Caruana’s Ruy Lopez: A White Repertoire for Club Players : GM Fabiano Caruana

From the book’s rear cover :
“The Ruy Lopez is arguably the most classic of chess openings. White immediately starts the battle for the centre, fighting for the initiative. This strategic clarity has made the Ruy Lopez, or Spanish Opening, an eternal favourite with chess players at all levels.
Inevitably, this popularity has also led to a wealth of opening theory. In this book, Fabiano Caruana takes you by the hand and lays out a complete and practical White repertoire for club players. He avoids complicated chaotic lines, but doesn’t shy away from sharp battles. Caruana loves to find and use the tactics to punish Black for risky choices.
This one-volume and crystal-clear repertoire covers fifteen main variations, from the classical lines to the anti-Marshall (8.a4), and from the Schliemann (3…f5) to the Modern Steinitz. In an easy-to-grasp manner Caruana explains general characteristics, such as permanent weaknesses long-term goals, and is always looking for an advantage for White. The insights of the World #2 in this classic opening, will not only greatly improve your results in the Ruy Lopez, but also sharpen your general chess knowledge.”
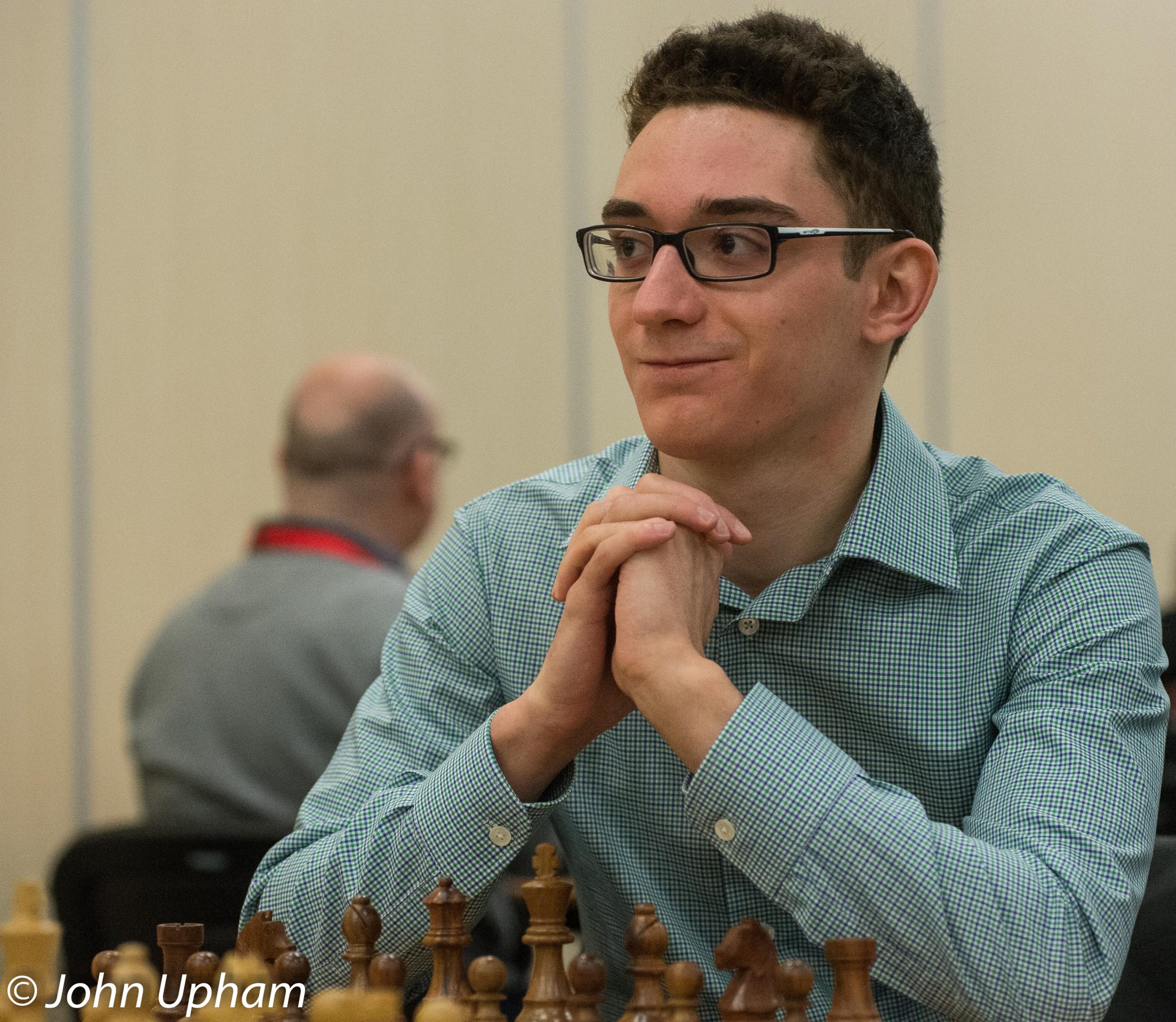

“Fabiano Caruana became a grandmaster at the age of 14. Ever since his majestic tournament win at the 2014 Sinquefield Cup, he has been the undisputed #2 in the Chess world. In 2018 he earned the right to challenge Magnus Carlsen in a match for the World Championship and only narrowly lost in the play-off.”
Before we proceed further it is worth inspecting the sample pages in pdf format provided by the publisher.
Fabiano Caruana became a Grandmaster aged 14 and challenged Magnus Carlsen for the World title in 2018.
and here we have the Table of Contents:

Caruana kicks-off by looking at the Anti-Marshall line which starts with the closed Lopez 5…Be7 6.Re1 b5 7.Bb3 00. Now fearing the Marshall Gambit, which has scored very highly for black, he avoids it with 8.a4.
This was Gary Kasparov’s choice in Game 1 of his 1993 match with Nigel Short and it would seem to be a sensible choice.
The two Black main replies discussed are 8…Bb7
and 8…b4.
In similar vein Chapter 2 covers Black playing 7…d6 instead of 7…00 and interestingly 8 a4 is again recommended as opposed to the vastly more popular 8.c3 thus:
Black has to be careful in these lines not to lose his b pawn!
The next few chapters look at the so-called main line of 7…d6 8.c3
giving White another choice than 8 a4. After 8…00 9.h3 Na5 we have the Chigorin variation which is covered in Chapter 3. After 10. Bc2 c5 11.d4 Qc7 12.d5 ! is a move the computers like and does seem to give white a space advantage.
\
Now White plans a Kingside attack with g4 and moving his f3 knight to f5. This line does not seem to be much fun for black.
Chapter 4 covers the Breyer variation, 9…Nb8
planning to reposition a knight to d7. White combines a plan of a4 attacking the Black’s Queen-side along with a King-side attack.
Chapter 5 examines Karpov’s favourite of the Zaitzev variation (9…Bb7). White will almost always play 10.d4 Re8 followed a knight coming round from b1 to f5 ensures an advantage. Black will need to get in f5 in to avoid being crushed.
Often more than one line is given for white as this book is written from a white perspective.
Chapter 6 switches tack to the Open variation where Black plays 5…Ne4
which was a favourite with Viktor Korchnoi who employed in his various matches with Anatoly Karpov. The main line is 6.d4 b5 7.Bb3 when the dubious 7…ed4? (7…is much better) played in Fischer – Trjfunovic (Bled, 1961) is analysed.
Better is the main line of 6…b5 7.Bb3 d5 8.de5 Be6 when White has several decent moves. Both Karpov and Kasparov have played 9.Nbd2 which is the move I always considered strongest in this line.
Surprisingly, the move given by Caruana is 9.Qe2 planning Rd1 and c4.
Black can play 9…Nc5 but the main line is 9…Be7 10.Rd1 00 11.c4 bc4 12.Bc4 Bc5 which seems to me to give clear equality . However both Caruana and Giri have played the white side of this position so maybe this line needs looking at more carefully.
Possibly the chapter many will turn to first is Chapter 7 covering the Berlin defence of 3…Nf6 which seems to have taken the terror out of the Lopez is discussed. Caruana prefers 4.00 leading to a middlegame without queens.
Players who, perhaps, have more confidence in their middle game abilities (with queens) than the previous line should probably try 4.d3 and I am surprised that Kasparov never tried this in his match with Vladimir Kramnik. Fabiano believes that this queenless middlegame is still more pleasant in practical play for White and Maxime Vachier-Lagrave regularly plays it with white.
Ian Nepomniachtchi won a miniature against Hikaru Nakamura quite recently as follows:
Chapter 8 discusses the Modern Archangelsk which is 3…a6 4.Ba4 Nf6 5.00 b5 6.Bb3 Bc5
which is really rather popular at present. Caruana, Magnus Carlsen, Gata Kamsky and Alexei Shirov all seem to like this line.
Following this we have 7.c3 d6 8.d4 Bb6 9.Be3
when the consequences of white next playing 9… 10.de5 need to be carefully considered. Black players playing for a win should consider this line seriously as it is a lot more interesting than the Berlin!
It is surprising that the old move 6…Bb7 (the Archangelsk of old) is not covered by the author as I have played many internet games with this line.
The last few chapters cover a collection rarely played moves such as 3…Bc5 (the Classical defence). White should play 4 c3 and d4 but black has the interesting f5 on move 4 mixing things up somewhat.
Other unusual moves are the Smyslov variation, 3…g6, the Bird’s defence, 3…Nd4 and the Cozio defence, 3…Nge7 which is aimed against Lopez exchange advocates.
However, two of the most interesting chapters look at the Schliemann defence (3…f5) and the Steinitz defence of 3…d6.
Caruana recommends 4.d3 against the Schliemann and only this or 4.Nc3 can give white a plus. After 4.d3 fe4 5.de4 Nf6 6.00 now black normally plays 6…Bc5 when white can win a pawn with 7.Bc6 and 8 Ne5.
Black can, of course, avoid this with 6…d6 but suffers the same problem as in the closed variation, that is a passive dark square bishop.
Finally, the Steinitz and Steinitz deferred are looked at in the last two chapters. After 3…d6 the line 4.d4 ed4 5.Nd4 Bd7 is examined. After 6.00 White has a space advantage a common feature in a number of variations chosen leaving white with the more pleasant positions to play.
Overall, from black’s point of the Modern Archangelsk seems one of the most interesting and sound lines to play if he is looking to play for a win.
There are a few omissions that are curious. As mentioned previously 6…Bb7 is not covered but most surprisingly there is no coverage of the so-called Neo-Møller which was recently covered, in depth, by FM Ioannis Simeonidis also for New in Chess in
Carlsen’s Neo-Møller : A Complete and Surprising Repertoire Against the Ruy Lopez
It might have been amusing to pit the two publications against each other!
In summary, Caruana’s first venture into writing yields a comprehensive repertoire for the white side of the Ruy Lopez with much material for anyone playing the black side.
Colin Lyne, North Camp, Farnborough, Hampshire, 30th September, 2021

Book Details :
- Paperback : 240 pages
- Publisher: New in Chess (29th June, 2021)
- Language: English
- ISBN-10:905691944X
- ISBN-13:905691944X
- Product Dimensions: 17.53 x 1.09 x 23.55 cm
Official web site of New in Chess




 If you’ve read my article about
If you’ve read my article about  There are also two inscriptions. The second is ‘Peter Elliott’: there were several people of this name in this area, none of whom mean anything to me.
There are also two inscriptions. The second is ‘Peter Elliott’: there were several people of this name in this area, none of whom mean anything to me.