. Here he is, on the right. John and his wife Sarah had five daughters (Ethel was the fourth), the oldest of whom married into a branch of the Gimson family, followed by a son.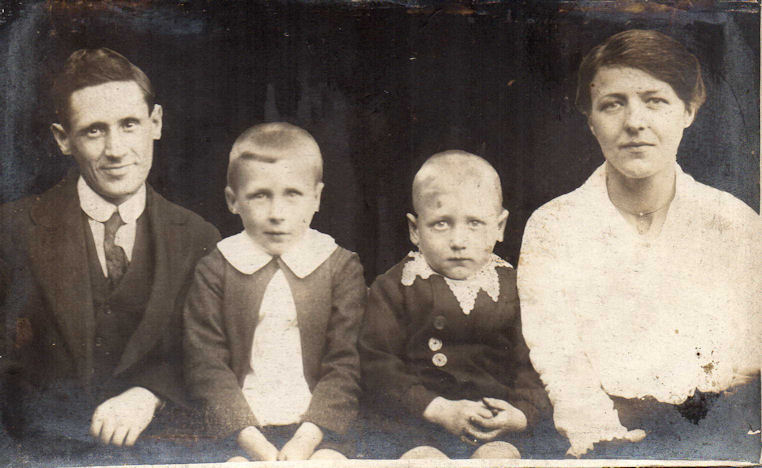



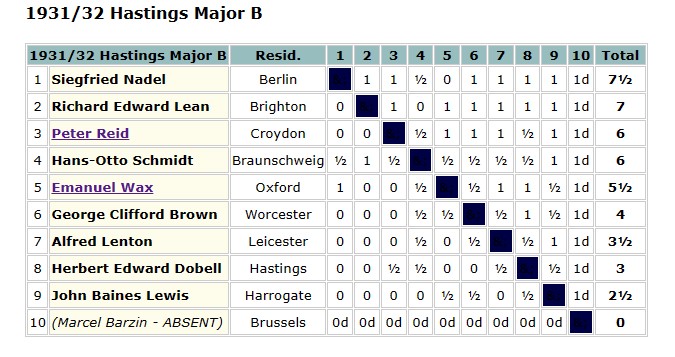


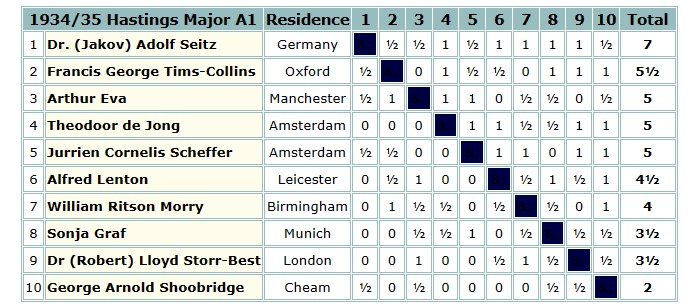

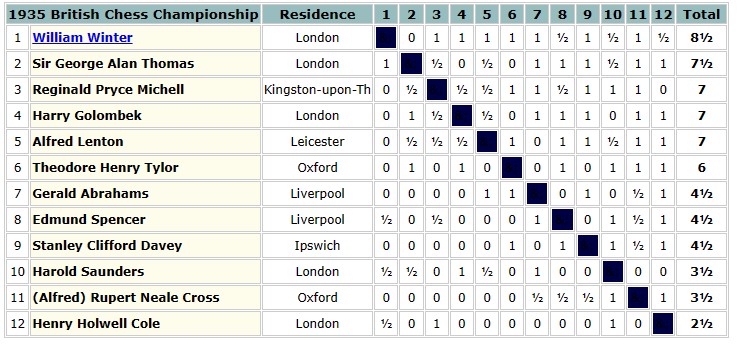
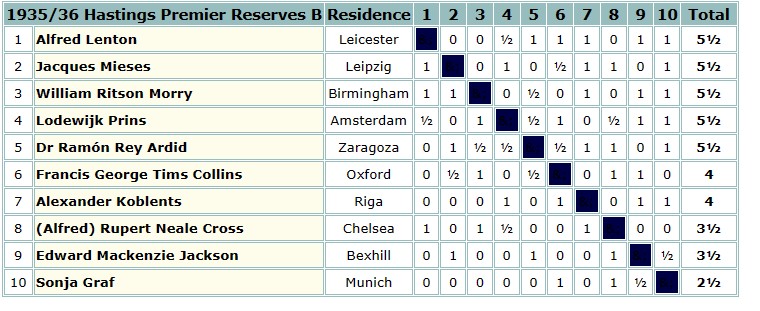
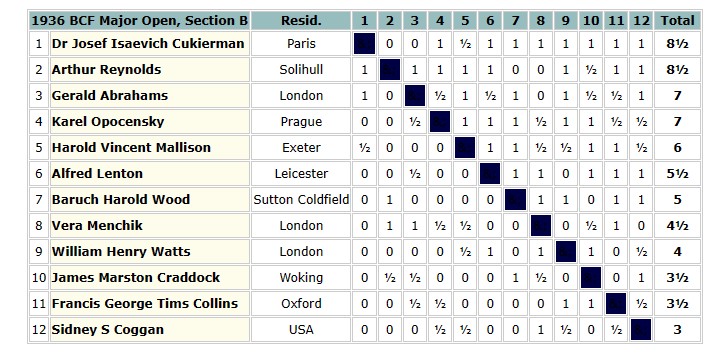
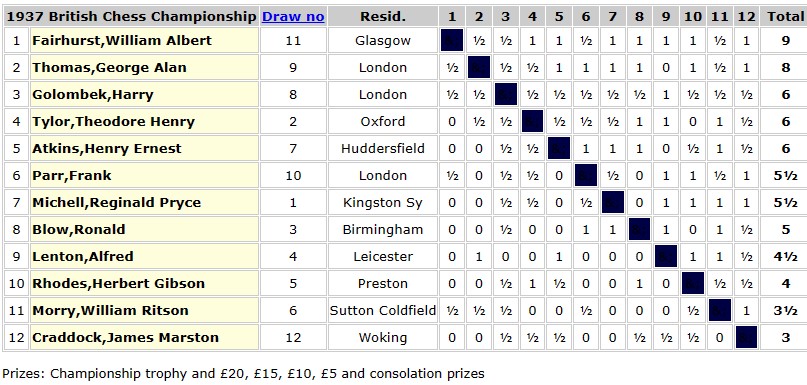










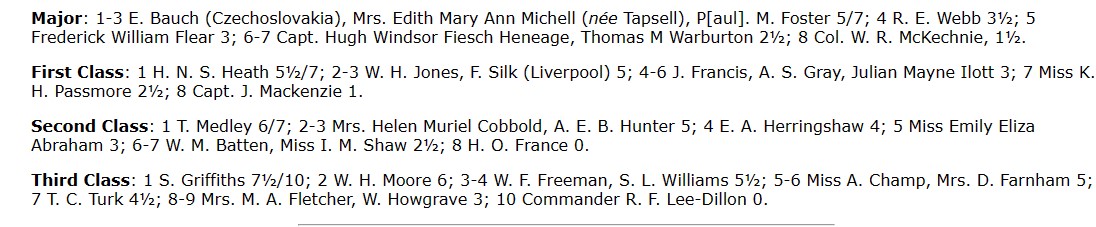

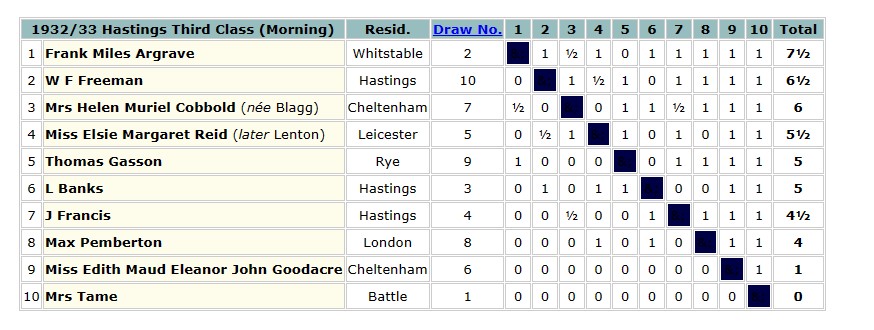

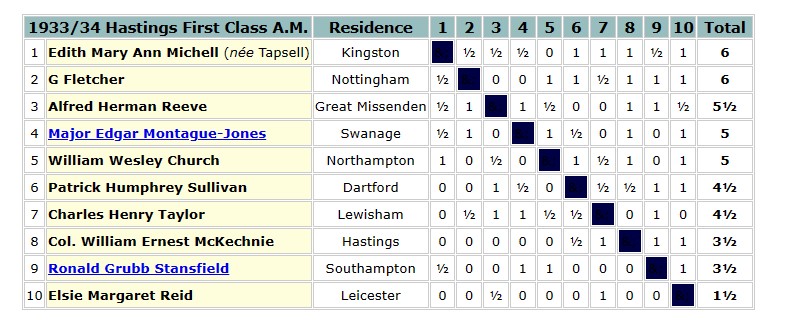
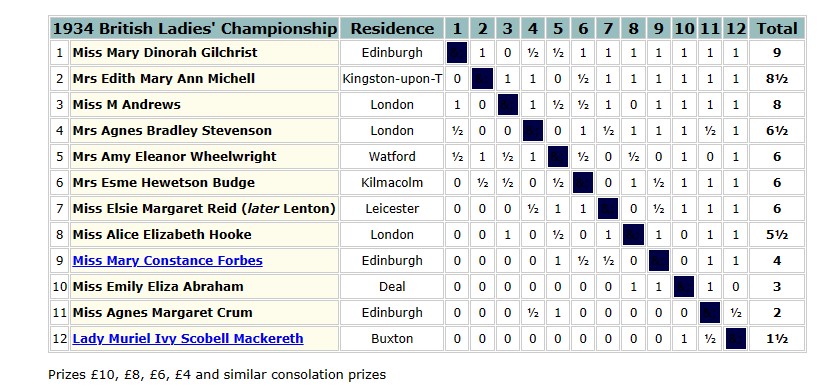

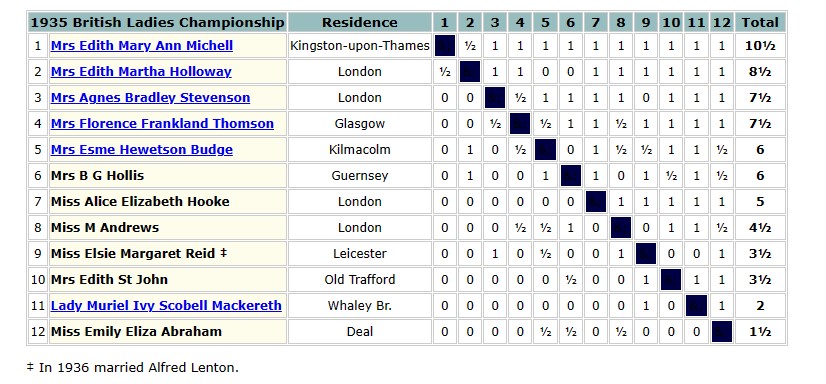
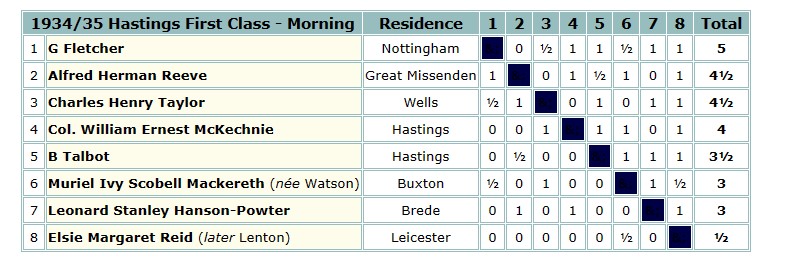 The 1935 British Championships took place in Great Yarmouth. Elsie was rather less successful this time round, only scoring 3½ points.
The 1935 British Championships took place in Great Yarmouth. Elsie was rather less successful this time round, only scoring 3½ points.