We send best wishes to GM Luke James McShane on his birthday, this day (January 7th) in 1984.
Here is Luke’s Wikipedia entry
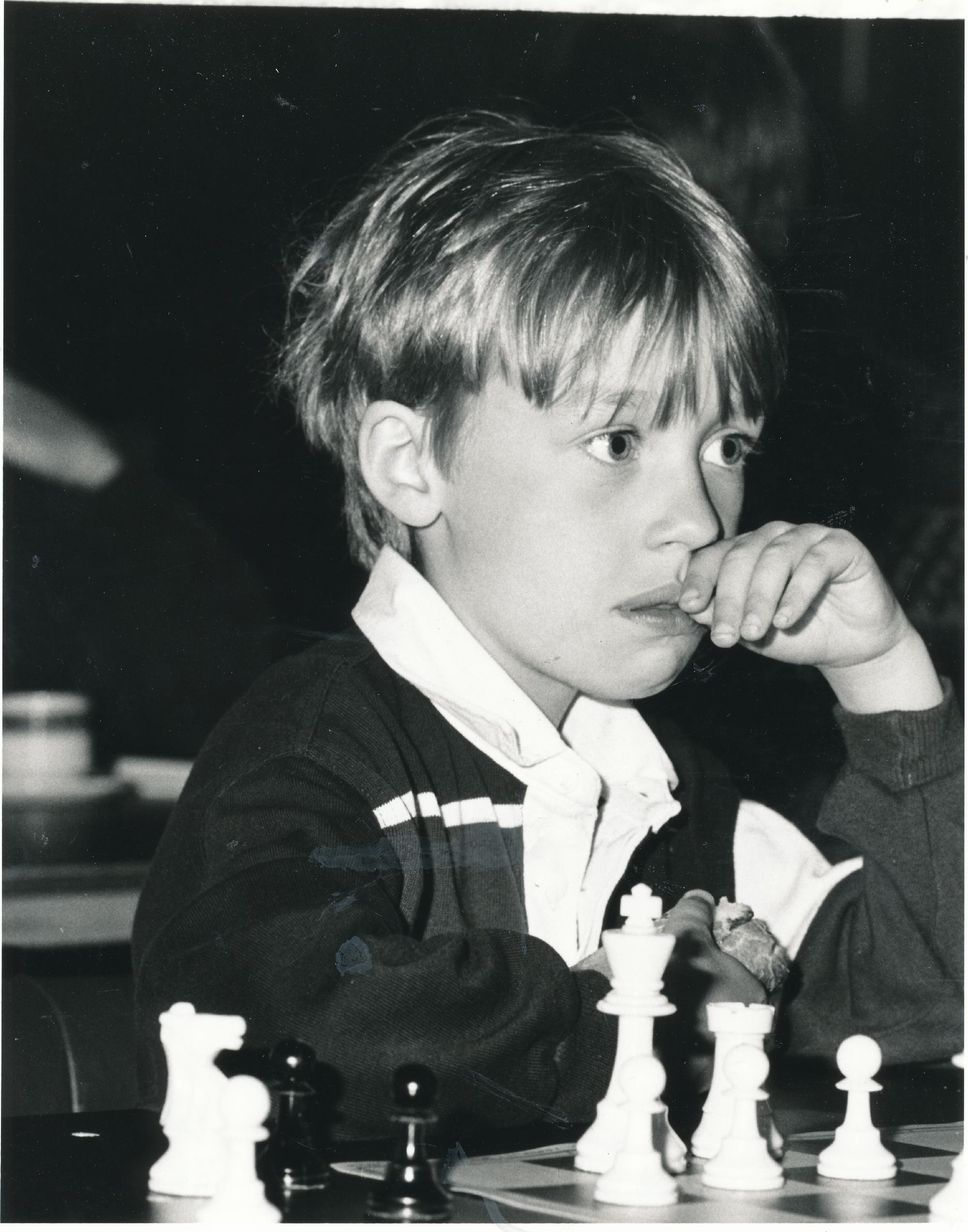
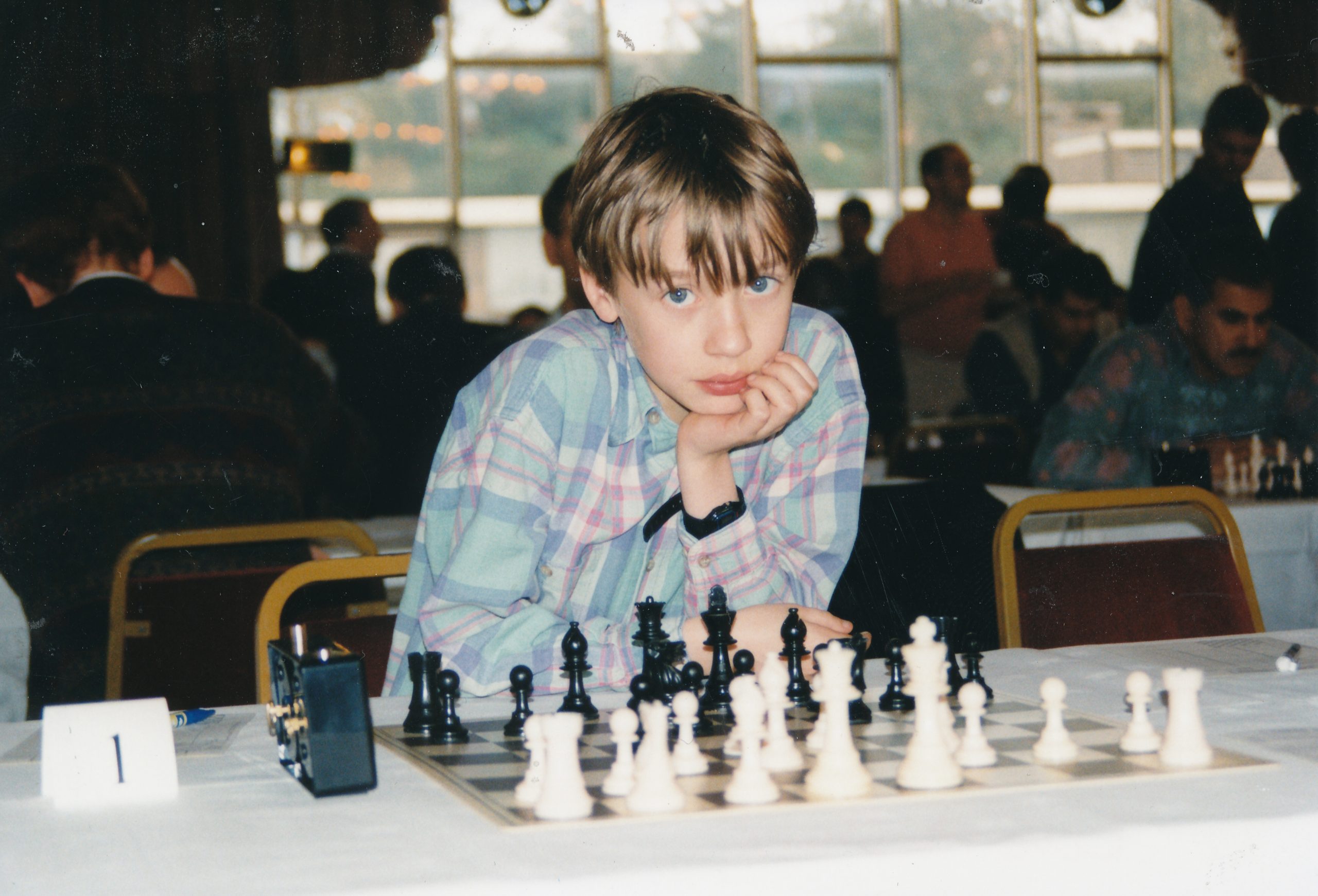


We send best wishes to GM Luke James McShane on his birthday, this day (January 7th) in 1984.
Here is Luke’s Wikipedia entry


We send best wishes to GM Luke James McShane on his birthday, this day (January 7th) in 1984.
Here is Luke’s Wikipedia entry


We remember Thomas Dawson who passed away seventy years ago on Sunday, December 16th, 1951.
He was also known by the pseudonym T. Dyke Robinson (we are looking for a primary source for this)
Thomas Rayner Dawson was born on Thursday, November 28th 1889 in Leeds, Yorkshire to Henry and Jane Dawson (née Rayner).
The early history of TRD and his family has been meticulously researched by Yorkshire chess historian, Steve Mann. We recommend you visit this page to discover the detail.
According to Edward Winter in Chess Notes TRD lived at the following addresses :
From The Oxford Companion to Chess (OUP, 1984 & 1996)by Hooper & Ken Whyld:
“English composer, pioneer of both fairy problems and retrograde analysis. His problems in these fields form the greater part of his output (about 6,500 compositions) and are better remembered than his studies and orthodox problems. For fairy problems he invented new pieces: grasshopper (1912) LEO (1912), NEUTRAL MAN (1912) NIGHT RIDER (1925), and VAO (1912); he codified new rules such as the maximummer (1913) and various kinds of series-mover; and he used unorthodox boards.

In 1915 he wrote Retrograde Analysis, the first book on the subject, completing the project begun several years earlier by the German composer Wolfgang Hundsdorfer (1879-1951).

From 1919 to 1930 Dawson conducted a column devoted to fairy problems in the Chess Amateur, In 1926 he was a co-founder of The Problemist , which he edited for its first six years and he founded and edited The Problemist Fairy Supplement (1931-6) continued as The Fairy Chess Review (1936-51).

Besides conducting columns in several newspapers and periodicals, one of them daily and one in the Braille Chess Magazine, Dawson edited the problem section of the British Chess Magazine from 1931 to 1951; he devised and published in its pages (1947-50) a systematic terminology for problem themes in the hope that it would supplant the extensive jargon then and now in use, Dawson wrote five hooks on fairy problems: Caissa’s Wild Roses (1935); C. M. Fox, His Problems (1936); Caissa’s Wild Roses in Clusters (1937); Ultimate Themes (1938); and Caissa’s Fairy Tales (1947).

Charles Masson Fox (1866-1935) was a patron whose generosity made possible the publication of four of these books and the two fairy problem magazines founded by Dawson. Ultimate Themes deals with tasks, another of Dawson’s favourite subjects. In 1973 all five books were republished in one volume. Five Classics of Fairy Chess.

Dawson found it difficult to understand the problemist’s idea of beauty because it is not susceptible to precise definition. The artist talks of “quiet” moves, oblivious that they are White’s most pulverizing attacks! This aesthetic folly, reverence, response thrill to vain-glorious bombast runs throughout chess.(See Bohemian for a problem showing 16 model mates, a task Dawson claimed as a record but a setting Bohemian composers would reject.) His genius did not set him apart from his fellows; he could find time for casual visitors and would explain his ideas to a tyro with patience, modesty, and kindness. Although he won many tourney prizes much of his work was designed to encourage others, to enlarge the small band of fairy problem devotees, He composed less for fame than to amuse himself, confessing to another composer ‘We do these things for ourselves alone.’

A chemistry graduate, Dawson took a post in the rubber industry in 1922 and rose to be head of the Intelligence Division of the British Rubber Manufacturer for which he founded, catalogued, and maintained a technical library. Unwell for the last year of his life, he died from a stroke. K. Fabel and C. E. Kemp, Schach ohne Grenzen or Chess unlimited (1969) is a survey, written in German and English, of Dawson’s contribution to the art of fairy problems.”

From The Encyclopedia of Chess (Robert Hale 1970 & 1976), Anne Sunnucks :
“British problemist. Born on 28th November 1889. Died on 16th December 1951. Universally known as TRD., the great master of Fairy problems. His wealth of invention held the chess world enthralled. His output comprised about 6,400 problems and 150 studies.
Dawson was a nephew of the late James Rayner, himself a noted chess problemist . From as early as about 1910, TRD had conducted the ‘Chess Endings‘ section in the Chess Amateur, and its Fairy section from 1919. He worked with BG Laws from Mark 1930 conducting the problem pages of the British Chess Magazine, and following Laws’ death he assumed complete charge of the section from October 1931 to February 1951 when ill health forced him to relinquish the work.

The Problemist Fairy Chess Supplement subsequently renamed The Fairy Chess Review was started by TRD in August 1930. TRD was concerned in a number of other chess publications ; chess for the Blind, several books of the AC White Christmas series, BCPS Honours 1926-29, and the CM Fox series.
He was largely instrumental in the publication of the first issue of The Problemist on 1st January 1926, and was editor until May 1931. He was President of The British Chess Problem Society from September 1931 to 1943.

Apart from chess, Thomas Dawson, MSc, FRIC, FIRI was an international authority on rubber, and was responsible for the creation of the world-famous rubber library at Croydon, as well as its ‘Dawson’ system of rubber literature documentation. A Guide to Fairy Chess and The Problemist March 1952 detail the remarkable life-time accomplishments of TRD.”
From The Encyclopaedia of Chess (Batsford, 1977), Harry Golombek OBE, John Rice writes:
“British problemist, output over 6,000, 5,000+ being fairies . Dawson is remembered especially for his enormous contribution to fairy chess, of which he was the world’s leading exponent. Not only did he invent new pieces (e.g. Grasshopper, Nightrider) and new forms (e.g. Serieshelpmate), he also popularised fairy ideas with unparalleled enthusiasm through his writing and editing.
Books include Caissa’s Wild Roses (1935), Caissa’s Wild Roses in Clusters (1937), Ultimate Themes (1938), and Caissa’s Fairy Tales (1947); and in collaboration Retrograde Analysis (1915) and Asymmetry (1928).
Editor of The Problemist (1922-31), fairy secretary of Chess Amateur (1919-30, Fairy Chess Review (previously Problemist Fairy Supplement) (1930-51) and problem pages of the British Chess Magazine (1931-51). Of these, the Fairy Chess Review was probably his greatest achievement.
President of British Chess Problem Society 1931-43.”
When TRD stepped down as Endings editor of British Chess Magazine in December 1947 he wrote this:
“With this page I reluctantly terminate on health grounds some forty years of work in the Endings field, and my contributions to this corner of the “British Chess Magazine”. To the many readers of these pages, a Merry Christmas and steadily improving years.”
He handed over his column to Richard Guy.
From British Chess Magazine, Volume LXXI (71, 1951), Number 3 (March) pp. 78-80 we have notice of the retirement of TRD written by Brian Reilly:
WITH the retirement of Mr. T. R. Dawson a wonderful chapter in the history of the “B.C.M.” is brought to a close. It is a profound truism that in England the Chess Problem has never possessed such an assiduous and devoted servant and although Mr. Dawson had already attained greatness when he joined us, the story of the Past twenty years is one of unparalleled intensive activity in which the ontological essays on “Systematic Terminology” may be considered the crowning
achievement of a unique career.
His immense influence in the realm of Fairy Chess is well known; indeed, when the next instalment in the history
of the subject comes to be written it will be mainly that of our own Colossus with his countless converts finding, not dishonourable graves, but new and entrancing visions of beautiful things made possible through him. The onus probandi of his contribution to the orthodox problem, as treated in the “‘B.C.M.,” lies with posterity and in the minds of men unencumbered by prejudice and receptive to new and startling ideas.
In this Editorial we can only say, on behalf of our many readers,
“Thank you, T. R. D., for everything that you have done: for your devotion to your cause and your inspiration to your fellows. It has been a privilege to be associated with you and in the well-deserved years of retirement may your days and those of your loved ones, be long, fruitful, and full of the greatest happiness.”
In the nature of things we must go on and in bidding. a reluctant farewell to the magic name of T. R. D. we welcome to Problem World the young and and enthusiastic Mr. S. Sedgwick. His first article, dealing with the work of T. R. D., appears overleaf, and we commend it to all our readers.
Here is that editorial as it originally appeared:

Following that we have this appreciation from the incoming Problem Editor, Stanley Sedgwick of 337 Strone Road, Manor Park, London E12:
RETIREMENT OF MR. T. R. DAWSON
The news that Mr. Dawson, through reasons of health, has to relinquish these pages will be received with a deep and universal regret.
In the T. R. D. Diamond Jubilee booklet, 1949, the Editor was constrained to remark that so far as Fairy Chess Review was concerned there were no signs of Mr. Dawson retiring to that otium cum dignitate which was unquestionably his due; for the “B.C.M.” that prophecy is now unfortunately fulfilled. I might well have called this article “Twenty Glorious Years,” for in that time he has poured forth from these pages, in a never ending stream, the
treasures of a unique creative mind that makes the lot of any successor in unenviable one. As befits the occasion this issue is devoted to T. R. D. and I have to thank the many kind friends who at short notice have joined me in this tribute.
Thomas Rayner Dawson, M.Sc., F.I.C., F.I.R.I.. was born on November 29th, 1889, in Leeds, Yorkshire. He was a nephew of the late James Rayner, who edited these pages from 1889 until his death in 1898. A study of the “B.C.M.” for those years reveals a man whose love for the bizarre and unorthodox far outstrips any regard for the conventional. Bearing in mind Mr. Dawson’s subsequent pre-eminence in Fairy Chess it can be truly said that he was nurtured in the correct Puck-like atmosphere and to use his own words: “l cut my teeth on some of his old round-headed pawns!”
By the year 1900 he had already assimilated the rules of the game from a book of boy’s pastimes and evidenced an interest, in local newspaper columns, The Leeds Mercury Supplement and Yorkshire Weekly Post. His first problem – a direct mate in two – fell under the solvers’ scrutiny in 1907 and within a short period, which saw further orthodox work, he had soon acquired technique and absorbed current tenets, jargon, dogma, and dicta. – His attraction for the unorthodox was fostered primarily by his relationship to James Rayner, by the Christmas issues of the Leeds Mercury Supplement, and three works Tolosa y Carreras’ Traite Analytique, Alexandre’s Beautes, and Samuel Loyd in American Chess Nuts.
Through these agencies developed a love of Fairy Chess which was later to be the single and enduring passion of his life.
The year 1909 saw him in charge of the Endings Section of the Chess Amateur and later in the same magazine the famous Fairy Corner. In l915 at the invitation of Mr. Alain White he joined with W. Hundsdorfer in an epoch making pioneer work Retrograde Analysis, a strange and beautiful field in which he had proved himself peculiarly facile. In 1922 he founded and edited with conspicuous success The Problemist, the bi-monthly journal of the British Chess Problem Society.
This important work continued until 1931 when he relinquished the Editorship to Mr. C. S. Kipping and commenced the editing of an unknown and delicate newcomer, The Problemist Fairy Supplement. Although the Fairies had been claiming his attention more and more, Mr. Dawson discharged his position as the Society’s Editor with characteristic thoroughness, ever ready to support its tourneys with his own work and the pages of its journal with theoretical articles, demonstrating that his true passion had in no way impaired a marked ability for orthodox technique.
Nineteen-thirty-one, which saw the first small beginnings of The Problemist Fairy Supplement (later to be known as Fairy Chess Review), was to prove a milestone in the history of Fairy Chess. From its pages Fairy Chess as preached by T. R. D. went out to all lands, Penetrating every barrier, enrolling new adherents, and carried onwards and
upwards by the magnificent enthusiasm of his greatest disciple and guiding star.
His unique ability to interpret the infinite new forms of Fairy Chess, which a fertile imagination made readily available, had already gained renown and by this time his pre-eminence was firmly established, founded on problems and articles scattered in countless magazines and journals throughout the world. The message of his work and personality was, for many serious minds, too strong to be resisted, and in his devotion to Fairy Chess Mr. Dawson stands as the architect who laid the foundations for all the undreamt glories and beauties that are to come.
He joined the “8.C.M.” in 1930 and became the Problem Editor in 1931, upon the death of B. G. Laws; he was later made responsible for the well-known Endings feature. To these pages Mr. Dawson brought a rare literary ability and a scientific single-mindedness of purpose that for many years has made him unique in chess journalism.
In 1933, with an article on pawn switch modes, he lit a tiny flame that burned and has gone on burning, illuminating one of the most complete investigations into any problem theme. In this article, small but very significant in itself, is mirrored Mr. Dawson’s insistence upon the scientific and methodical approach to all problem work.
The same sincere belief that order and method are indispensable to any progress in the chess problem resulted fifteen years later in the historical essays on Systematic Terminology – one of the most remarkable contributions to pure thought on the problem domain yet conceived. The desire to bring order out of chaos has led him over the period of years to collect 100,000 Fairy Chess problems in a classified. system, a unique compilation with each individual member precisely assigned its place in the chess cosmos. His philosophy is, perhaps, best exemplified by his closing remarks to the Systematic Terminology essays, in which he states that with the assistance of orderly terminology “chess problem study is lifted far out of the morass of confusion of inspiration, into the freedom and dignity of an exact geometrical science.” It will not
have escaped attention that despite this uncompromising rejection of the artistic nature of the chess problem, Mr. Dawson’s best work, both orthodox and fairy, is the very embodiment of everything that good work should be. Pointed like an arrow,
complete and final as to the idea depicted, great regard paid to economy, the best attributes are ever present and there are many students of themes who have had occasion to profit from the clarity of his constructive powers.
The 1930’s saw great activity in the publication of the important Fairy Chess books, Caissa’s Wild Roses (1935), Caissa’s Wild Roses in Clusters (1937), and Ultimate Themes (1938). In each one a complex subject was treated in a thoroughly scientific manner. Broadly speaking these three works summarized Fairy Chess to date, demonstrating
its great achievements with crystal clarity. A close study of these books reveals the whole magnificent sweep of a unique intellect, at the same time showing how many of these achievements were really due to him. ln 1936 he gave to Fairy Chess lovers C. M. Fox, His Problems, a tribute to his great friend. His other literary works include the truly delightful Caissa’s Fairy Tales, which, with Sam Loyd and his Chess Problems shares the honour of being the only two problem books to be translated from the English language. Fata Morgana (1922), in conjunction with Dr. Birgfeld, W. Nanz,W. Massmann and W. Pauly, dealt with over 800 self mates and here Mr. Dawson’s Symbolic Notation was the binding thread in a masterly book. Asymmetry, with W. Pauly was published in 1928 and remains the classic exposition of afield to which he has devoted considerable attention.
In addition to his work for the “B.C.M.,” Mr. Dawson has at various times been responsible for the Problem Department of Eco degli Scacchi, The Half Hour, L’Alfiere di Re, the London Evening Standard, and the
Braille Chess Magazine, the last named an unremitting labour of love that continued for thirteen years. He also assisted in the inauguration of the annual British Chess Federation Award Pamphlets and edited them for three years. As a mark of great respect for his work he was elected President of the British Chess Problem Society in 1931 and remained constantly in that office until 1943.
A study of Mr. Dawson’s output is truly impressive and includes, inter alia, 5302 Fairies, 885 direct mates, 97 self mates and 138 endings, of which 110 Fairies have gained prizes with 89 Hon. Mentions and 75 commendations; in the other group 10 have been awarded prizes, with 47 Hon. Mentions and commendations. A composer’s contribution to any particular domain cannot and must not be judged by reference to tourney results alone, but in these achievements the First Prize Essay, L’Echiquier, 1928, and the treatise on Pawn Promotions, British Chess Federation, 1936, highlight a brilliant career.
Mr. Dawson has thus run the entire gamut and experience of composition ever revealing himself both in his work and writings as a seeker of essential truths and beauties, endowed with the ability to pass his discoveries on to others so that their wonders may be shared, enjoyed, and carried forward. He was kind enough to make a personal selection from his problems to round off this article and from these I have chosen six.
Many composers have expressed a desire to be associated with this small, but quite inadequate, tribute to his genius and many problems have been contributed for this purpose, some of which appear in this issue and others will follow. With each
and every one has come a warm personal message of esteem for our retiring Editor, coupled with the sincere hope that time and rest will repair the harm left by the past years of unremitting labour. That this event is not too long delayed is the fervent wish of us all.
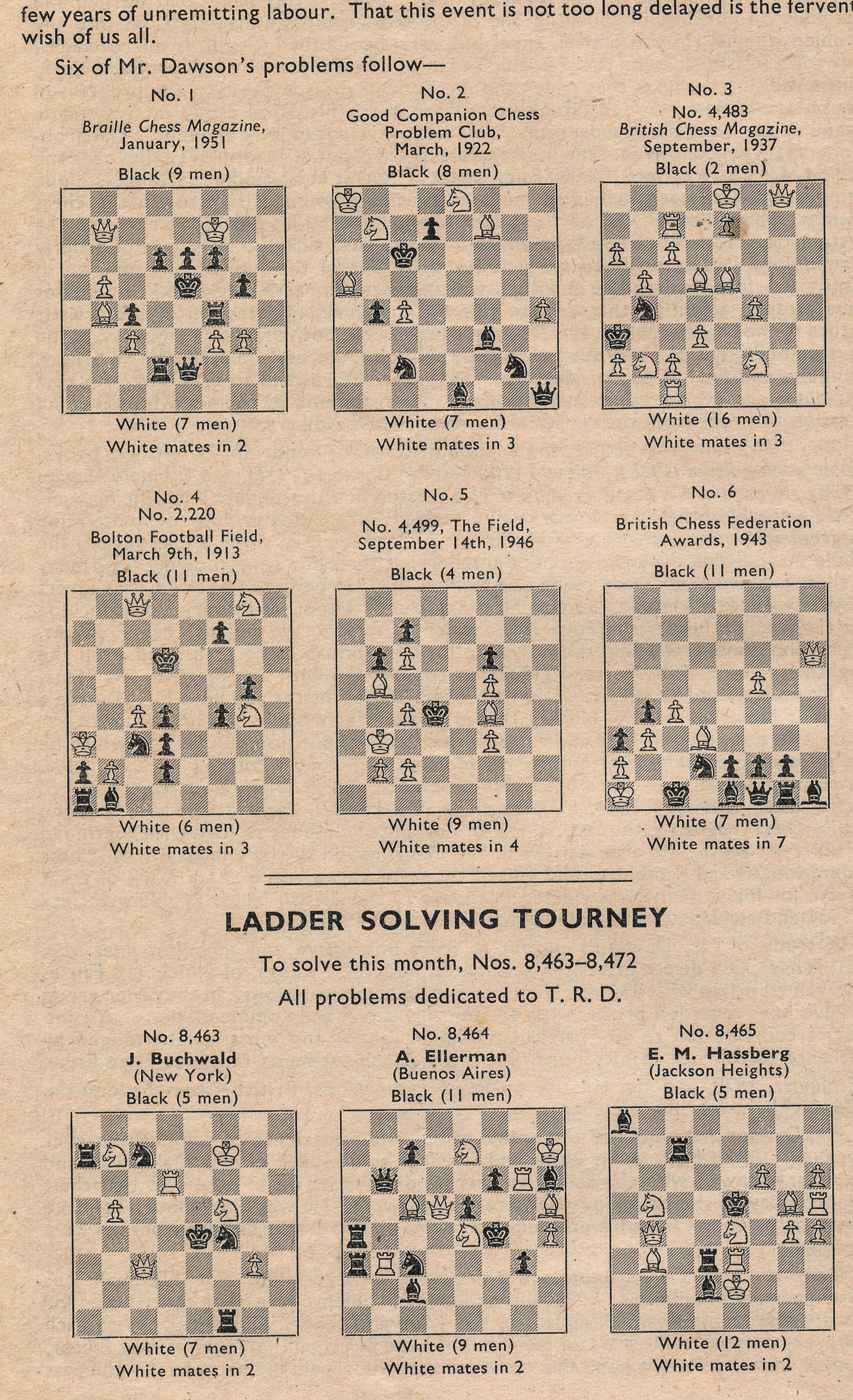
Six of Mr. Dawson’s problems follow –
No. 1
British Chess Magazine, January, 1951
White mates in 2
No. 2
Good Companion Chess Problem Club, March, 1922
White mates in 3
No. 3
British Chess Magazine, September, 1937
White mates in 3
No. 4
Bolton Football Field, March 9th, 1913
White mates in 3
No. 5
The Field, September 14th, 1946
White mates in 4
No. 6
British Chess Federation Awards, 1943
White mates in 7
and here follows the original article:


Unfortunately TRD was to pass away not much more than a year after the retirement notice and in British Chess Magazine, Volume LXXII (72, 1952), Number 4 (April) pp. 107 – 108 we have this obituary also from Stanley Sedgwick :


The same obituary contains the following appreciation by Gerald Abrahams :

According to Edward Winter in Chess Explorations (Cadogan Chess, 1996) page 106, Chess Note 457, :
“George Jellis suspects that a chess man has been named after a street:
Just south of St. Paul’s Cathedral in London is a private gated road called Nightrider Street which, I believe belongs to the Post Office and presumably derives its name from the night mail coaches of earlier days. It is only a short walk from the St. Bride’s Institute, where the British Chess Problem Society has held its meetings since its foundation in 1918. Among the founder members was TR Dawson, who published his first Nightrider problem in 1925.

From Wikipedia :
“Thomas Rayner Dawson (28 November 1889 – 16 December 1951) was an English chess problemist and is acknowledged as “the father of Fairy Chess”.[1] He invented many fairy pieces and new conditions. He introduced the popular fairy pieces grasshopper, nightrider, and many other fairy chess ideas.
Dawson published his first problem, a two-mover, in 1907. His chess problem compositions include 5,320 fairies, 885 directmates, 97 selfmates, and 138 endings. 120 of his problems have been awarded prizes and 211 honourably mentioned or otherwise commended. He cooperated in chess composition with Charles Masson Fox.
Dawson was founder-editor (1922–1931) of The Problemist, the journal of the British Chess Problem Society. He subsequently produced The Fairy Chess Review (1930–1951), which began as The Problemist Fairy Chess Supplement. At the same time he edited the problem pages of The British Chess Magazine (1931–1951).
Publications
Caissa’s Playthings a series of articles in Cheltenham Examiner (1913)
Retrograde Analysis, with Wolfgang Hundsdorfer (1915)
Fata Morgana, with Birgfeld, Nanz, Massmann, Pauly (1922)
Asymmetry, with W. Pauly (1928)
Seventy Five Retros (1928)
Caissa’s Wild Roses (1935)
C. M. Fox, His Problems (1936)
Caissa’s Wild Roses in Clusters (1937)
Ultimate Themes (1938)
Caissa’s Fairy Tales (1947)
The last five titles were collected as Five Classics of Fairy Chess, Dover Publications (1973), ISBN 978-0-486-22910-2.”
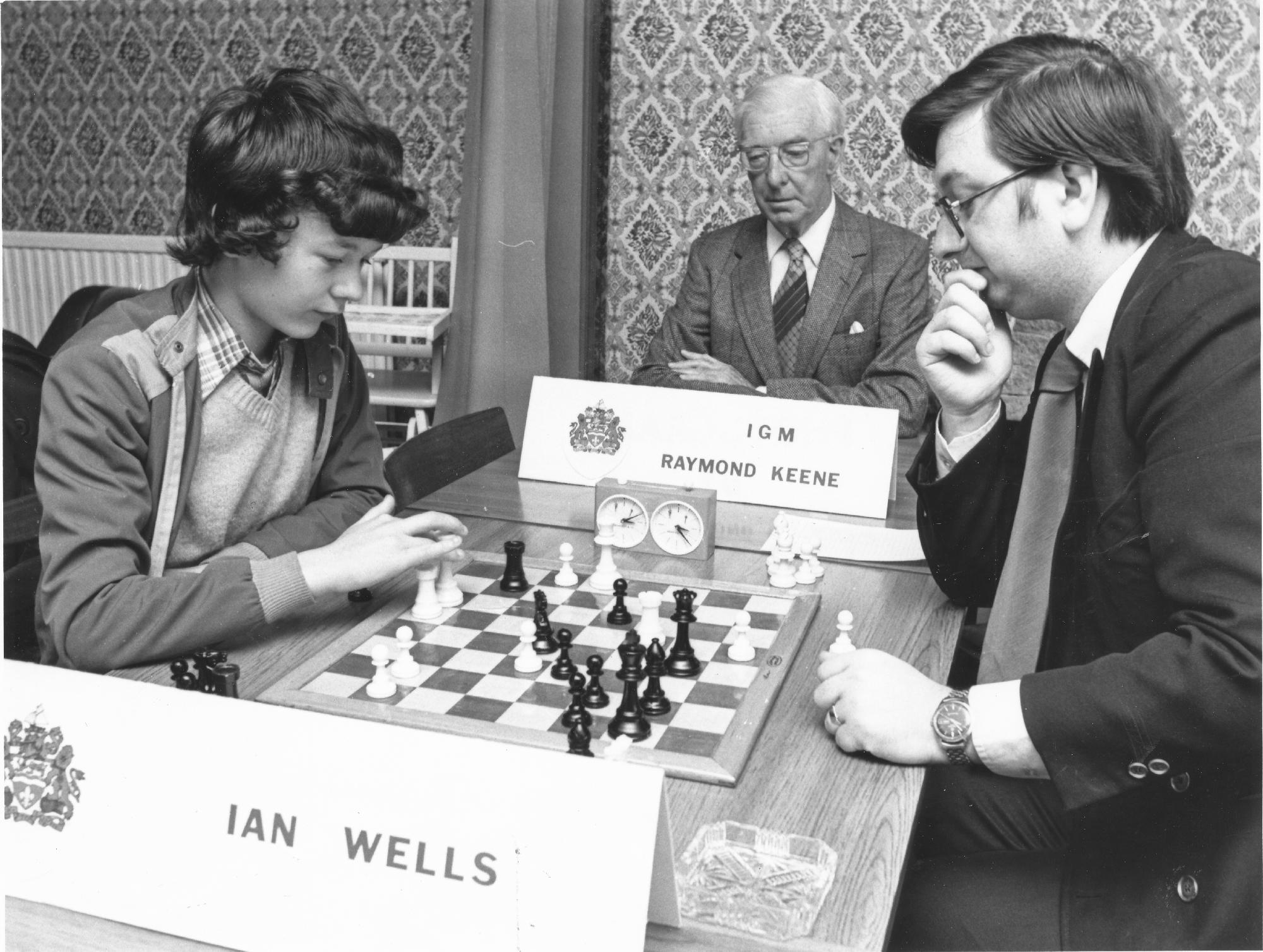
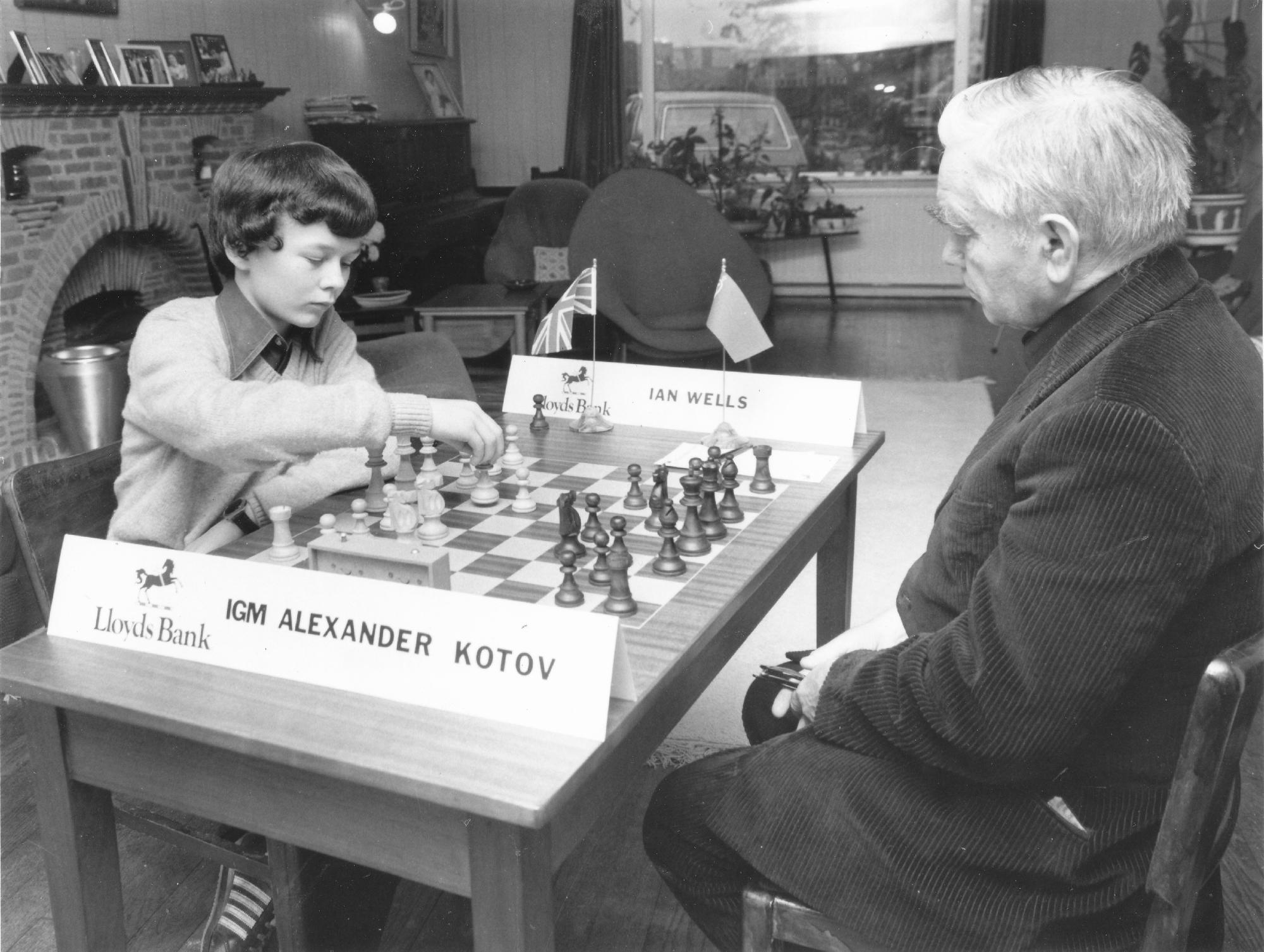
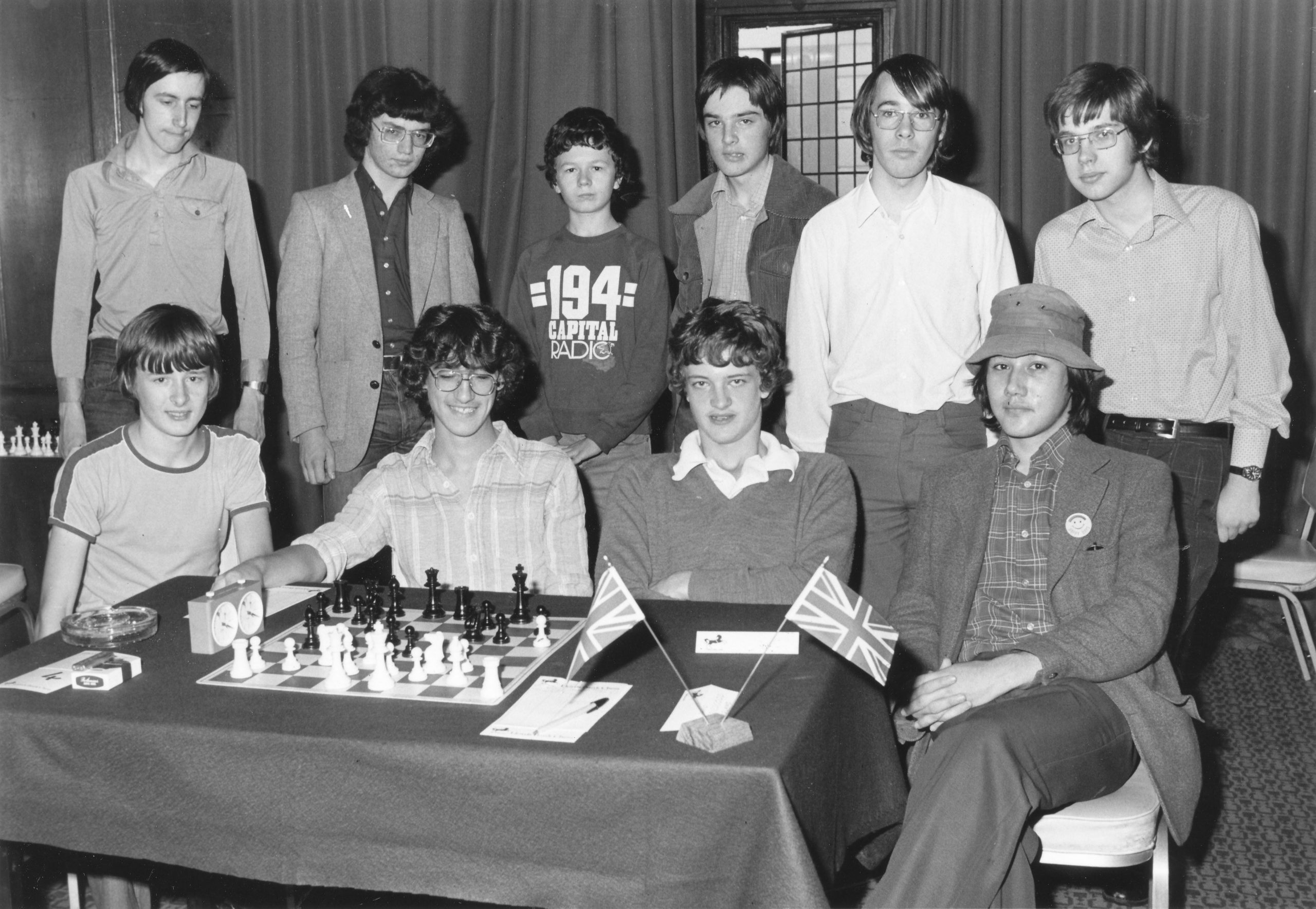
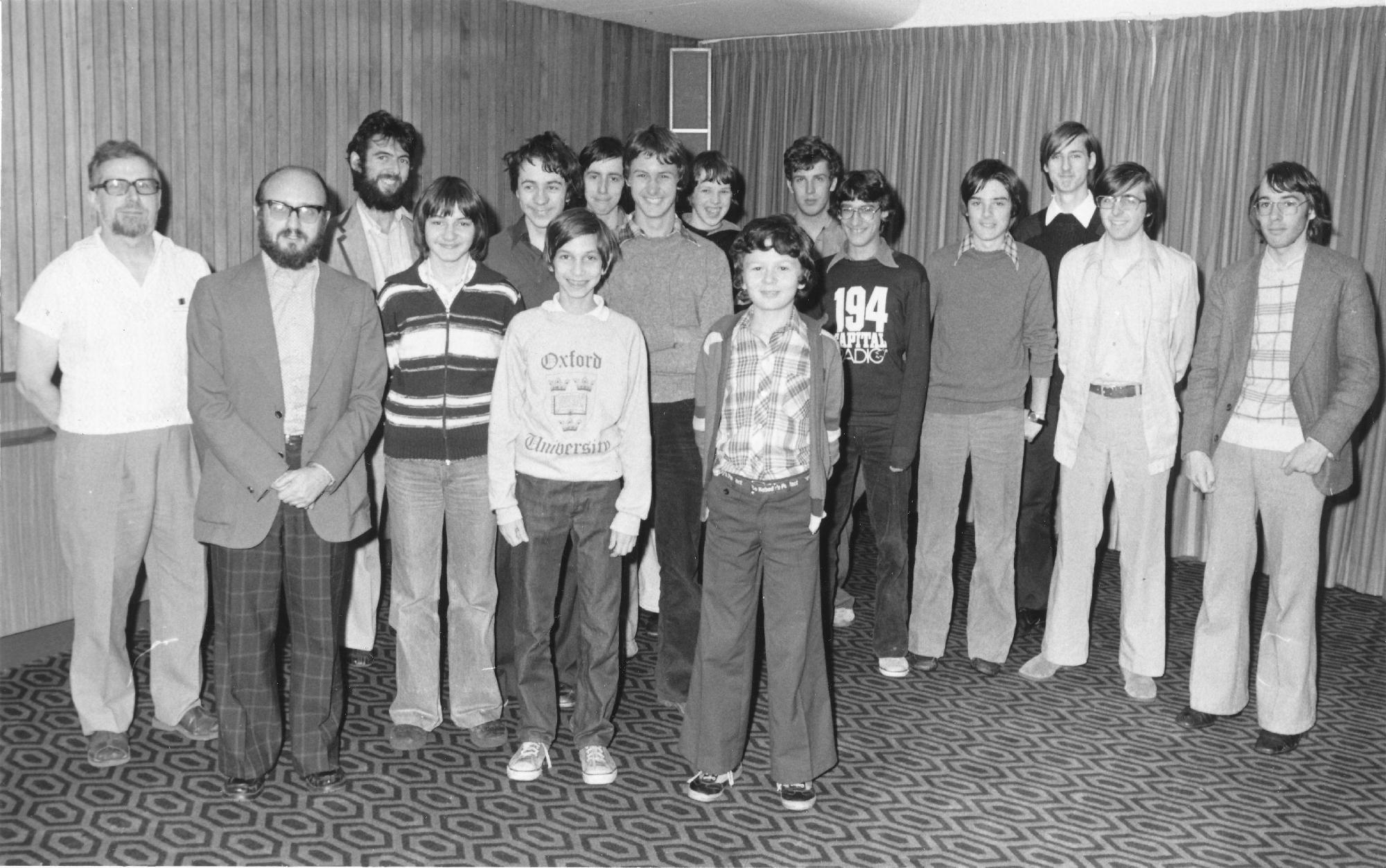
We remember Ian Duncan Wells who very sadly passed away on this day (January 25th) in 1982 aged seventeen years.
From Chessgames.com :
Ian Duncan Wells was born in Scarborough, England. He was awarded the FM title in 1982. At the Islington Open in December 1981 he finished 1st= with John Nunn and Tony Miles. Following a 5th= placing in the Golden Pawn of Brazil Junior tournament held in Rio de Janeiro he and other players went swimming outside their hotel. He got into difficulties and although he was brought ashore by lifesavers he died after six days in a coma.
Here is an excellent article from chess.com written by Neil Blackburn.




We remember FM Peter Clarke who passed away on Thursday, December 11th, 2014 whilst living at Chapel House, Bude, Cornwall, EX23 9SQ
Peter Hugh Clarke was born on Saturday, March 18th 1933 in West Ham, London. His mother’s maiden name was Ekblom.
From The Modest Master of Morwenstow by James Pratt (sadly, as yet, unpublished) :
“Peter Hugh Clarke was born in London on 18th March, 1933. At the age of eight or nine he taught himself the game from ‘The Book of Knowledge’ and played friendly games with his cousin, who was about a year older. Peter’s father supported his game for many years. PHC was a student at St. Bonaventures School and London University. World War II, and its even longer aftermath, robbed him of a number of playing opportunities. It is surprising that he had no childhood heroes, although later the play of Botvinnik, Keres and Smyslov impressed him.”
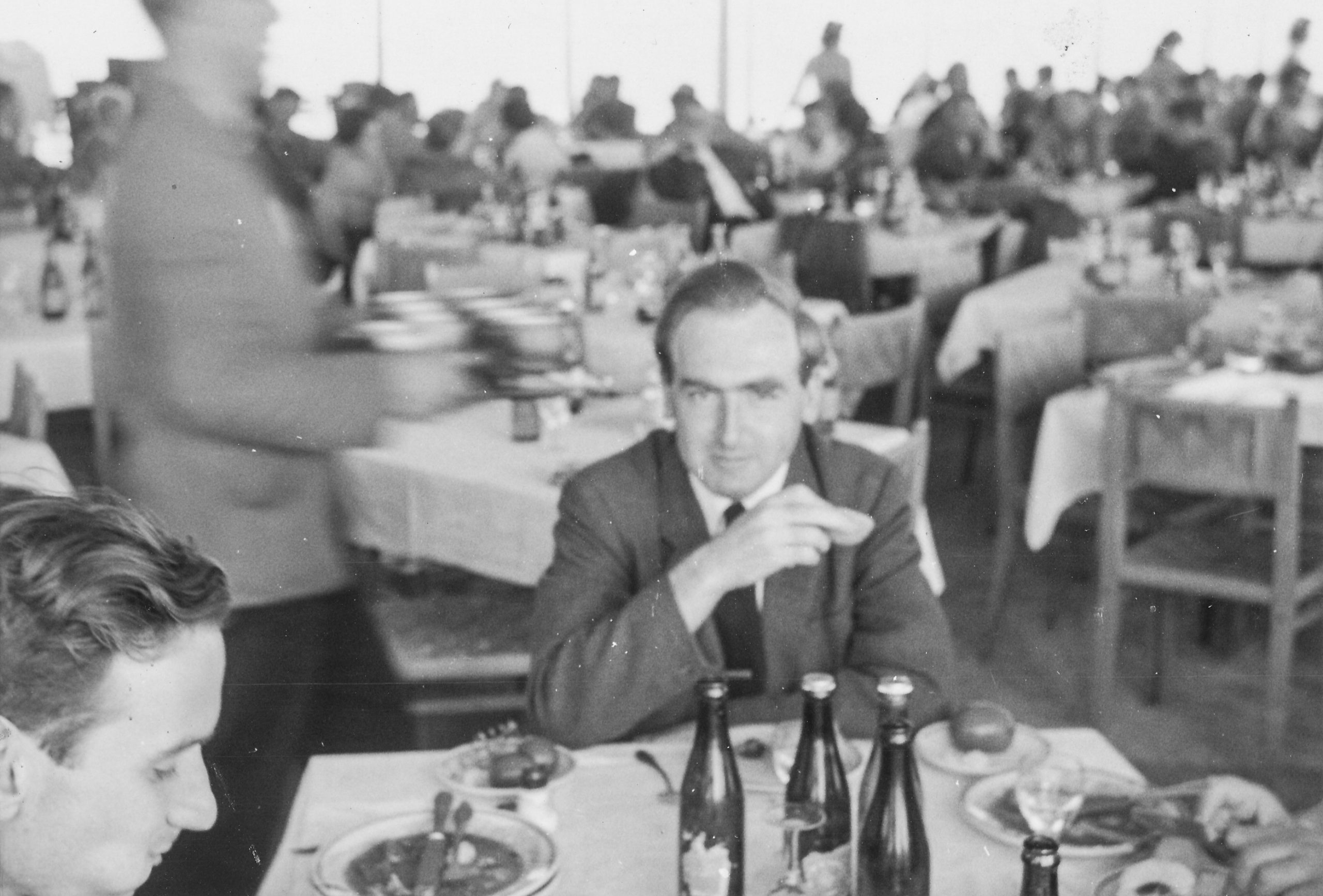
From British Chess (Pergamon, 1983) written by George Botterill :
Chess correspondent of The Sunday Times, Clarke played for England in the Olympiads of 1954, 56, 58, 60, 62, 66 and 68. He has never won the British Championship but has come 2nd on 5 occasions.
A fine writer. His best books are Mikhail Tal’s Best Games of Chess

and Petrosian’s Best Games of Chess 1946-1963 both published by Bell.

The most remarkable thing about Clarke’s chess career was they way in which he became transformed, in about 1968-9, into the most drawish of players. In British tournaments he has become notorious for correct but dull solidity.”
Peter was Southern Counties (SCCU) Champion for the 1945-55 season.
Peter was England’s third Correspondence Grandmaster (CGM) in 1980 after Keith Richardson and Adrian Hollis.

From BCM / ECF :
“FIDE and British Master P.H. Clarke will be best remembered as biographer to Tal and to Petrosyan, but he was so much more. The young Clarke played for Ilford CC in the London League and for Essex at county level. Doing national service he was to learn the Russian that was to so shape his writings.
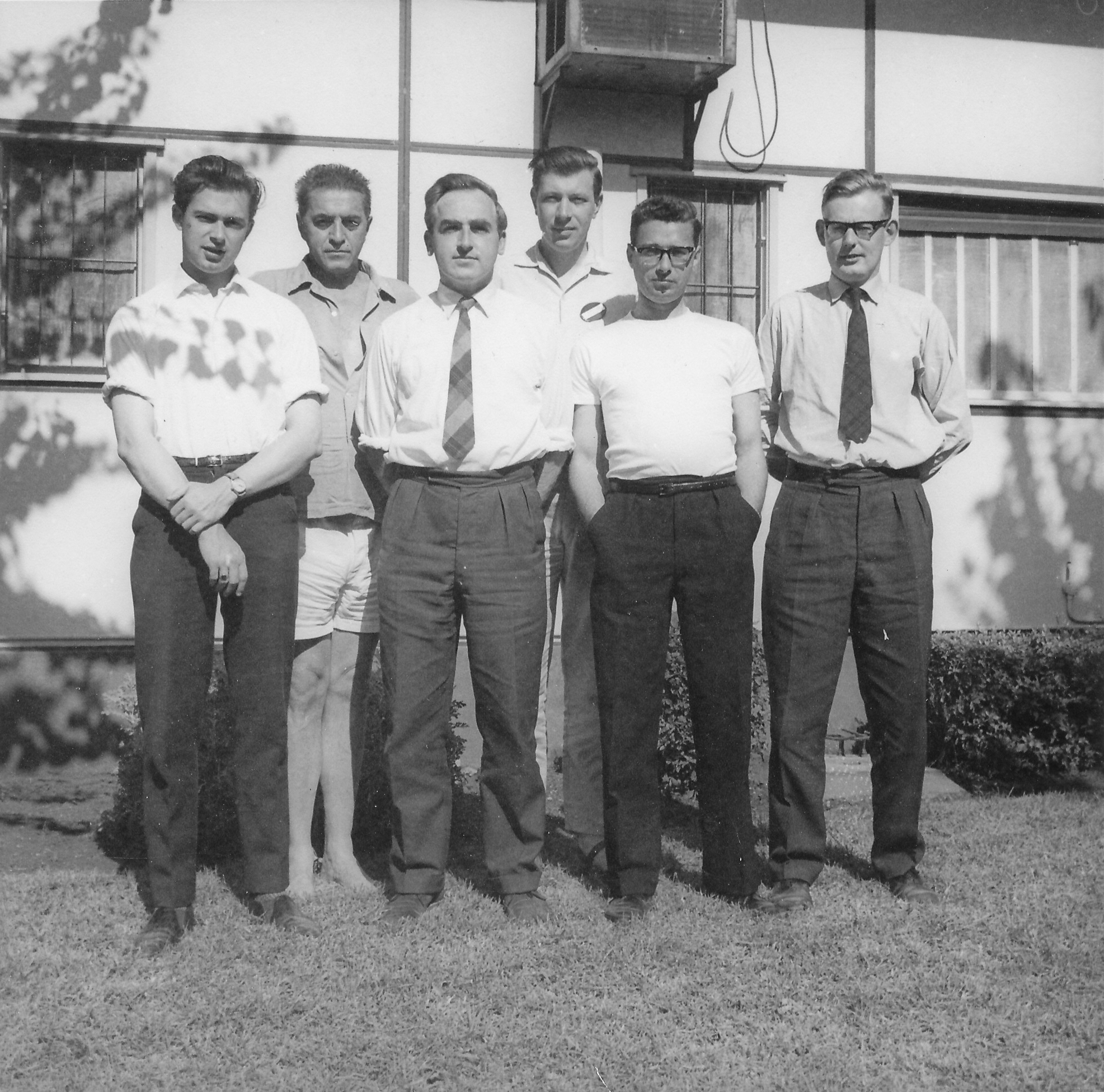

For a brief period in the late 1950s, and early sixties, he was the number two player in England, ahead of the vastly more experienced Alexander and Golombek. He played, of course, below Jonathan Penrose, a partnership that bore fruit when preparing openings; latterly they both became Correspondence Grandmasters.”
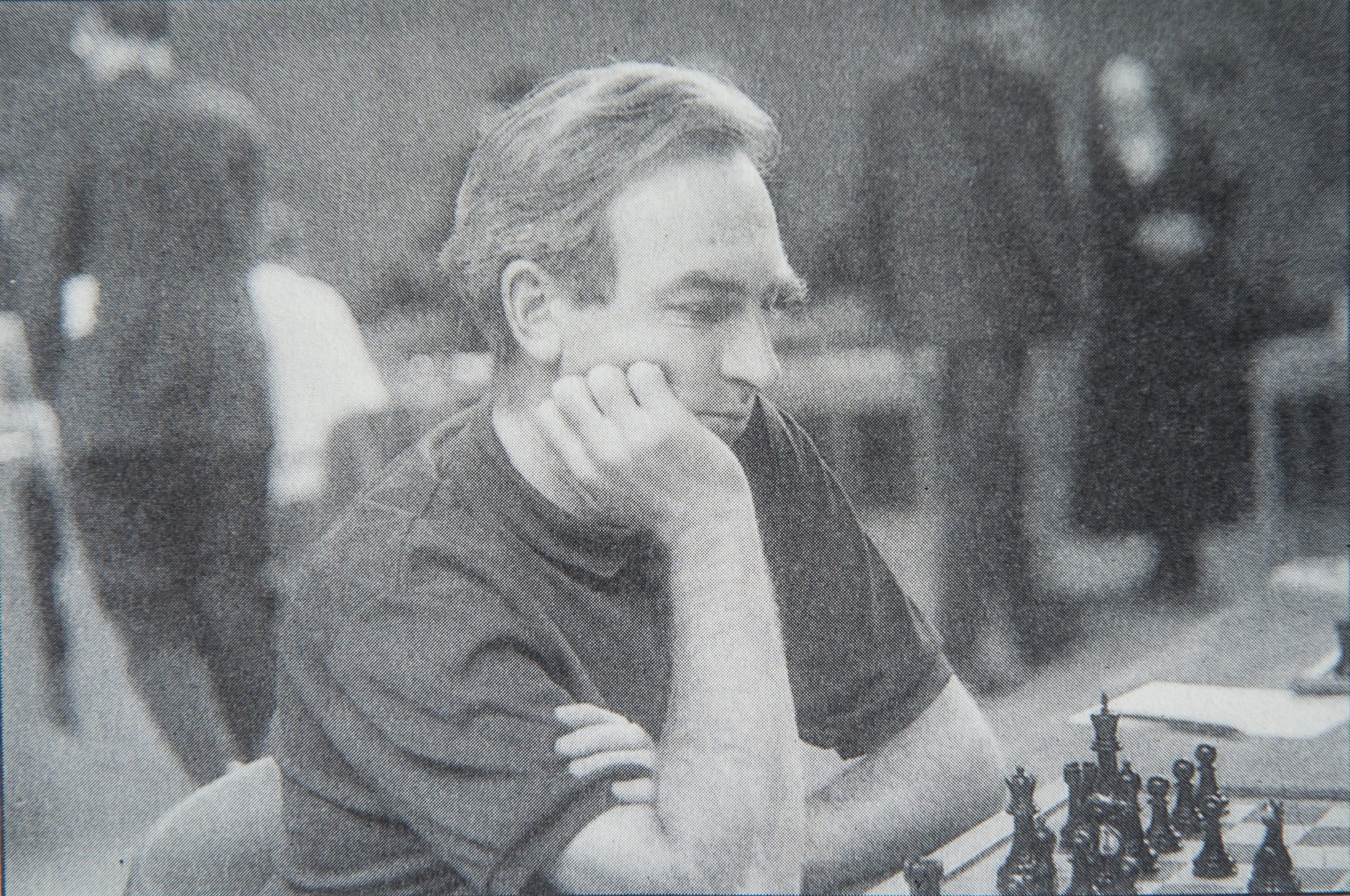

“At the British Championships itself he finished second on his first appearance; he was to tie for silver medal on no less than five occasions, appearing, almost without a break for thirty years, a run that ended in 1982. He represented the BCF – as it then was – in eight Olympiads, playing on top board in 1966.

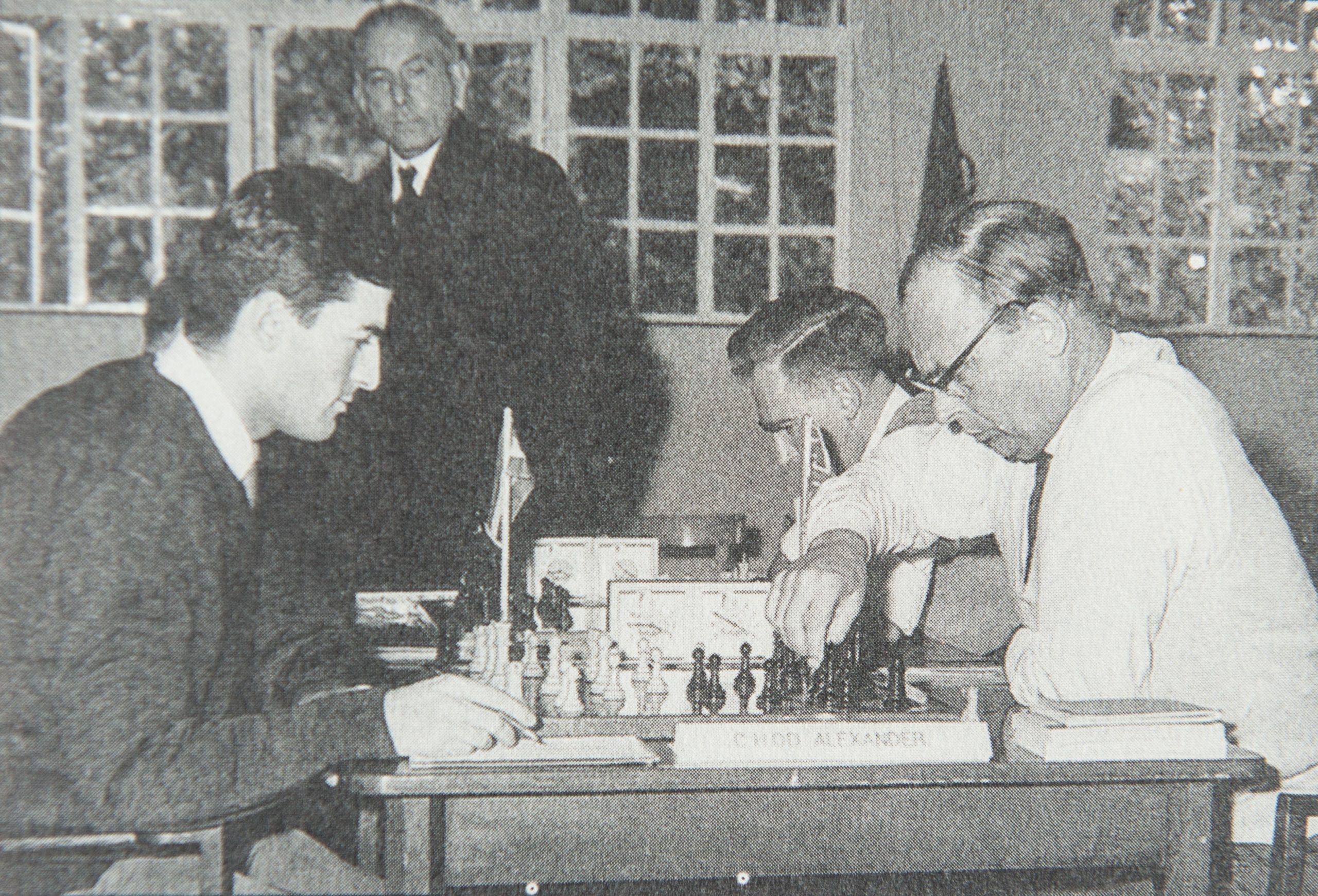
The Clarke family moved to the West of England in the late Sixties. PHC played in thirteen WECU Championships, and lost only twice. As a player he could be cautious, agreeing too readily to draws. Accuracy and respect meant more to him than ambition. The biographer became a journalist as illness cut short his playing career. In his time he beat Larsen, Penrose and Szabo.

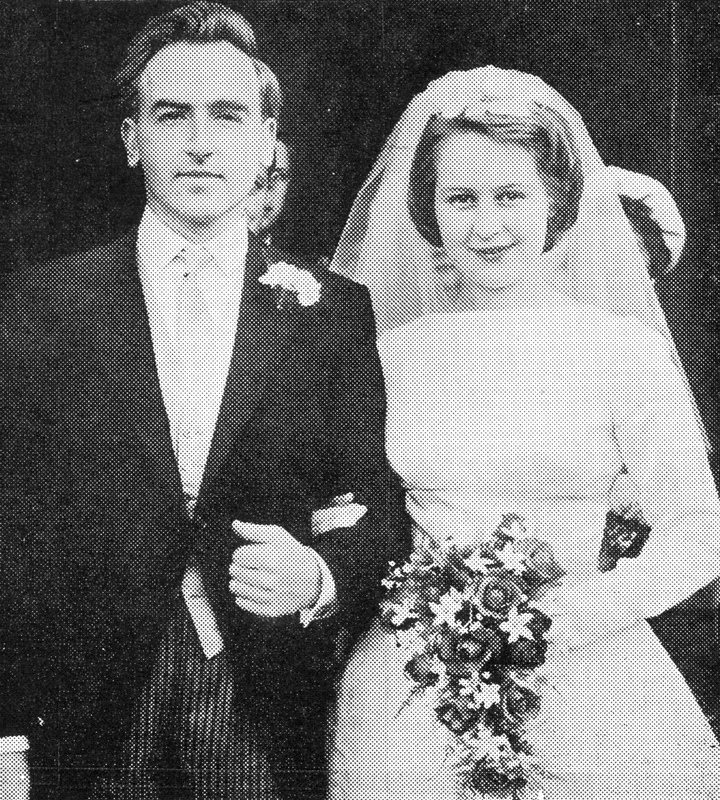
In 1962 he married BH Wood’s daughter, Peggy. They had three daughters. In 1975 my mother happened across Peter and Peggy on Morecambe prom. ‘Never’ she was later to tell me, ‘have I seen a couple more in love.'”

We are grateful to James Pratt to allow us to quote from the the sadly unpublished “Modest Master from Morwenstow” as follows :
PHC by John Littlewood :
“Peter had a relatively short career at the top and it is interesting to comment on his style. In essence, his great strength lay in positional understanding which backed-up his defensive skills rather than helped his ability to create wins; in other words, he won games in which his opponents over-pressed or opted for dubious positional moves.
After doing well in English chess, he was perhaps pushed into international chess too early for him to develop his own personal creative style. Playing for England and meeting strong players, he tended towards a rather negative approach that may have been necessary for the team but was not good for his own personal progress, as shown when he later met English opponents who outstripped him in their positive will-to-win. His friendship with Penrose (a far stronger player) led to far too many draws which did neither of them any good.

To be fair, Peter was not an easy player to beat but, on the other hand, he was not too hard to draw against if you felt so inclined. His forte lay in his knowledge of the game and his excellent writing skills, where he was at his happiest; there is hardly a book of his that I haven’t enjoyed.”

Writing in BCM 04/64, John Littlewood called PHC a self-style non-tactician and disagreed with Clarke’s belief in the inner logic (‘I have made no mistakes and therefore my position is OK.’) of positions where tactics are to the fore.
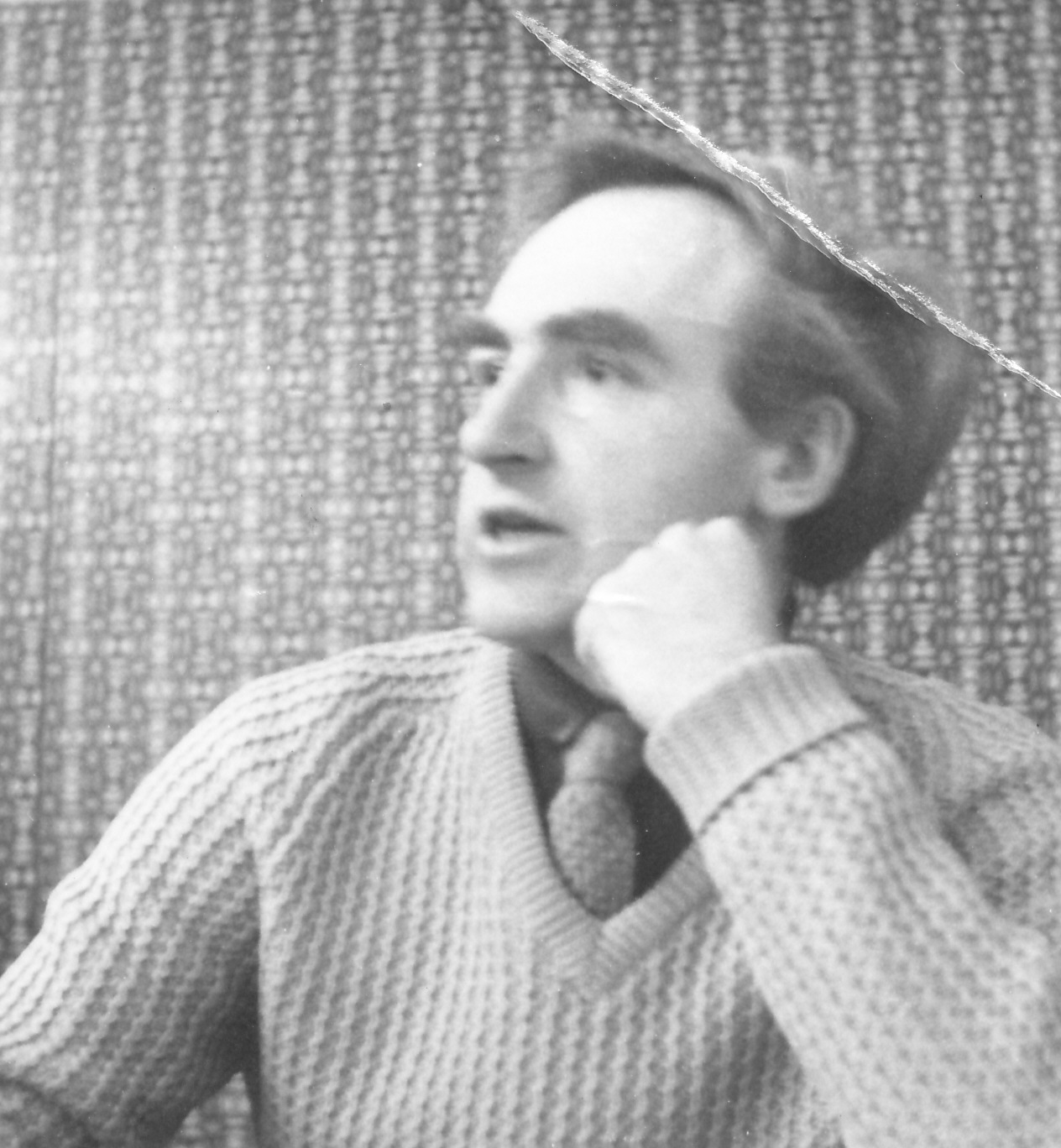

PHC by Leonard Barden :
“Peter’s contribution to British Chess was important as a player and even more so as a writer. His best period was 1956-61. He, Penrose and myself used to stay in the same hotel during the British Championships and prepare and analyse together, although we played hard when actually paired. Peter was the solid man in the English team, gradually taking over the role of Golombek. It was important that we did reasonably well in this period which provided a bridge between the Alexander/Golombek era and the rise of Keene/Hartston.
Peter was always a good friend to me and his family gave me hospitality each year during the Ilford Congress. Peter’s books, especially the one about Tal, were real works of scholarship in an era where there were no computers to facilitate the job. He could have achieved more as a player if he had been able to concentrate fully on that, but the economic climate then was poor for professionals.”
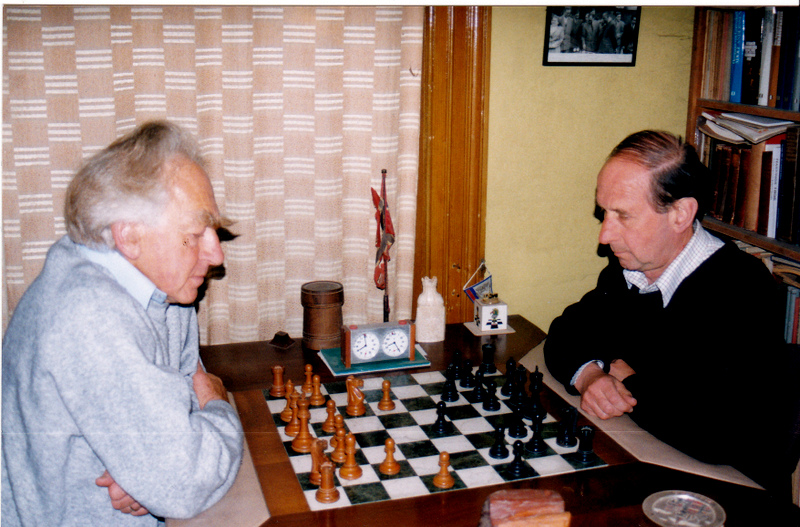

PHC by Bernard Cafferty :
“Right up to that point of his illness in the 1980’s he had worthily defended the reputation of the older generation in the British Championship, as the last survivor, still active at that level, from the Penrose era. I first saw Peter at the 1951 British Championship at Chester and first played him at the 1952 Bristol Universities individual contest.

He left the University of London before taking his degree (study of chess rather taking over his life), but then had the good fortune to go on to study Russian while doing his National Service, around 1954-55. Or was he still in the Army when the Moscow 1956 Olympiad took place? He certainly did well there, perhaps less affected than other Westerners by the strangeness of the place that was just recovering slightly from the depths of Stalin’s baleful influence.

I do recall that for a couple of years Peter changed his cautious style. This was around 1957-58 when he scored one of his two wins against Penrose. Was it at Ilford? I remember that the game appeared with notes by B.H. Wood in ‘The Illustrated London News’ column.

I used to see Peter regularly at the Paignton and Hastings Congresses in the 1990’s but not in the last couple of years. His health seems restored.”
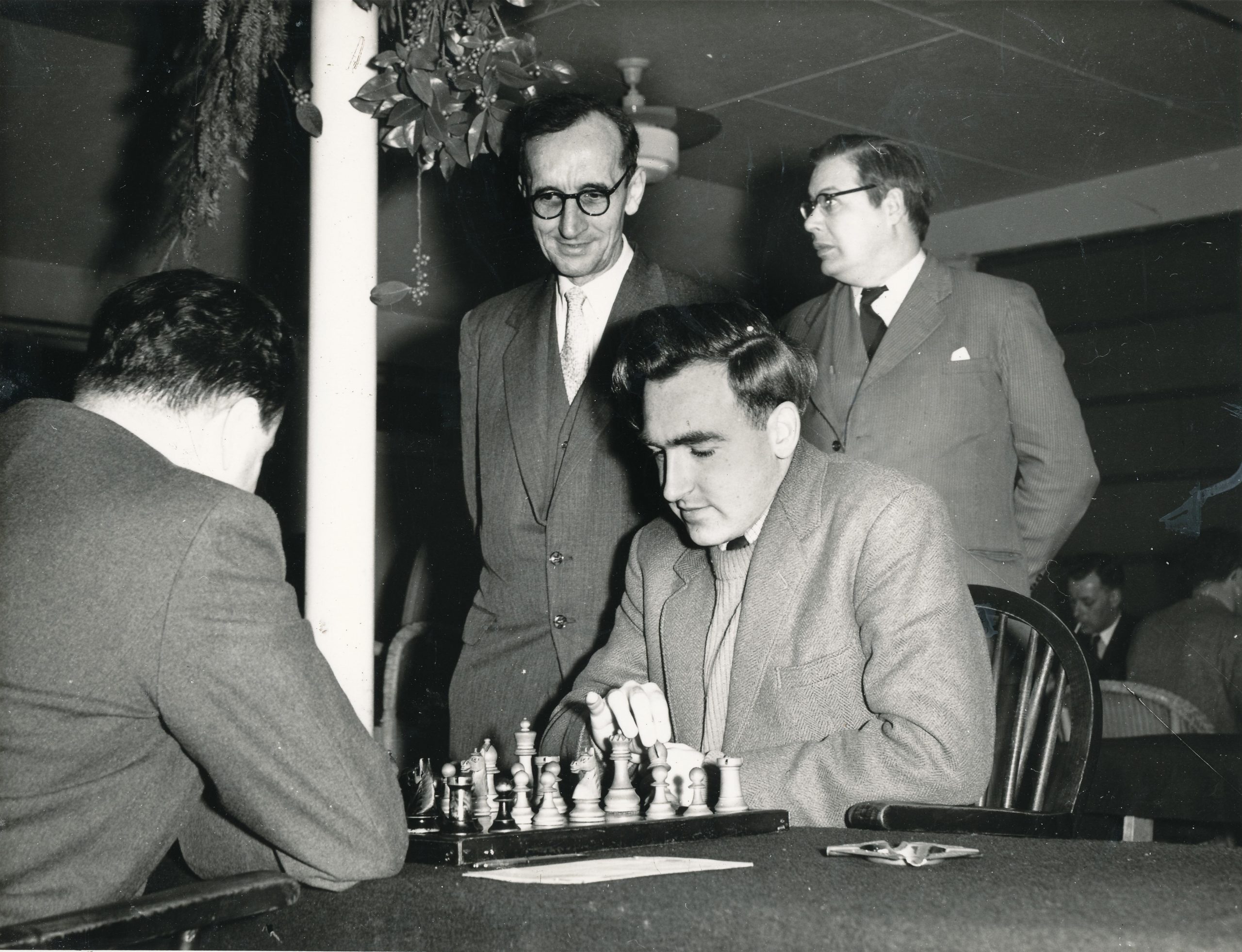

PHC by Ken Harman :
“I am very pleased to hear about your book about Peter Clarke; not sure I can contribute much as I wasn’t a friend of his so only knew him through seeing him and Margaret at chess tournaments. He was a quiet spoken gentleman who played such quiet positional chess that I would call it ‘monastic chess’. I think Clarke thought chess a search for spiritual truth, only to be found in the cloisters of spiritual truth, only to be found in the cloisters of contemplative life – ‘The Thomas Merton of Chess’, if you like. Of course, I have no idea if he was a spiritual man in real life but his chess always struck me as if he was reaching for heaven and found hell in a doubled pawn. He seemed like a nice man and I suspect his wife Margaret was the dominant one. I have his book on Mikhail Tal’s Best Games of Chess (Bell 1961) which is signed by him and may well have been his copy, because as you open the book – there is a small newspaper clipping and a photo of Clarke sellotaped which is rather unusual being that the book is about Tal, and not him. ”
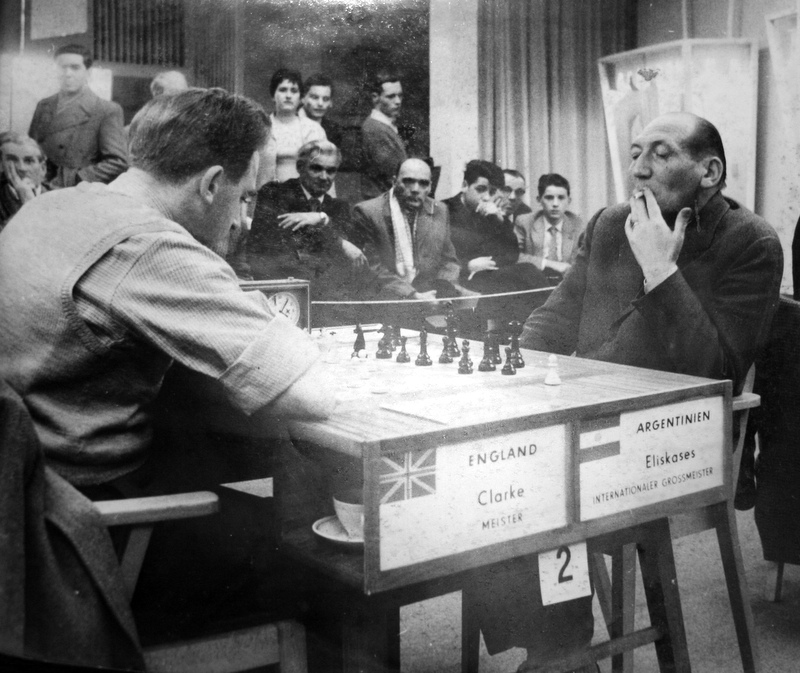

PHC by Alan P. Borwell (ICCF Honorary President) :
“I first met Peter at the 1959 BCF Congress in York when I was a member of local organising committee and then at Paignton and when York played & won the National Club Championship in 1964/5.
In 1966 I played Peter in the British Chess Championship in last round in Sunderland.”
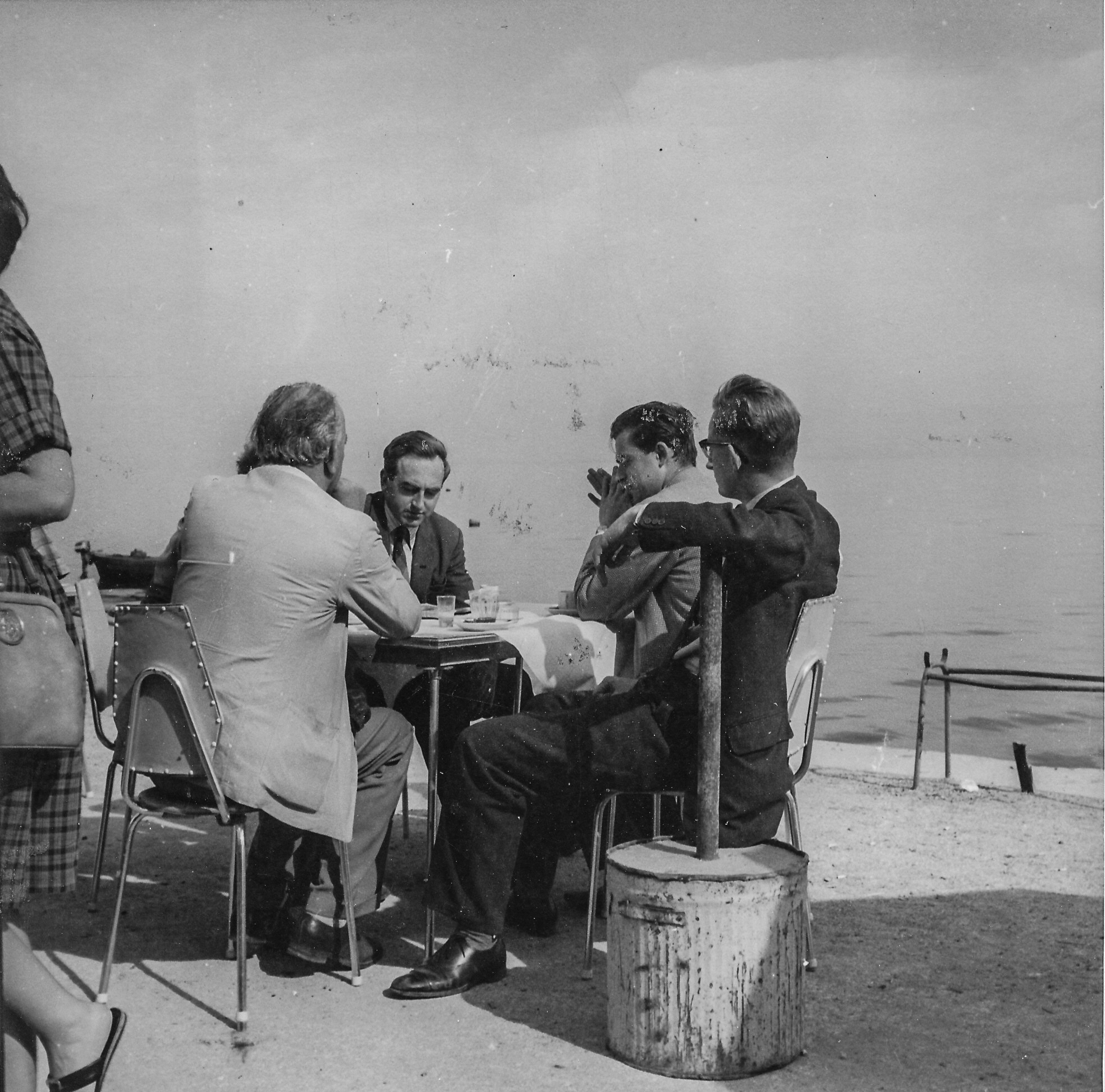

and from Wikipedia :
Peter Hugh Clarke (18 March 1933 – 11 December 2014) was an English chess player, who hold titles FIDE master (FM) and International Correspondence Chess Grandmaster (1980), FIDE International arbiter (1976), Chess Olympiad individual silver medal winner (1956).
Peter Clarke started playing chess at the age of six. He twice won the London Boys’ Chess Championship (1950, 1951). He was British Chess Championship multiplier participant where five times won silver medal.
Since 1959, Peter Hugh Clarke has been working as a chess journalist in the newspaper Sunday Times and magazine British Chess Magazine. He known as the biographical book’s author of Mikhail Tal (1961) and Tigran Petrosian (1964). Thanks to his good knowledge of Russian language, he translated the book about Vasily Smyslov in 1958. In 1963 he wrote a book 100 Soviet Chess Miniatures.
Peter Clarke played for England in the Chess Olympiads :
In 1954, at second reserve board in the 11th Chess Olympiad in Amsterdam (+2, =2, -3),
In 1956, at reserve board in the 12th Chess Olympiad in Moscow (+7, =5, -0) and won individual silver medal,
In 1958, at fourth board in the 13th Chess Olympiad in Munich (+2, =10, -3),
In 1960, at third board in the 14th Chess Olympiad in Leipzig (+4, =7, -3),
In 1962, at second board in the 15th Chess Olympiad in Varna (+3, =10, -2),
In 1964, at second board in the 16th Chess Olympiad in Tel Aviv (+2, =8, -2),
In 1966, at first board in the 17th Chess Olympiad in Havana (+2, =10, -1),
In 1968, at third board in the 18th Chess Olympiad in Lugano (+0, =7, -1).
Also he played for England in the World Student Team Chess Championship (1954, 1959)and in the Clare Benedict Chess Cup (1960-1961, 1963, 1965, 1967-1968) where won team silver medal (1960) and 4 bronze medals (1961, 1963, 1967, 1968).
In later years, Peter Clarke active participated in correspondence chess tournaments. In 1977, he won British Correspondence Chess Championship. In 1976, Peter Clarke was awarded the International Correspondence Chess Master (IMC) title and received the International Correspondence Chess Grandmaster (GMC) title four years later.
We remember FM Peter Clarke who passed away on Thursday, December 11th, 2014 whilst living at Chapel House, Bude, Cornwall, EX23 9SQ
Peter Hugh Clarke was born on Saturday, March 18th 1933 in West Ham, London. His mother’s maiden name was Ekblom.
From The Modest Master of Morwenstow by James Pratt (sadly, as yet, unpublished) :
“Peter Hugh Clarke was born in London on 18th March, 1933. At the age of eight or nine he taught himself the game from ‘The Book of Knowledge’ and played friendly games with his cousin, who was about a year older. Peter’s father supported his game for many years. PHC was a student at St. Bonaventures School and London University. World War II, and its even longer aftermath, robbed him of a number of playing opportunities. It is surprising that he had no childhood heroes, although later the play of Botvinnik, Keres and Smyslov impressed him.”
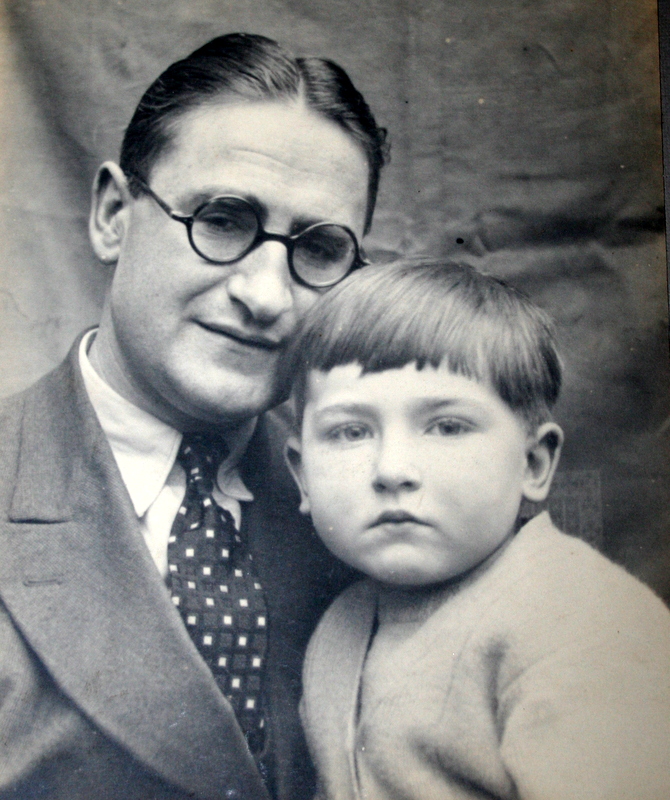
From British Chess (Pergamon, 1983) written by George Botterill :
Chess correspondent of The Sunday Times, Clarke played for England in the Olympiads of 1954, 56, 58, 60, 62, 66 and 68. He has never won the British Championship but has come 2nd on 5 occasions.
A fine writer. His best books are Mikhail Tal’s Best Games of Chess

and Petrosian’s Best Games of Chess 1946-1963 both published by Bell.

The most remarkable thing about Clarke’s chess career was they way in which he became transformed, in about 1968-9, into the most drawish of players. In British tournaments he has become notorious for correct but dull solidity.”
Peter was Southern Counties (SCCU) Champion for the 1945-55 season.
Peter was England’s third Correspondence Grandmaster (CGM) in 1980 after Keith Richardson and Adrian Hollis.

From BCM / ECF :
“FIDE and British Master P.H. Clarke will be best remembered as biographer to Tal and to Petrosyan, but he was so much more. The young Clarke played for Ilford CC in the London League and for Essex at county level. Doing national service he was to learn the Russian that was to so shape his writings.

For a brief period in the late 1950s, and early sixties, he was the number two player in England, ahead of the vastly more experienced Alexander and Golombek. He played, of course, below Jonathan Penrose, a partnership that bore fruit when preparing openings; latterly they both became Correspondence Grandmasters.”


“At the British Championships itself he finished second on his first appearance; he was to tie for silver medal on no less than five occasions, appearing, almost without a break for thirty years, a run that ended in 1982. He represented the BCF – as it then was – in eight Olympiads, playing on top board in 1966.

The Clarke family moved to the West of England in the late Sixties. PHC played in thirteen WECU Championships, and lost only twice. As a player he could be cautious, agreeing too readily to draws. Accuracy and respect meant more to him than ambition. The biographer became a journalist as illness cut short his playing career. In his time he beat Larsen, Penrose and Szabo.

In 1962 he married BH Wood’s daughter, Peggy. They had three daughters. In 1975 my mother happened across Peter and Peggy on Morecambe prom. ‘Never’ she was later to tell me, ‘have I seen a couple more in love.'”

We are grateful to James Pratt to allow us to quote from the the sadly unpublished “Modest Master from Morwenstow” as follows :
PHC by John Littlewood :
“Peter had a relatively short career at the top and it is interesting to comment on his style. In essence, his great strength lay in positional understanding which backed-up his defensive skills rather than helped his ability to create wins; in other words, he won games in which his opponents over-pressed or opted for dubious positional moves.
After doing well in English chess, he was perhaps pushed into international chess too early for him to develop his own personal creative style. Playing for England and meeting strong players, he tended towards a rather negative approach that may have been necessary for the team but was not good for his own personal progress, as shown when he later met English opponents who outstripped him in their positive will-to-win. His friendship with Penrose (a far stronger player) led to far too many draws which did neither of them any good.

To be fair, Peter was not an easy player to beat but, on the other hand, he was not too hard to draw against if you felt so inclined. His forte lay in his knowledge of the game and his excellent writing skills, where he was at his happiest; there is hardly a book of his that I haven’t enjoyed.”

Writing in BCM 04/64, John Littlewood called PHC a self-style non-tactician and disagreed with Clarke’s belief in the inner logic (‘I have made no mistakes and therefore my position is OK.’) of positions where tactics are to the fore.

PHC by Leonard Barden :
“Peter’s contribution to British Chess was important as a player and even more so as a writer. His best period was 1956-61. He, Penrose and myself used to stay in the same hotel during the British Championships and prepare and analyse together, although we played hard when actually paired. Peter was the solid man in the English team, gradually taking over the role of Golombek. It was important that we did reasonably well in this period which provided a bridge between the Alexander/Golombek era and the rise of Keene/Hartston.
Peter was always a good friend to me and his family gave me hospitality each year during the Ilford Congress. Peter’s books, especially the one about Tal, were real works of scholarship in an era where there were no computers to facilitate the job. He could have achieved more as a player if he had been able to concentrate fully on that, but the economic climate then was poor for professionals.”

PHC by Bernard Cafferty :
“Right up to that point of his illness in the 1980’s he had worthily defended the reputation of the older generation in the British Championship, as the last survivor, still active at that level, from the Penrose era. I first saw Peter at the 1951 British Championship at Chester and first played him at the 1952 Bristol Universities individual contest.

He left the University of London before taking his degree (study of chess rather taking over his life), but then had the good fortune to go on to study Russian while doing his National Service, around 1954-55. Or was he still in the Army when the Moscow 1956 Olympiad took place? He certainly did well there, perhaps less affected than other Westerners by the strangeness of the place that was just recovering slightly from the depths of Stalin’s baleful influence.

I do recall that for a couple of years Peter changed his cautious style. This was around 1957-58 when he scored one of his two wins against Penrose. Was it at Ilford? I remember that the game appeared with notes by B.H. Wood in ‘The Illustrated London News’ column.

I used to see Peter regularly at the Paignton and Hastings Congresses in the 1990’s but not in the last couple of years. His health seems restored.”

PHC by Ken Harman :
“I am very pleased to hear about your book about Peter Clarke; not sure I can contribute much as I wasn’t a friend of his so only knew him through seeing him and Margaret at chess tournaments. He was a quiet spoken gentleman who played such quiet positional chess that I would call it ‘monastic chess’. I think Clarke thought chess a search for spiritual truth, only to be found in the cloisters of spiritual truth, only to be found in the cloisters of contemplative life – ‘The Thomas Merton of Chess’, if you like. Of course, I have no idea if he was a spiritual man in real life but his chess always struck me as if he was reaching for heaven and found hell in a doubled pawn. He seemed like a nice man and I suspect his wife Margaret was the dominant one. I have his book on Mikhail Tal’s Best Games of Chess (Bell 1961) which is signed by him and may well have been his copy, because as you open the book – there is a small newspaper clipping and a photo of Clarke sellotaped which is rather unusual being that the book is about Tal, and not him. ”

PHC by Alan P. Borwell (ICCF Honorary President) :
“I first met Peter at the 1959 BCF Congress in York when I was a member of local organising committee and then at Paignton and when York played & won the National Club Championship in 1964/5.
In 1966 I played Peter in the British Chess Championship in last round in Sunderland.”

and from Wikipedia :
Peter Hugh Clarke (18 March 1933 – 11 December 2014) was an English chess player, who hold titles FIDE master (FM) and International Correspondence Chess Grandmaster (1980), FIDE International arbiter (1976), Chess Olympiad individual silver medal winner (1956).
Peter Clarke started playing chess at the age of six. He twice won the London Boys’ Chess Championship (1950, 1951). He was British Chess Championship multiplier participant where five times won silver medal.
Since 1959, Peter Hugh Clarke has been working as a chess journalist in the newspaper Sunday Times and magazine British Chess Magazine. He known as the biographical book’s author of Mikhail Tal (1961) and Tigran Petrosian (1964). Thanks to his good knowledge of Russian language, he translated the book about Vasily Smyslov in 1958. In 1963 he wrote a book 100 Soviet Chess Miniatures.
Peter Clarke played for England in the Chess Olympiads :
In 1954, at second reserve board in the 11th Chess Olympiad in Amsterdam (+2, =2, -3),
In 1956, at reserve board in the 12th Chess Olympiad in Moscow (+7, =5, -0) and won individual silver medal,
In 1958, at fourth board in the 13th Chess Olympiad in Munich (+2, =10, -3),
In 1960, at third board in the 14th Chess Olympiad in Leipzig (+4, =7, -3),
In 1962, at second board in the 15th Chess Olympiad in Varna (+3, =10, -2),
In 1964, at second board in the 16th Chess Olympiad in Tel Aviv (+2, =8, -2),
In 1966, at first board in the 17th Chess Olympiad in Havana (+2, =10, -1),
In 1968, at third board in the 18th Chess Olympiad in Lugano (+0, =7, -1).
Also he played for England in the World Student Team Chess Championship (1954, 1959)and in the Clare Benedict Chess Cup (1960-1961, 1963, 1965, 1967-1968) where won team silver medal (1960) and 4 bronze medals (1961, 1963, 1967, 1968).
In later years, Peter Clarke active participated in correspondence chess tournaments. In 1977, he won British Correspondence Chess Championship. In 1976, Peter Clarke was awarded the International Correspondence Chess Master (IMC) title and received the International Correspondence Chess Grandmaster (GMC) title four years later.