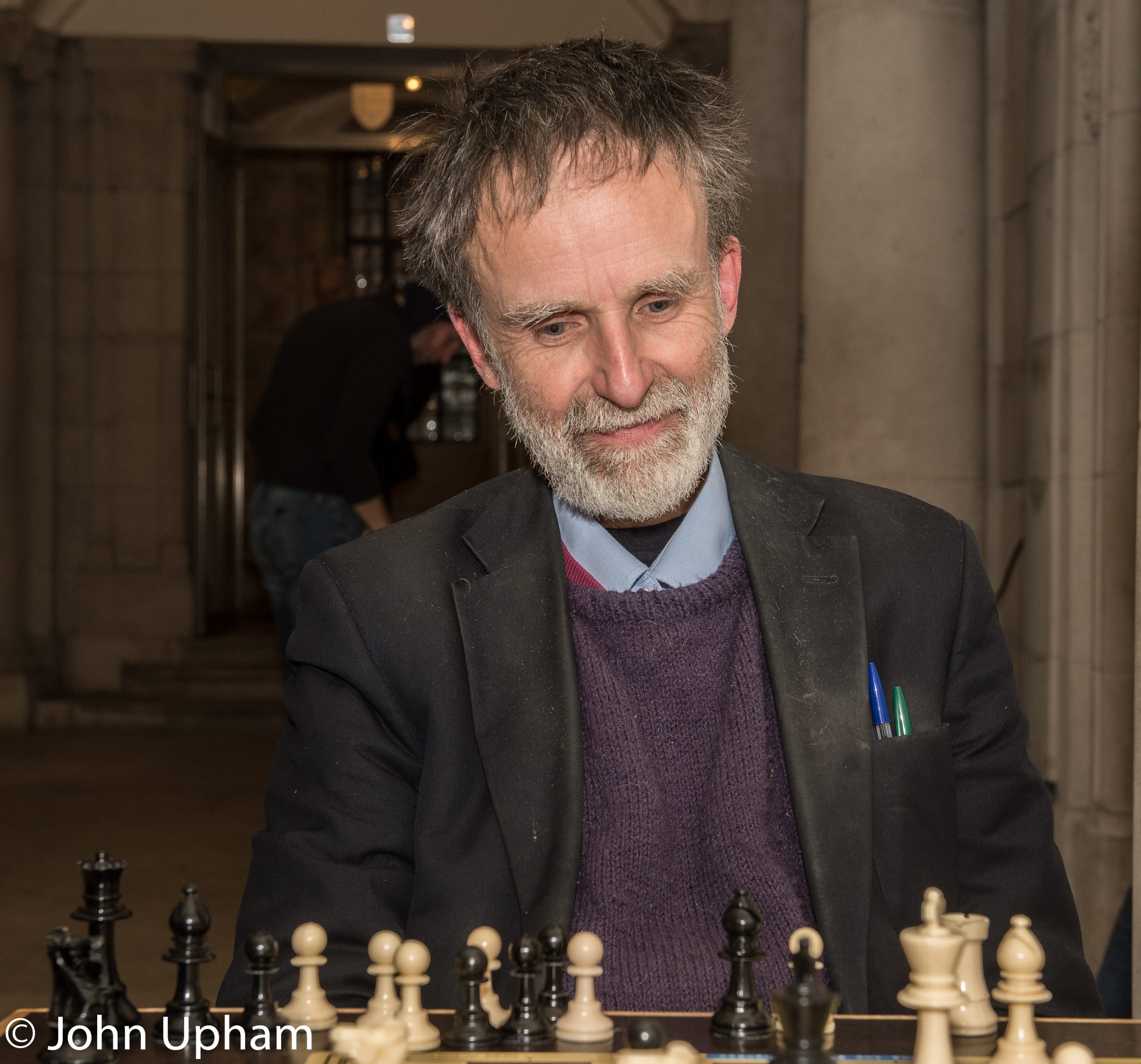
BCN sends best wishes to John Rice on his birthday, July 19th in 1937.
John Michael Rice was born in Scarborough, Yorkshire, North Riding, his mother’s maiden name was Blake. John lives in Surbiton, Surrey and teaches Modern Languages at Tiffin School, Kingston-Upon-Thames.

From An ABC of Chess Problems :
“The author is one of the country’s most prolific foremost composers and problem critics. He has gained mainly tourney honours, both at home and abroad, and since 1961 has been editor of a flourishing problem section in the British Chess Magazine, the country’s leading chess periodical. He lives in London and teaches Modern Languages at Tiffin School, Kingston-Upon-Thames.”
From chesscomposers.blogspot.com :
John Rice was the chief editor of the problems section of the “British Chess Magazine” from 1961 until 1974 and is a faithful collaborator of “The Problemist“. He has written “Chess Problem: Introduction to an Art” (1963) together with Robin Matthews and Michael Lipton and “The Two-Move Chess Problem” (1966), “Serieshelpmates” (1978) with Anthony Dickins or “Chess Wizardry: The New ABC of Chess Problems” (1996).
Translated from https://peoplepill.com/people/john-michael-rice/ :
“Since the mid-fifties he has composed problems of all kinds, but above all in two moves. In the 1960s he was editor of the problems section of the British Chess Magazine. Since 1999 he has been editor of The Problemist magazine.
International Master of Composition since 1969 and International Judge for Composition since 1972.
President of the PCCC (Permanent Commission for Chess Composition) from 2002 to 2006.
He worked as a teacher of modern languages in a school in Kingston-upon-Thames.

Together with Barry Barnes and Michael Lipton he wrote the book Chess Problems: Introduction to an Art (Faber & Faber, London 1963).

He composes mostly direct mates, but can composes as well in other genres, including fairies. He is an International Judge for twomovers, helpmates and fairy problems and the former President of the PCCC from 2004 until 2006.
John was awarded the title of “International Grandmaster for chess compositions” in 2015.
From British Chess, Pergamon Press, 1983 by GS Botterill, DNL Levy, JM Rice and MJ Richardson :
“I was taught the moves of chess in 1947 at the age of ten and quickly realised that I liked the game no more than Ludo or Snakes and Ladders where the chances of losing seemed to me unfairly high. But the chess pieces and their moves fascinated me, so it is hardly surprising that before long I had turned to problems and become an ardent fan of Brian Harley in his Observer column, especially as I had come across and paid two shillings (!) for his Mate in Two Moves in a second-hand bookshop in Reigate. Harley, together with T. R. Dawson in the British Chess Magazine and C. S. Kipping in CHESS, provided the sources of my first solving pleasure and the inspiration for my first efforts at composition. Among my early successes was problem l, heavily constructed but strategically rich, a first prize winner in a tournament for composers under 21, one of a series organised by the British Chess Problem Society.
1
1st Prize, BCPS Under-21 Tournament, 1955
White mates in 2.
1 Bd6 (threat Qg4)
1…Nxd6+;2.Qf3
1…Nh6+;2.Qf3
1…Nxh4+;2.Nf4
1…g4;2.Rh6
1…gxh4;2.Qxh4
I had grown up in Scarborough (Yorkshire), out of contact with other problem enthusiasts, and a chance meeting in December, 1954 with Michael Lipton in Cambridge, where we were both taking Scholarship examinations, brought the realisation that there was far more to the two-move chess problem than the solidly entrenched traditionalism espoused in those days by the columns of The Problemist and CHESS. Very soon the bulk of my output was in the modern style (with set and try-play) and published abroad, notably in Die Schwalbe, whose two-move editor, Hermann Albrecht, did much to stimulate my interest. Problem 2 gained a coveted prize in an extremely strong formal tournament judged by Michael
Lipton, following an article of his on the potentialities of the half-battery theme (illustrated here by the arrangement on the c-file).
2
5th prize, 133rd Theme Tournament, Die Schwalbe, 1961.
White mates in 2
1.N2~? Bg7+!
1.Nd4!? e2!
1.N3~? Bxc5!
1.Ne2! d~!
1.Ne4!!
The half-battery is only one of several themes which have commanded my attention over the past 20 years, others being white self-pin in try and key (illustrated by problem 3), Grimshaw and Nowotny (problem 4), reciprocal and cyclic play (problem V, the first published example of cyclic mates in three phases), pawn-promotion effects, and tasks of various types, especially open gates. My total problem output numbers about 600.
3
The Tablet, Commended, BCPS Ring Tournament 1958; Brian Harley Award
White mates in 2
1.Rxf4? (threat 2.Rhxf3)
Ne5; 2.Re4
Ng3; 2.Rfxf3
1.Nxf4! (threat 2.Rxf3)
Ne5;2.Ng2
Ng3;2.Nd5
In 1961 I took over from S. Sedgwick the editorship of the problem section of the British Chess Magazine, which post I held until December, 1974. It was a source of pride to me that I was now doing the job once done by the great T. R Dawson, though I knew that I could never bring to it the same tireless energy and all-round expertise which he had displayed so impressively. At about the same time I embarked with Michael Lipton and Robin Matthews on a venture which was to have repercussions throughout the entire problem world,
namely a series of books on problems published by Faber and Faber. The first, Chess Problems: Introduction to an Art (Lipton, Matthews and Rice), appeared in 1963, and was followed three years later by The Two-move Chess Problem: Tradition and Development, also with Michael Lipton, but this time the third collaborator was Barry Barnes, who has long been a close friend and influence. The third book in the series, An ABC of Chess Problems (1970), was a solo effort.
4
4th prize, BCF Tournament 123, 1970
White mates in 2
1.N5b6?, Rxb6/Bxb6/Qd3/Qd6;
2.Qc5/Ne5/Nc5/Qd1 … Qg5!
1…Qg5!
1.N7b6!, Rxb6/Bxb6/Qd3/Qd6/Qxc7;
2.Bc5/Nf4/Nc3/Bc3/Nxc7
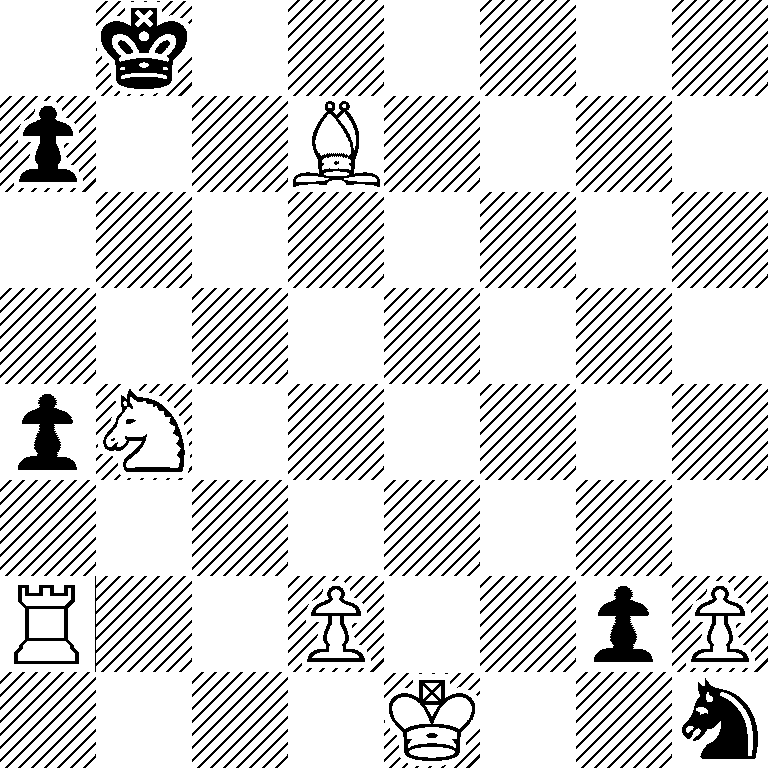
My interest in Fairy Chess dates from a meeting in the mid-1960s with the late John Driver, whose enthusiasm for the pleasures to be derived from non-orthodox forms I found highly infectious. Fairy problems soon began to appear in the BCM column and were favourably received. The serieshelpmate, where White remains stationary while Black plays a sequence of moves to reach a position where White can mate in one, has perhaps interested me more than any other non-orthodox form (see problem Vl), and in 1971 I collaborated with Anthony Dickins to produce a book on the subject, The Serieshelpmate (published by the Q Press, first edition 1971, second edition 1978).
5
1st Prize, Problem 37th Theme Tournament, 1961-62
White mates in 2
Set: 1…Kc6; 2. Qe8 (A)
1…Ke6; 2. Qc8 (B)
Try: 1.Nb6+?, Kc6;2.Qc8 (B)
Ke6;2.Qd6 (C)
Ke7!
Key : 1.Nf6+! Kc6;2.Qd6 (C)
Ke6;2.Qe8 (A)
Since 1974 my problem activities have necessarily been restricted by the demands of family life (wife and two sons, none of them much interested in chess) and my career (schoolmaster, formerly Head of Modern Languages Department and now Director of Studies at Tiffin School, Kingston Upon Thames. Other leisure-time interests (not that there is much leisure time) include cricket and classical music.”
6
2nd Prize, BCF Tournament 127, 1971
Serieshelpmate in 13
1.Bd8;2.Kc7;3.Kc6;4.Rf7;5.Rf3;6.Rc2;7.g2;8.Rf7;9.Rb7;10.Kc7;11.Kb8;12.Rc8;13Bc7, Nd7 mate.

From The Encyclopaedia of Chess (Batsford, 1977), Harry Golombek OBE, John Rice write about himself:
“British problem composer, output about 500, mainly modern-style two-movers but also several helpmates, serieshelpmates and fairy problems. Editing: problem section of British Chess Magazine (1961-1974). Author of An ABC of Chess Problems(1970), and co-author of Chess Problems: Introduction to an Art (1963), The Two-move Chess Problem: Tradition and Development (1966) and The Serieshelpmate (1971). International master (1969): International Judge (1972).”