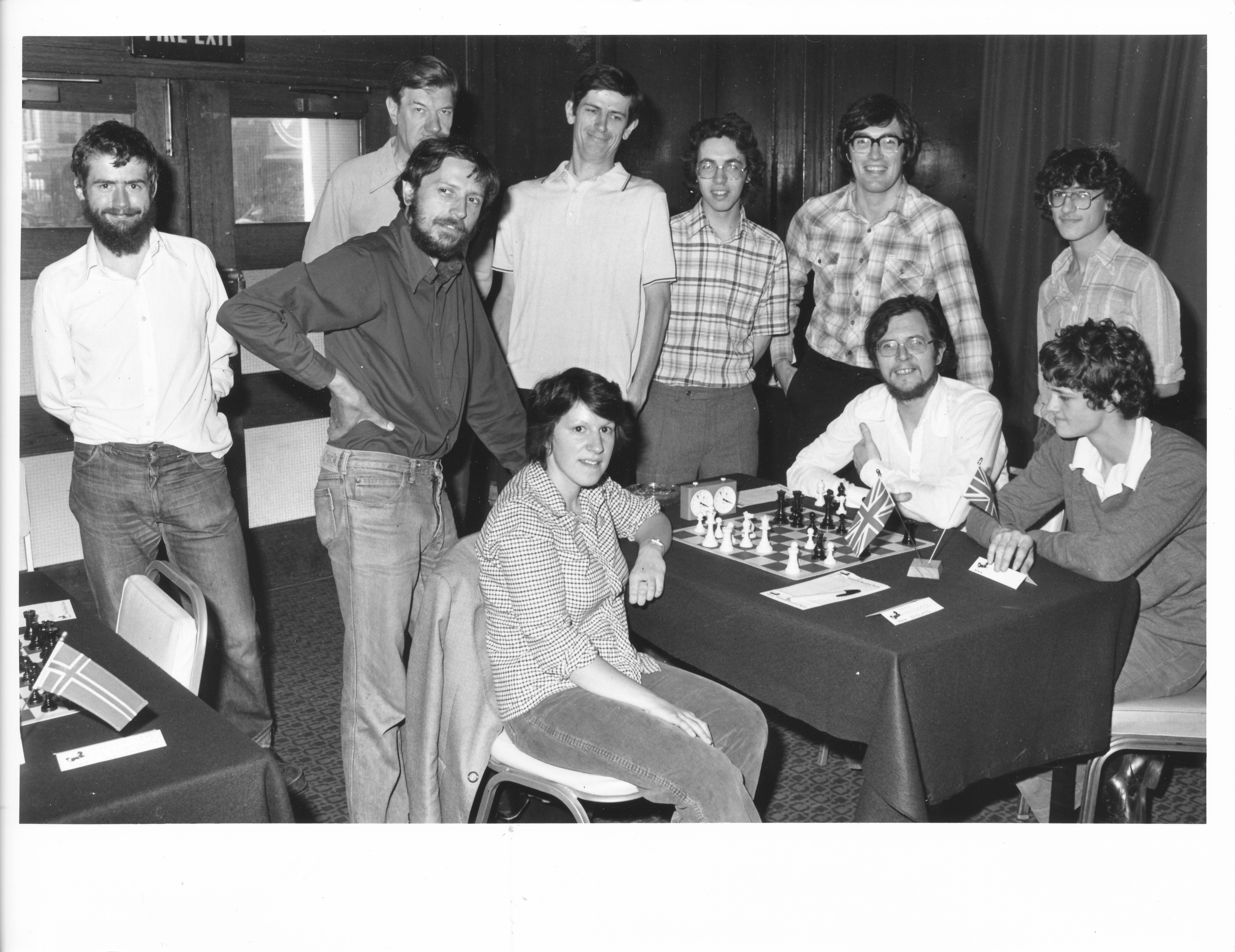
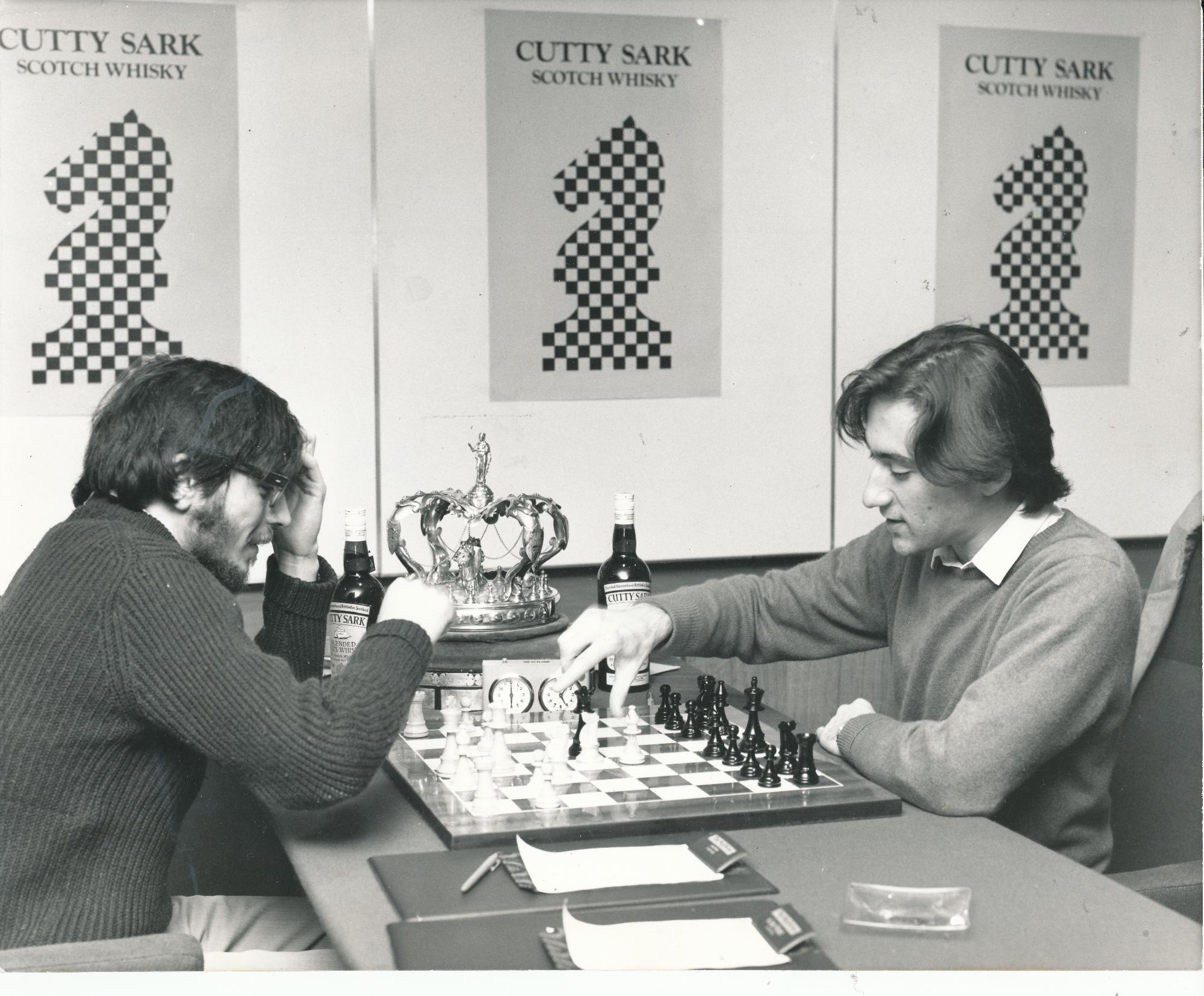
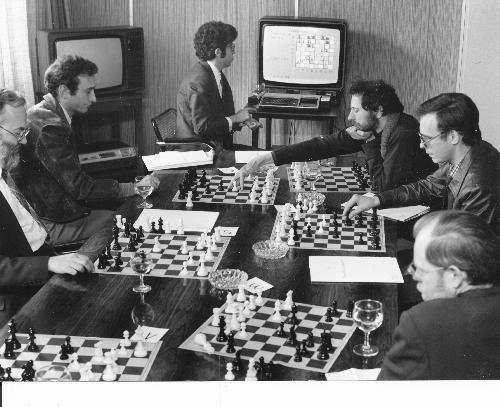
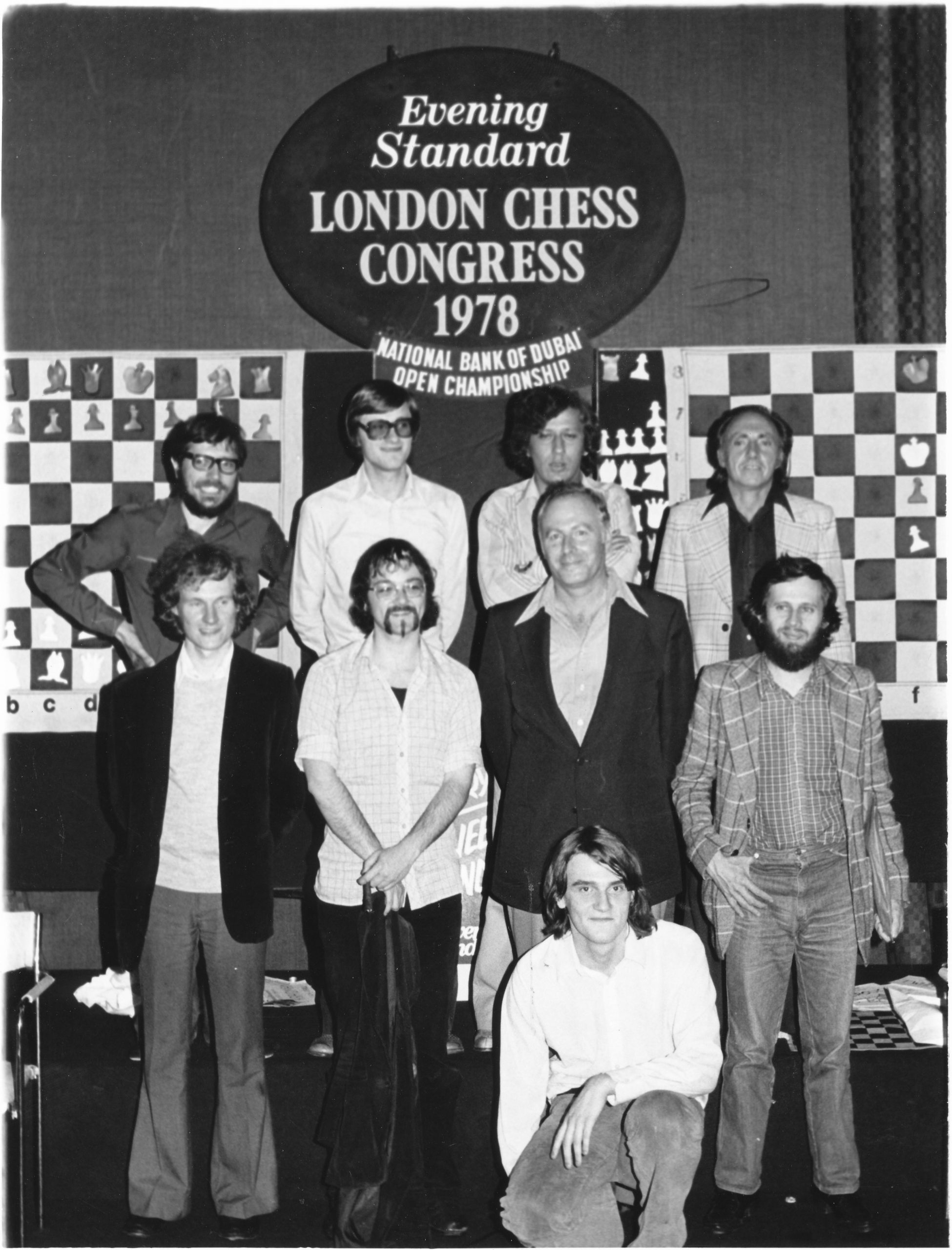
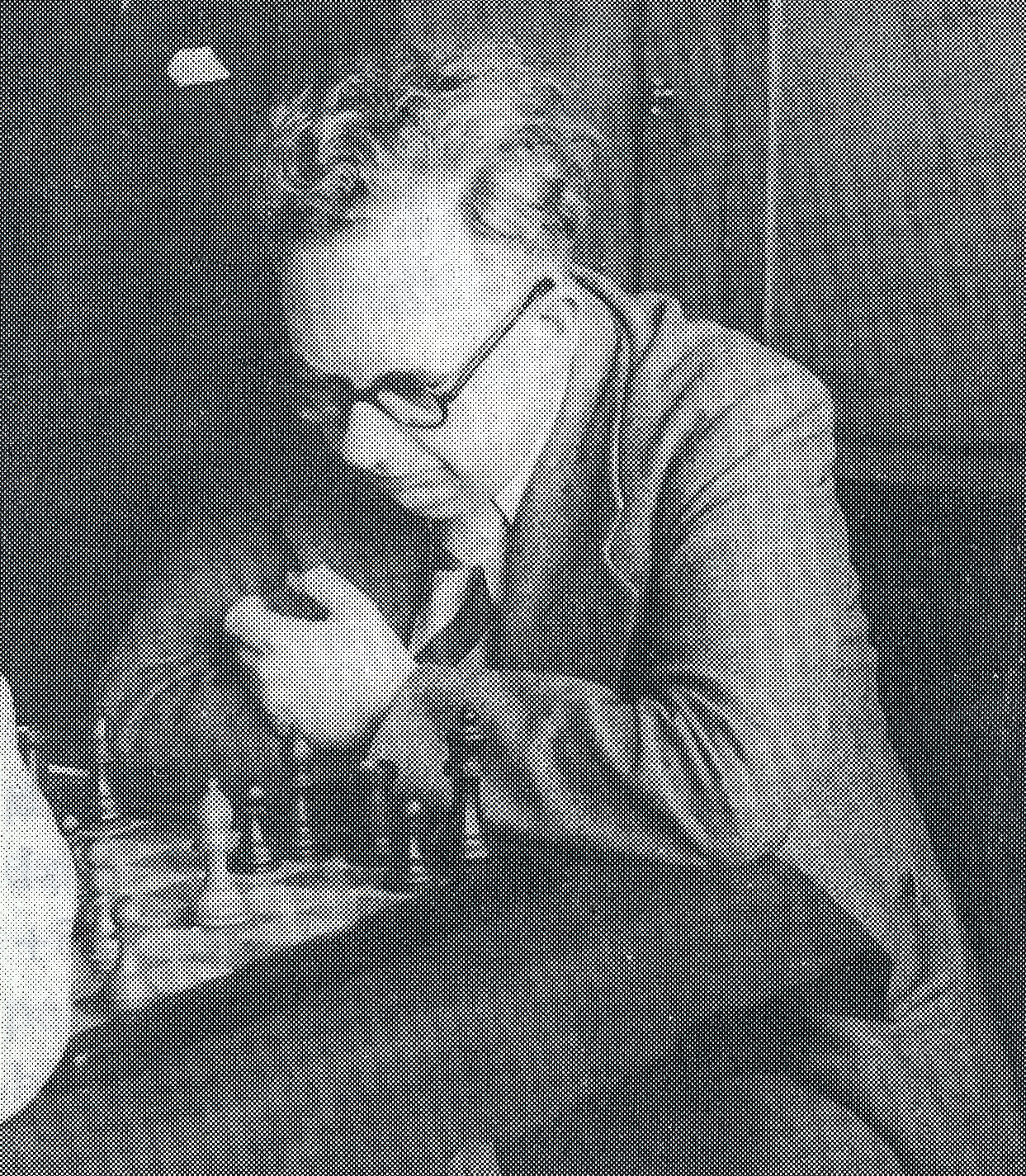
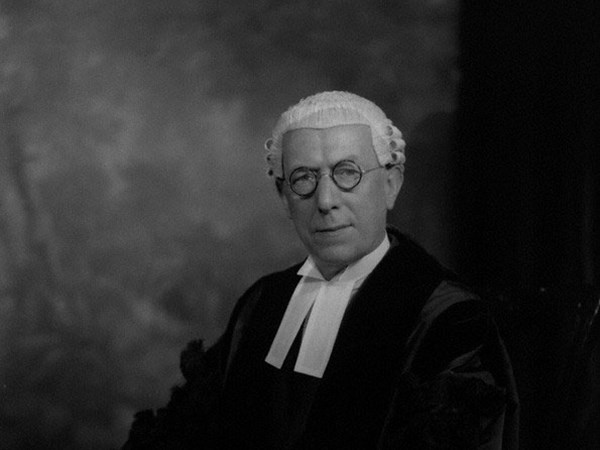
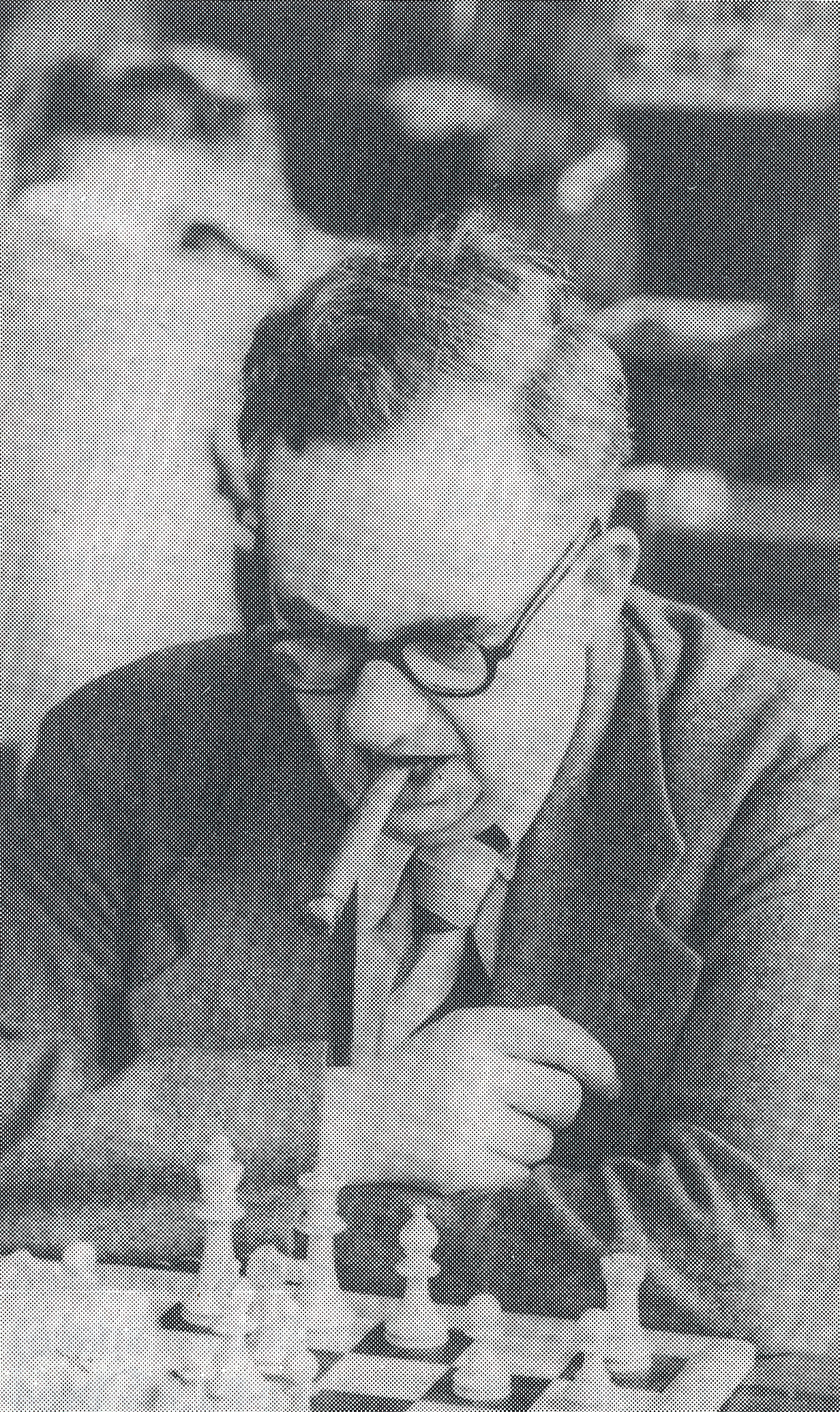
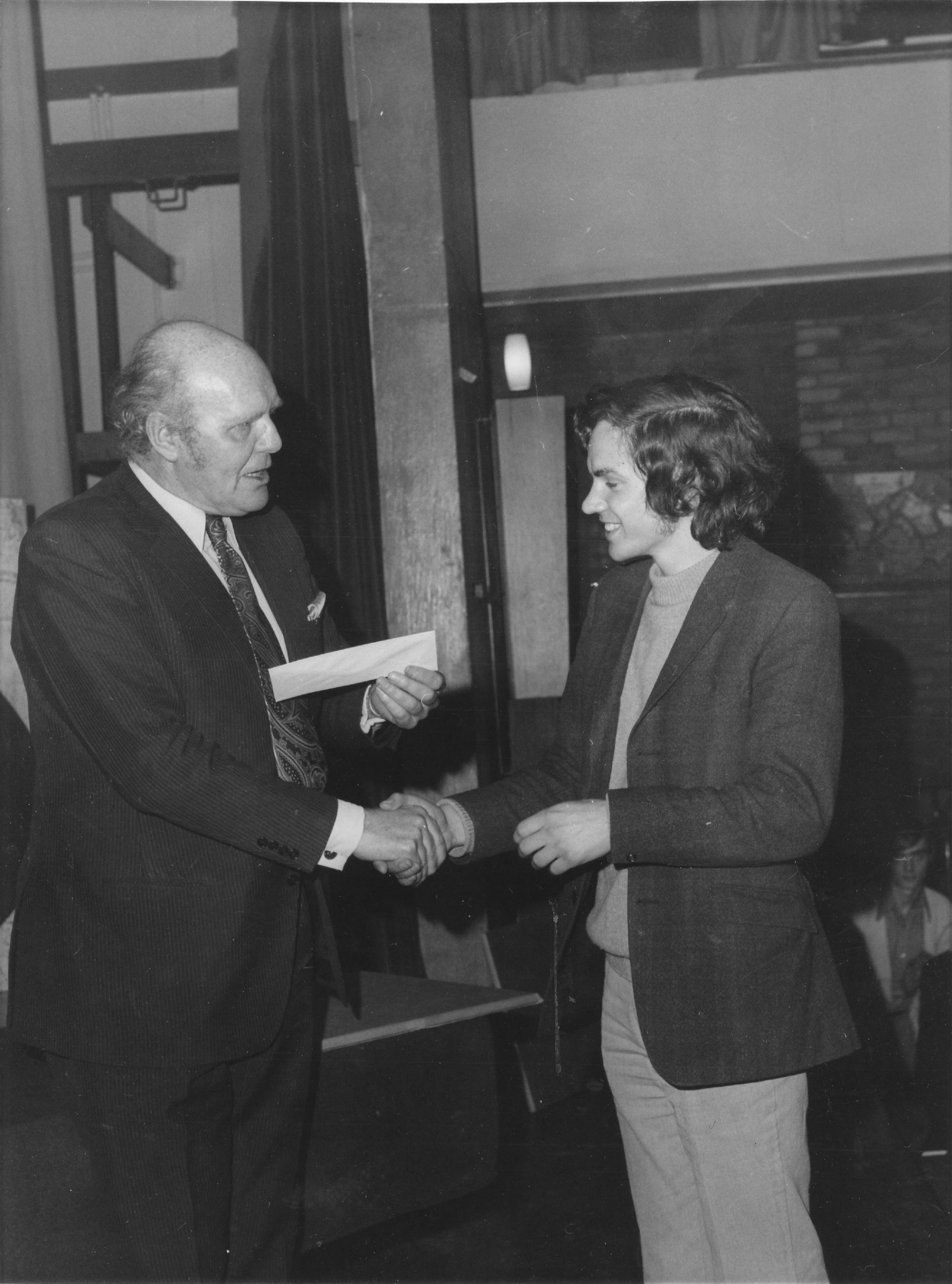
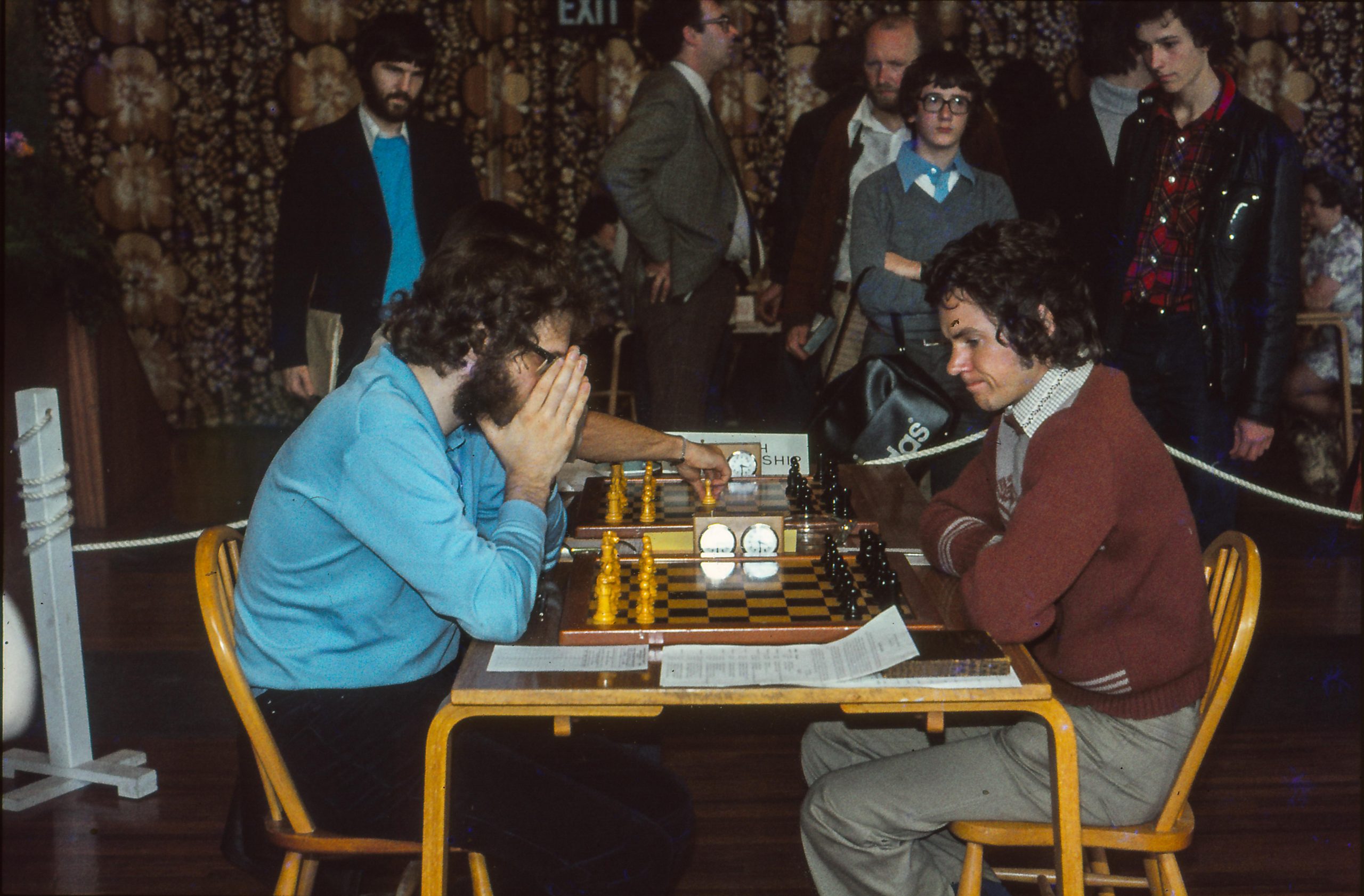
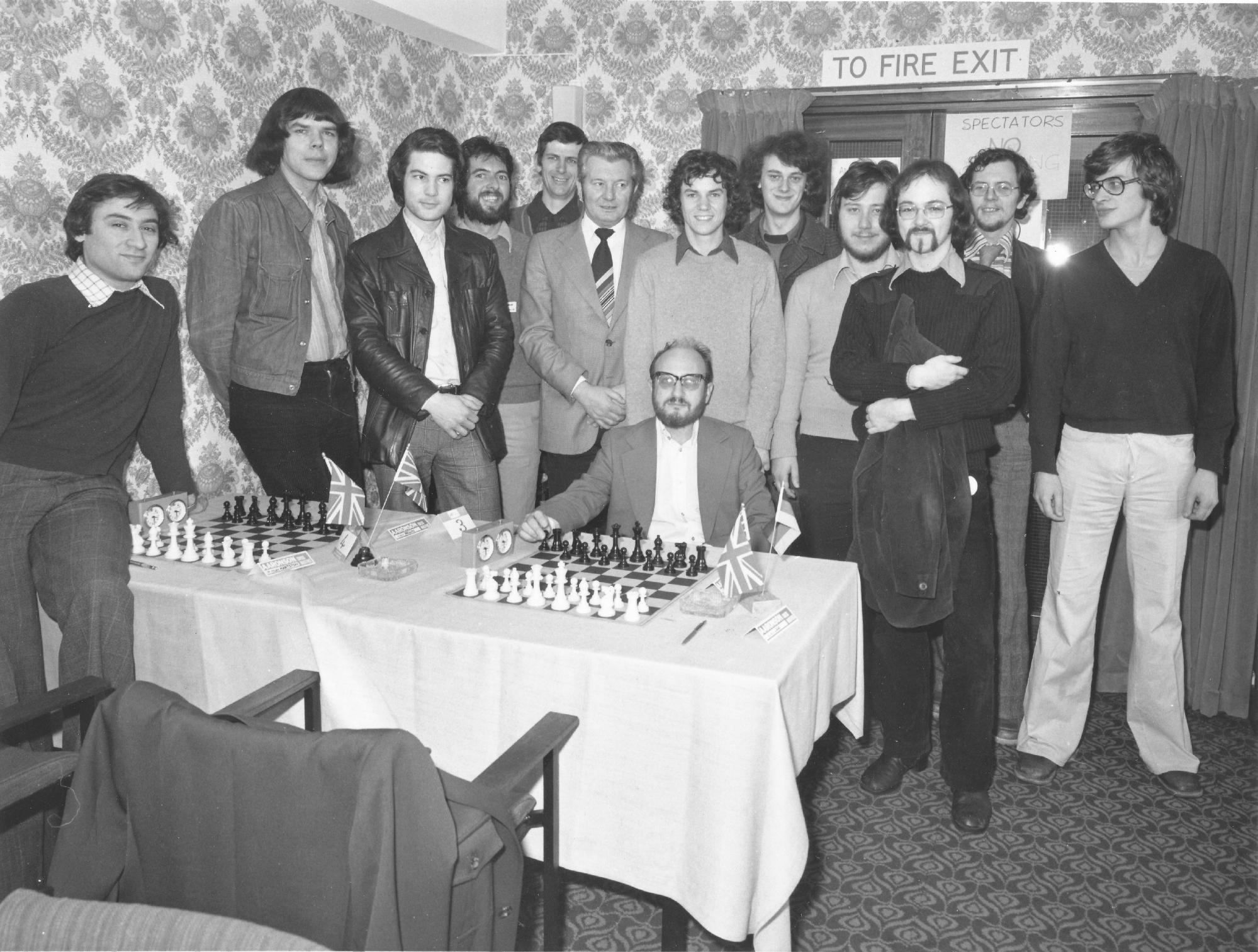
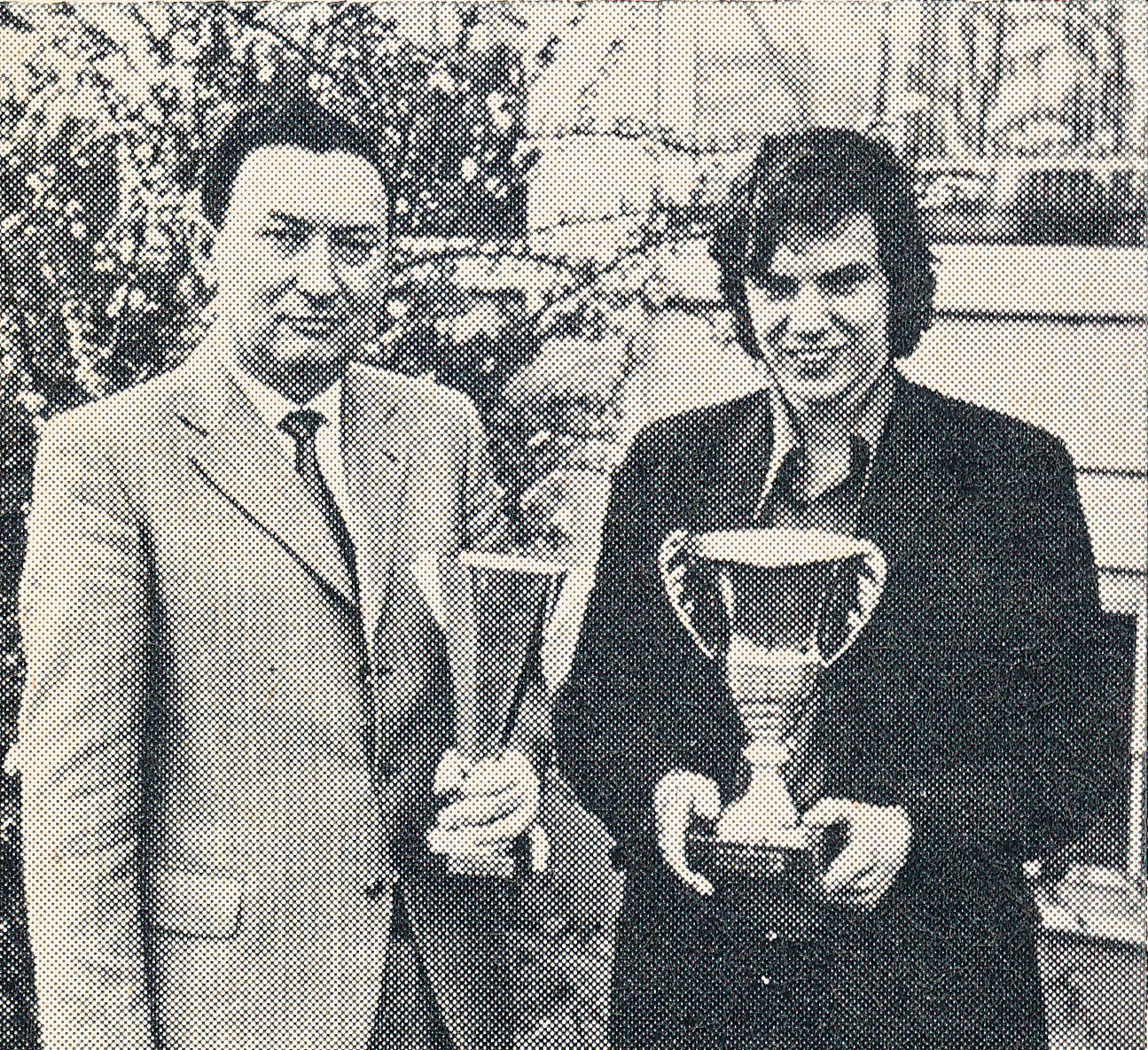
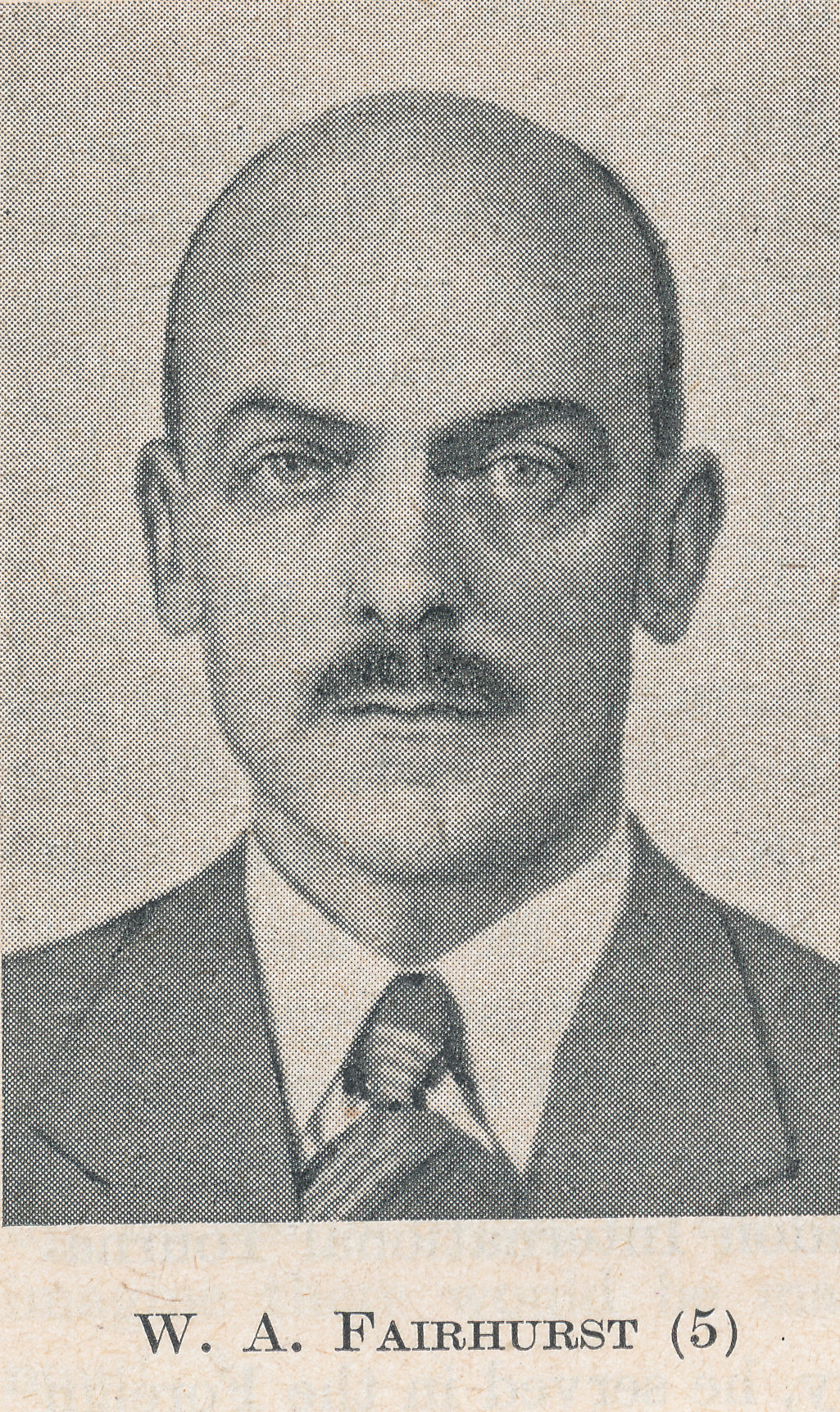
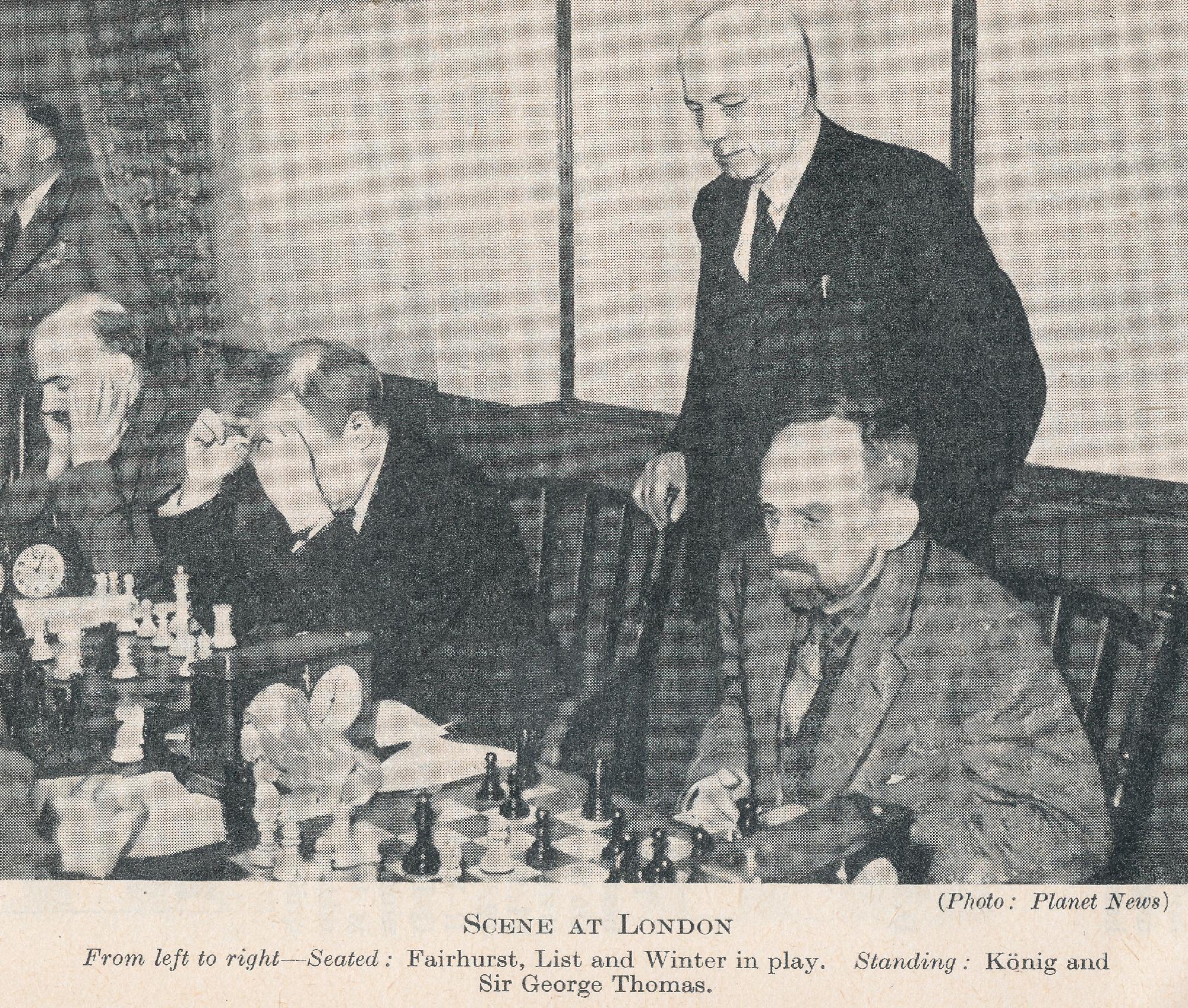
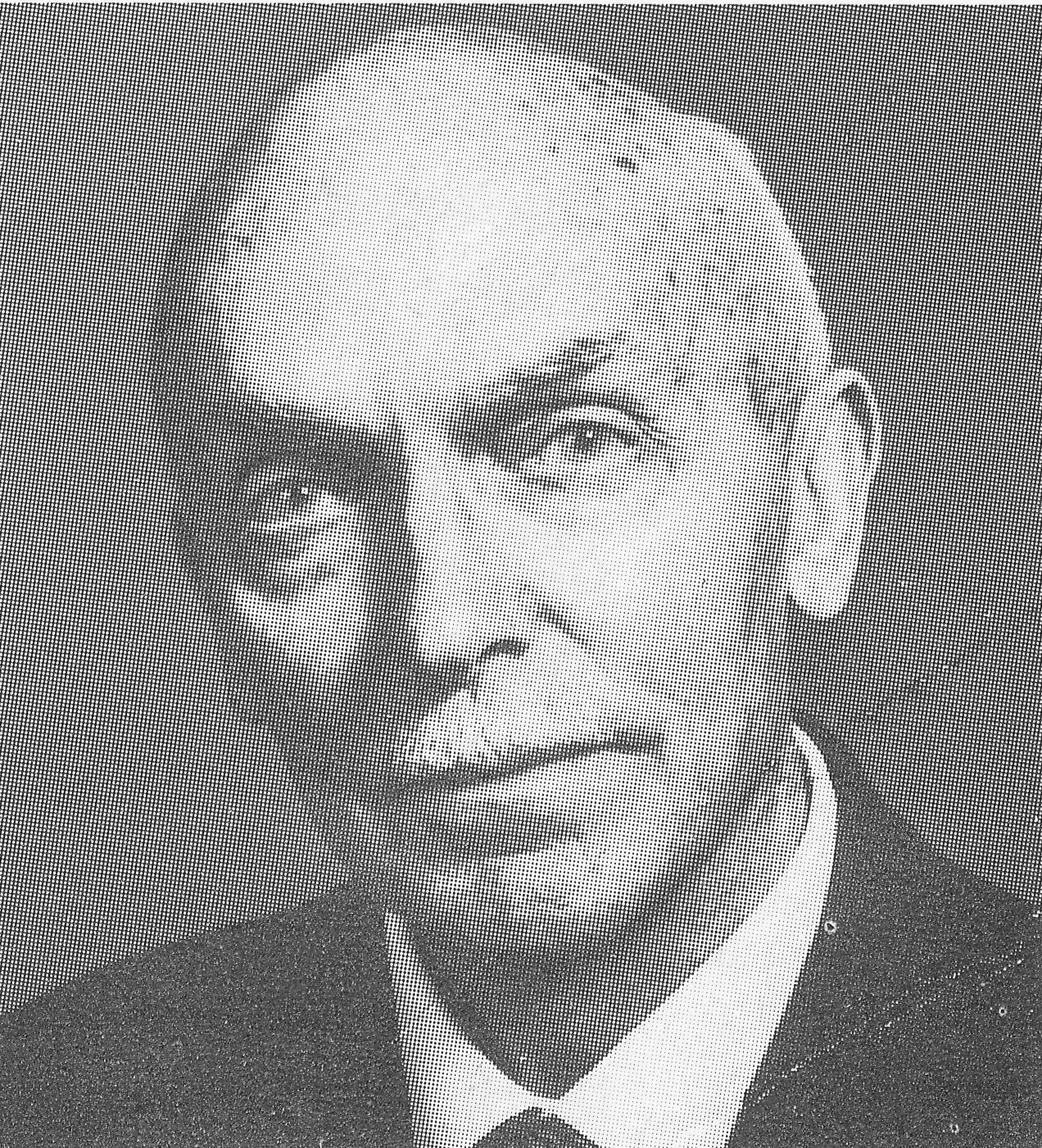
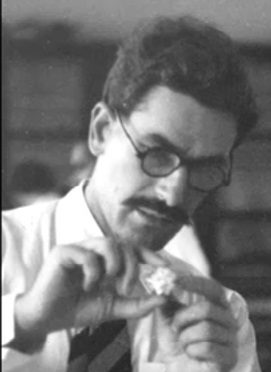
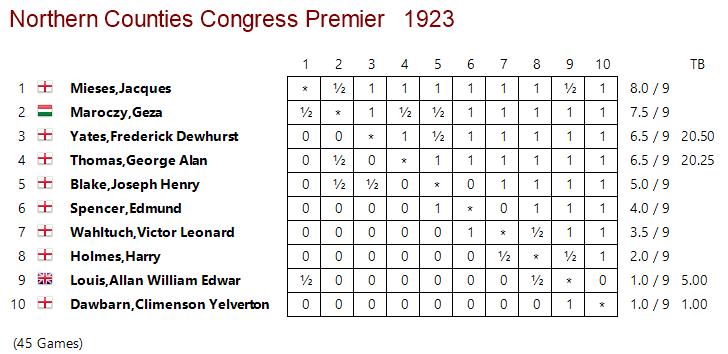
BCN remembers Dr. A(lfred) Christopher Reeves who passed away on Monday, December 3rd, 2012 in St. Agnes, Cornwall. His probate record (#4073868) is dated December 3rd, 2012 being recorded in the Bristol registry.
Alfred Christopher Reeves was born in Wharfedale, Yorkshire on Sunday, February 19th, 1939. His mother’s name was Tomlin.
Alfred detested his first name to the extent that he asked people to call him Christopher and, when asked, told them that the A was for Arthur. For this reason much of the chess literature uses Arthur whereas public records use Alfred.
In British Chess Magazine, Volume 133 (2013), Number 1 (January), page 2 we have this obituary from James Pratt:
“Alfred Christopher Reeves (Leeds, 19 ii 1939 – St Agnes?, 3 xii 2012). Chris Reeves was a FIDE Master of Composition. He toyed with entering the priesthood but became a child psychotherapist. He started composing (“…my solace and diversion …”) in 1960, largely specialising in the orthodox two move field. Though not a prolific composer, his work was known worldwide.
He was Sub-Editor of The Problemist”
From the The Encyclopaedia of Chess (Batsford, 1977), Harry Golombek OBE, John Rice writes:
“British problemist, output consists of skilfully constructed two-movers in the modern style.”
From The Encyclopedia of Chess (Robert Hale, 1970 & 1976), Anne Sunnucks wrote: :
“Problem composer. Since 1960 he has composed about 70 modern-style two movers, and is considered to be one of the most talented British composers. His originality and technique enable him to build into tangible form what would be no more than a passing idea for most composers. He has edited the problem section of Correspondence Chess, and he controlled BCF tourneys and International Team matches.”
From British Chess (Pergamon Press, 1983) Botterill, Levy, Rice and Richardson we have this:
“I was born on February 19th, 1939, the second son of a doctor who practised in a busy Yorkshire coal-mining town. As a youngster I acquired a taste for chess problems as soon as I learnt the moves of the game.
I owe my initiation to the admirable column which DM Davey used to run in the weekly review The Tablet and to the enterprise of one of the masters of the boarding school to which I was sent when still quite young. Davey’s column catered for novice chess problemists like myself by conducting graded solving tournaments with modest handicaps.
These tournaments ran conveniently the length of the school term, just long enough to sustain a young person’s enthusiasm, The teacher in question used to put the week’s problem up on the school noticeboard and dozens of small schoolboys participated as a result. The Tablet column was not only a boon for beginners like me. It had a very discriminating band of solvers who were given ample space to express their views on each week’s problems. This had the additional effect of making it a popular forum for budding composers who need the stimulus and encouragement of audience response in what is, after all, a very solitary sort of pastime.
My fascination with chess problems soon diverted my energies away from the game itself. I was eight when I began solving. Another 13 years elapsed before I seriously tried my hand at composing. My immediate inspiration was the example of the then young trio of British composers, Barry Barnes, Michael Lipton and John Rice. Their latest work incorporating, try-play, and often exploiting complex patterns of relationships between mates, was regarded as unacceptably, ultramodern, in some quarters but found ready appreciation with the solvers of Davey’s column.
Other sorts of problems I had enjoyed; these I wanted to emulate. The powerful attraction their work had on me has made me chary ever since of the strictures of self-appointed guardians of chess problem ‘taste’, who suggest that the modern two-mover cannot hold the same interest for the solver as the more traditional type. It certainly did not have a negative effect on me.
Problem I was one of my earliest compositions, in fact the first to gain any sort of award. At the time I was a theological student destined for the priesthood. I recall having felt some scruples about indulging in the frivolous pastime of chess problem composition not that it prevented me from becoming thoroughly addicted!
I have found that a bad conscience makes a good chess problem, and the greatest spur for composition is the feeling that one should really be busy doing something else. The problem shows a duel between the white queen and the black knight on d5, each of whose eight possible moves feature as a unique defence against one of the white queen tries. Solvers have often found the key to this problem’ quite elusive.
Problem I
The Tablet, 30th June, 1962
3rd Honorary Mention BCPS Ring Tournament
White to play and mate in 2
1.Qa1?…Nc7!
1.Qa4?…Nb6!
1.Qb1?…N5b4!
1.Qc1?…Nc3!
1.Qe1?…Ne3!
1.Qf1?…N5f4!
1.Qg4?…Nf6!
1.Qg1?…Ne7!
Key! Qb3!
The 1960s were my golden period of problem composition. They were my solace and diversion as I passed by way of theological studies through an Oxford degree to the foothills of a different career from the one I had originally envisaged, not the ‘cure of souls’ but the management and treatment of emotionally disturbed children and their families. By the end of the decade I was
already engaged in working as a Child Psychotherapist. Since then I have found that human problems have tended to displace my former involvement with problems of the chess pieces. Whereas
between 1960 and 1970 I composed seventy problems, in the subsequent decade I could manage only a dozen more. The reason for this slowing down in production, however, has not only been the demands of personal, family and professional life.
As a composer I have concentrated almost exclusively on the orthodox two-move field, one which if not yet exhausted nevertheless presents a major challenge to the composer to find something new to say or some new way of saying it. It is no accident (though I admit to a slight feeling of regret) of heterodox problems has expanded enormously in the past few years.
Of my eighty or so problems, fifty have been honoured in tournaments, ten with First prizes, ten with other prizes and the rest with Honourable Mentions and Commendations. My ambition is to
reach a respectable century of compositions, though I being to wonder whether I shall ever make the mark. I would also like to reach the FIDE Master norm for problem composition. I have
had twenty of my problems included in the triennial FIDE Albums so far, a few of them joint compositions. Here again, however, my productivity (or lack of it) may eventually tell against me.
Still, the problemist must always keep the business of honours in perspective. Composing problems is an essentially private business. Your opponent is the power of the pieces, not a fellow sitting opposite Vou. Unlike the chess player, one can keep one’s defeats to oneself when one puts the pieces away after a fruitless evening pondering over a board, so it seems only fair that
one’s successes likewise should be modestly recorded.
By a coincidence two of the three problems which I have selected to round off this brief note about myself and my compositions are ones which got no recognition from the tournament judge
at the time, although I count them amongst my best works.
I have chosen a trio of problems all roughly on the same theme, namely, the four possible moves of the pawn from its starting square. In chess problem parlance this is called the BP4M* theme when applied to the Black pawn, and the Albino theme when applied to the White pawn.
II and III show two ways in which four mates can be provided to meet each of the BP4M moves, only to be changed in the next phase of play. In II, the change is between mates set before the key and those operative after it; in III, the change is more radical, involving the transfer of the WR from one position to another, thereby creating two separate but related (or ‘twin’) problems. Incidentally, a good way to begin to get a taste of what composing involves is to take a problem like III and try to express the theme in full (here the changed BP4M) without resorting to the twinning device.
My last example, IV, shows a duel between white and black pawns, with the four Albino tries being met by the four possible BP4M defences.
(* BP4M is BCNs replacement for a word starting with p now considered by some as offensive.).
Whilst the player may rejoice in a victory soundly accomplished I can think of few pleasures to compare with the satisfaction which comes from accomplishing the sort of task which IV entails, especially when one is fairly sure that it has not been successfully achieved before. For me, at all events, this is what two-mover chess problem composition is all about: its is the ‘art if the all-but-impossible’!”
Problem II
Die Schwalbe August, 1965
White to play and mate in 2
1…dxc6+ 2. Bxc6
1…d6 2.Nd5
1…d5 2.Qb4
1…dxe6 2.Bc8
Key 1.Qxe5! (2.exd7)
1…dxc6 2.Nxc6
1…d6 2.Qf6
1…d5 2.Qc7
1…dxe6 2.Qxe6
1…Rd5+ 2.Nd5
Problem III
1st Prize
Problemist Twin Tournament 1966-67
White to play and mate in 2
Problem IV
Probleemblad, May, 1965
White to play and mate in 2
Clearly Chris was a hugely popular figure in the problem world. Here is a collection of tributes from the BCPS.