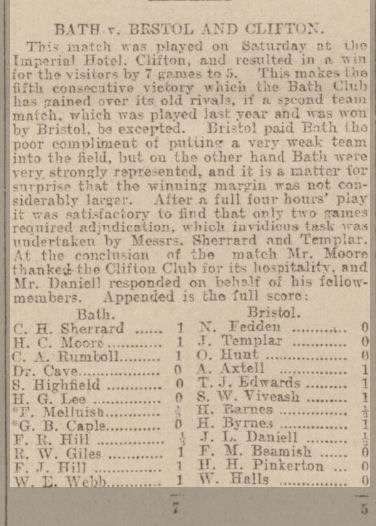
We’ve met, briefly, one or two lady chess players in Leicester, and, while we’re still in the home of the 2023 British Championships, it’s time to look at the subject in more detail.
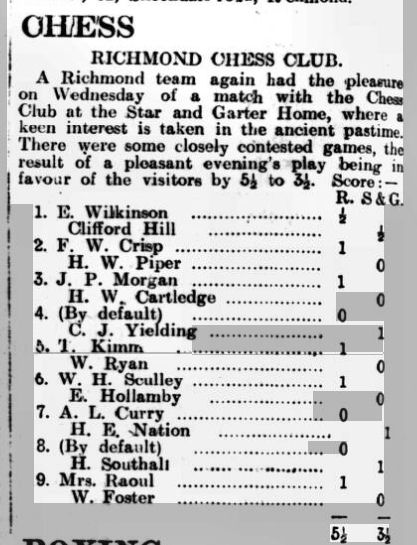
Our story starts in 1912, when, at the Leicestershire Chess Club’s annual social evening, an informal tournament took place between four ladies.
The winner was Mrs Shardlow, ahead of Mrs Collier followed by the Misses N Wilkinson and M Chappin.
Mrs Collier was Eliza Mary (née Webb), the wife of Edward Heath Collier, one of the county’s leading players, and the mother of Philip Edward Collier. The Collier family played a vital role in Leicestershire chess over almost a century: you may well meet them again in a future Minor Piece.
Mrs Shardlow was born Emily Preston in Lancashire in 1877: her husband, works manager Howard William Shardlow, also a chess player, had been born in Lincolnshire in 1878. They didn’t stay very long in Leicestershire before moving on.
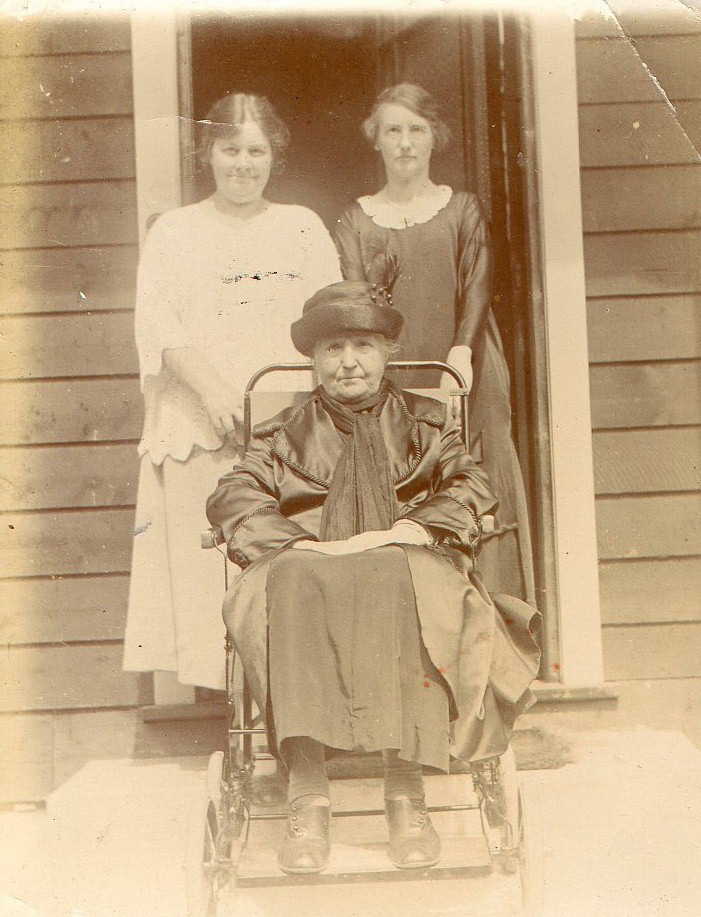
Here’s a delightful photograph of Emily, standing on the right, with her sister Edith on the left, and their mother Ellen seated in front of them.

We also have a correspondence game played by her husband, which, for some reason, was published in a local newspaper in New Zealand. Howard’s 13th move fatally opened up the position, allowing his opponent, an accountant from South Manchester, a fairly easy tactic to score a swift victory. (Click on any move of any game in this article for a pop-up window.)
Then we have the Misses Wilkinson and Chappin. Muriel Cicely Chappin was the daughter of Frederick Chappin, whom you met here. Born in 1896, she was only 16 at the time, and must have come along with her father for some casual games. I’m guessing Miss Wilkinson was Nelly Wilkinson, also born in 1896, the daughter of a pork pie and sausage manufacturer (nearby Melton Mowbray has always been famous for its pork pies): the two girls lived a short walk away from each other, and, I’d imagine, were schoolfriends.

Here’s Muriel, pictured at her wedding 16 years later: her bridegroom, Frederick Archibald Sowter, was a textile salesman.
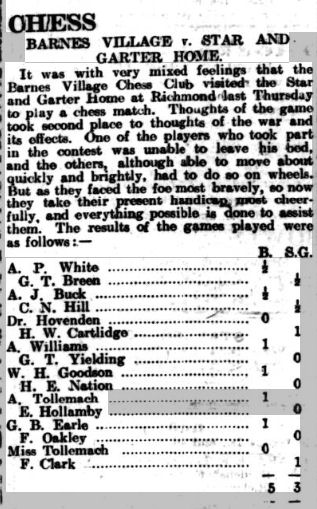
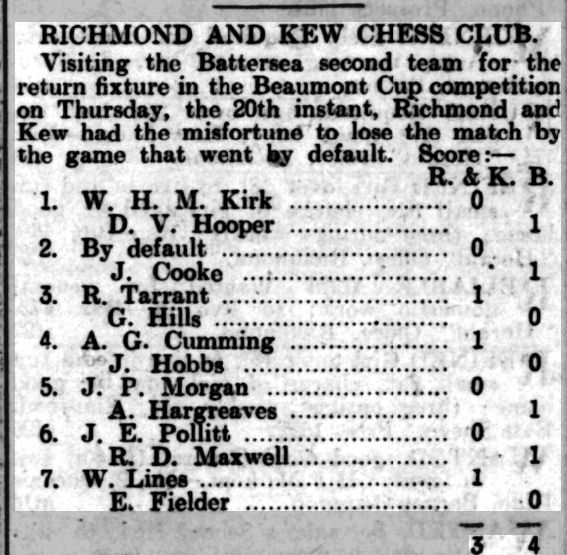
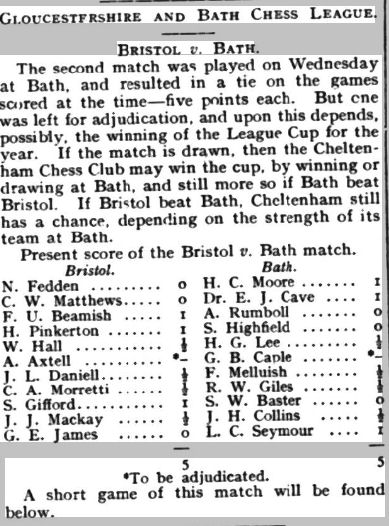
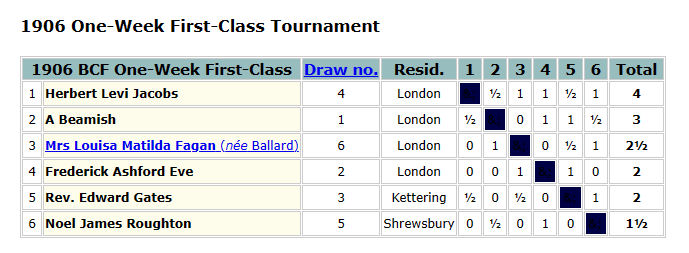
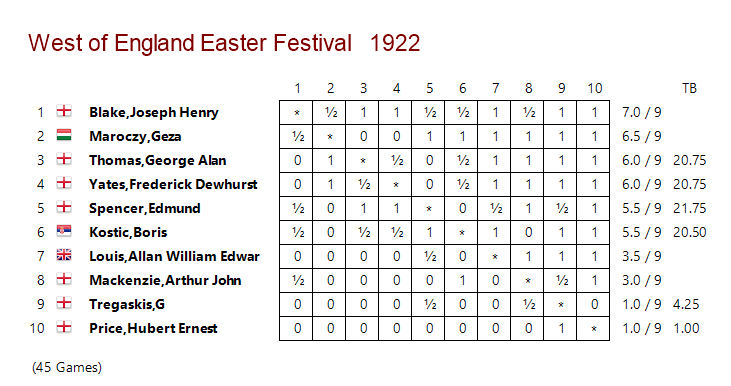
It was decided to hold a more formal ladies’ tournament during the 1912-13 season. There were three entries, each playing two games against the other competitors.
In a close finish, Emily Shardlow scored 2½/4, Lucy Storr-Best 2/4, and Agnes Champ 1½/4. Lucy was the wife of (Robert) Lloyd Storr-Best, from another celebrated chess family. Again, they didn’t stay long in Leicestershire, later turning up in London, and then in Sussex. You may perhaps find out more about them in a future Minor Piece.
The social evening in 1913 included a pick-up match in which Emily, Eliza and Agnes all took part, the first two winning their games. Muriel and her friend Nelly were paired together, making an amicable draw. You’ll note that Mr Collier selected his wife for his team, but not his son.
The Ladies’ Championship took place again in the 1913-14 season. I haven’t found out how many took part, but, as you might have read here, if you were paying attention, Miss Champ, living up to her name, moved from last place to first.
Agnes Champ: interesting name. If you reverse it you get CHAMP AGNES, which is perhaps what she drank to celebrate her success in the tournament. (A century or so later, another Agnes Champ made sporting news. A French racehorse of that name – male rather than female – had an unusually long but rather unsuccessful career, running no less than 93 times, but only winning on three occasions, all at Deauville, in 2012, 2014 and 2015.)
The chess playing Agnes Champ also had a rather long (25 years or so) but not very successful chess career, spanning the same three counties as the Storr-Bests.
Agnes was born in Chelmsford, Essex in 1859, the daughter of a wine merchant (you might wonder whether that was why he called his daughter ChampAgnes) , so she was well into her fifties when she started her chess career. Her brother John was a doctor who moved to Tasmania, and her sister Jessie married a doctor and settled in Leicester. The 1911 census found Agnes staying in a boarding house in Bournemouth, a lady of private means, but shortly afterwards she moved to Leicester, living with Jessie and her husband. In 1912 she joined the Leicestershire Chess Club. She was still living with her sister in the 1921 census, but described as a ‘visitor’.
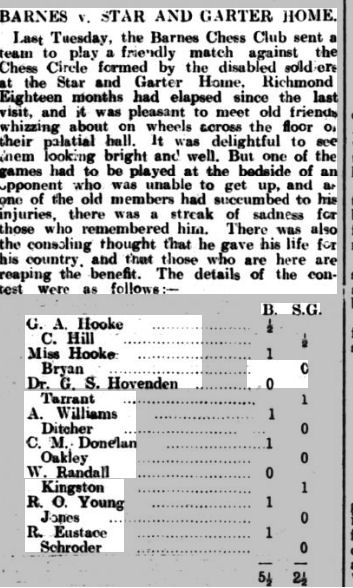
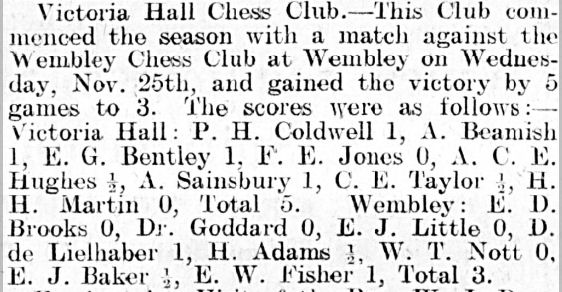
It looks like she remained in Leicester throughout the 1920s, but by 1932 she was living in a boarding house in the Notting Hill area of London. It was there that she resumed her chess career, joining the Imperial Chess Club, and here playing in a friendly match against the confusingly similarly named Empire Social Chess Club.
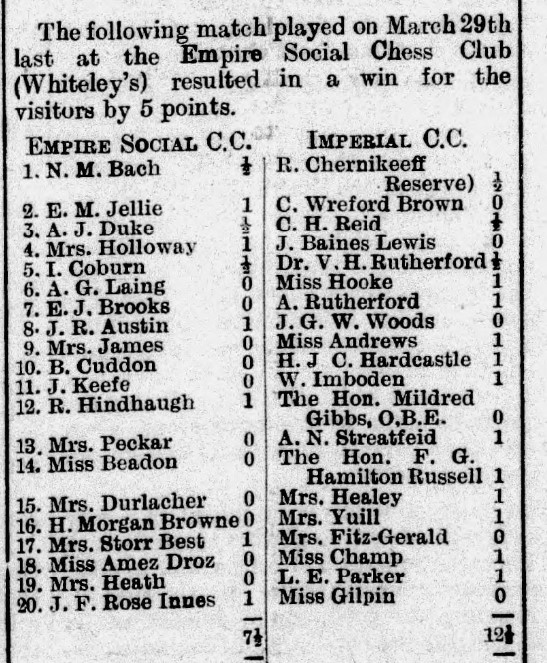
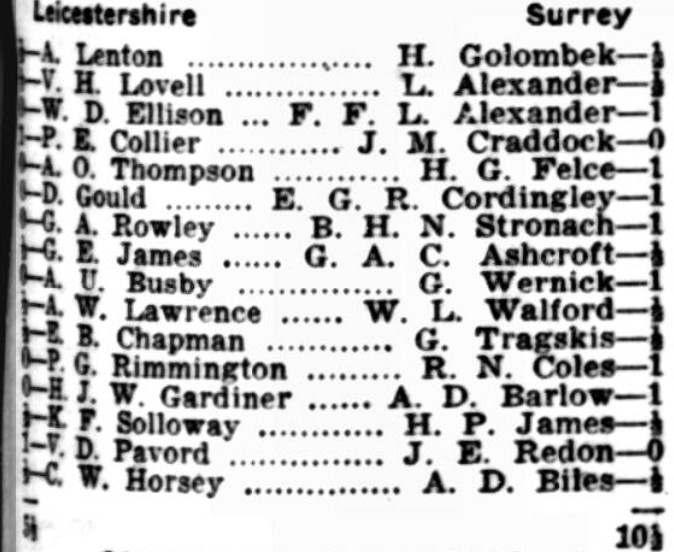
You’ll notice a few things here. Firstly, that there were eight ladies out of twenty on each side, an impressive 40%. One of Agnes’s teammates was Alice Elizabeth Hooke (see here and here). She just missed by one board her old Leicester opponent Lucy Storr-Best (at least I presume it was her). Her opponent, Claire Amez Droz, was very interesting: a violinist and future London Ladies’ Chess Champion, who would later be involved with West London Chess Club. Mrs James was almost certainly not related to me.

There’s much to be written about these two clubs and their members, and there was clearly a considerable crossover in membership. Here, in 1934, she was taking part in the Empire’s Women’s (interesting choice of word: Ladies was usually used at the time) Championship, alongside several of the country’s top female players.
By the time of the 1939 Electoral Roll, Agnes was living in a different boarding house in the same part of London: among those next door was Leonard Messel, who may or may not have given his name to a magnolia.
Very soon afterwards, it seems she retired, like all good chess players at the time, to Hastings, where, at the age of 80, she made her debut in open competition, taking part in the Third Class section of the 1939-40 Hastings Congress, scoring a very respectable 5 points out of 9 games.
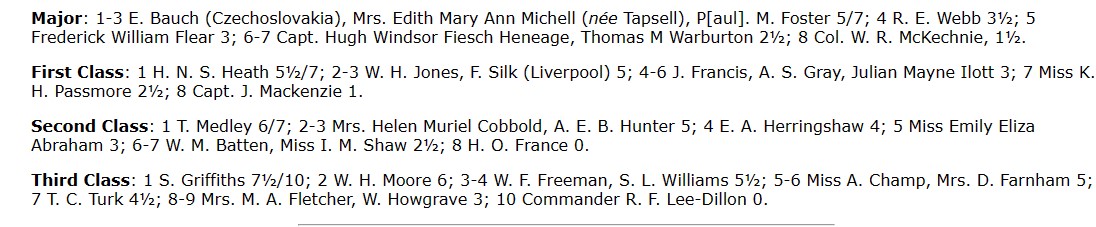
But this would be her swansong: her death was recorded, again in Hastings, in the first quarter of 1940.
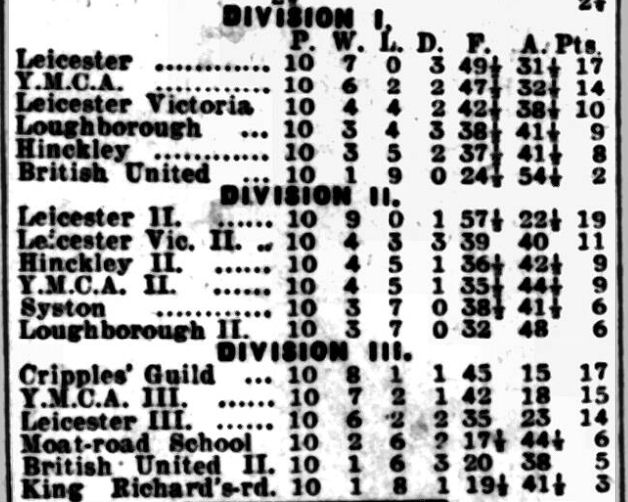
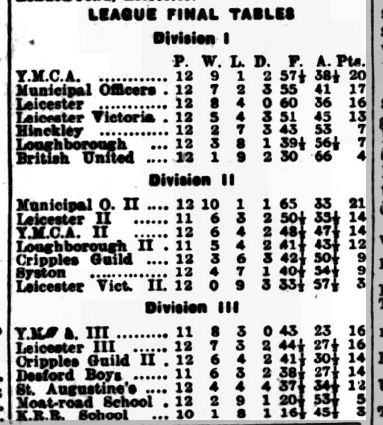
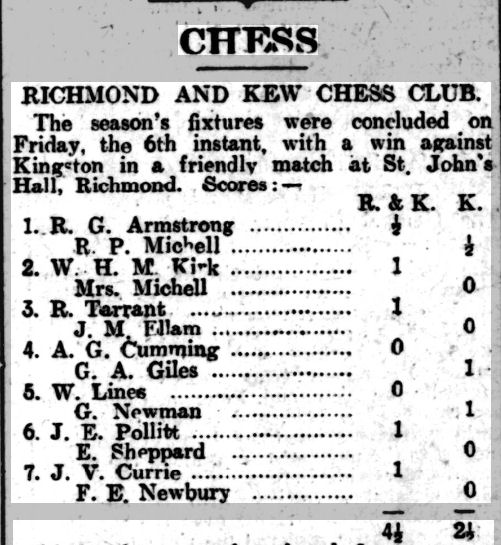
It would appear that the Leicestershire Ladies Champion didn’t survive the First World War, and it was some time before we’d encounter another female player.
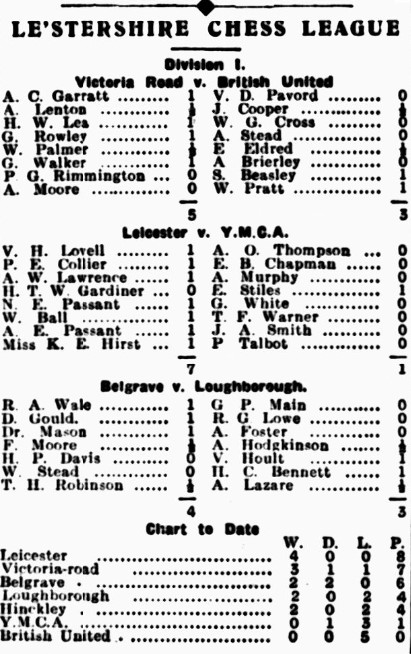
Here is Miss KE Hirst, selected to play for the league leaders in the first division of the league.
Kate Eleanor Hirst was born in 1896, the youngest child of a Baptist Minister. Kate and her immediately older sister Ethel stayed at home their whole lives, Ethel caring for her widowed mother, and Kate doing secretarial work for her brother Thomas, who ran a hosiery business.
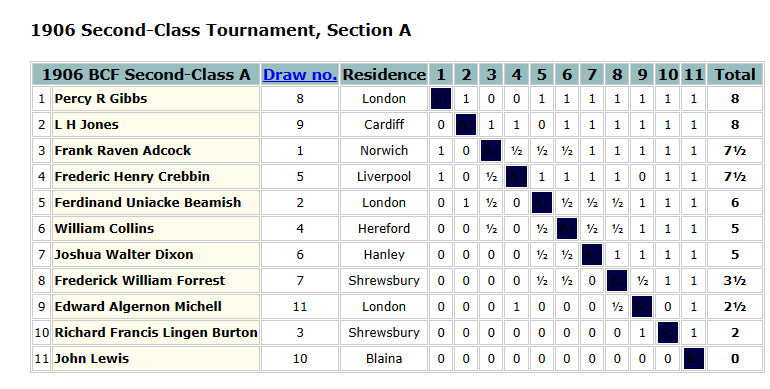
She was a club member for more than three decades, but played rarely in club matches. In 1936 she shared second place in the third division (of four) of the county championship. She also enjoyed a few chess holidays in Margate. In 1936 she scored 2/5 in the Second Class Short Tourney A, where one of her opponents, scoring 1/5, was former Leicester chess lady Lucy Storr-Best. In 1938 she’d been promoted to the Short First Class C section, where she shared second prize on 3/5. One of her fellow competitors in both these events was Marjorie Strachey, sister of Lytton.
In the 1940s she was recorded as playing correspondence chess for her county, and competing in the second division (of three) in the county championship. Kate, it seems, was a player of average club standard, but one who preferred the more social atmosphere of internal competitions to matches against other clubs.
She was still recorded as a member in Don Gould’s Chess in Leicester 1860-1960, but, sadly, her membership didn’t last very much longer.

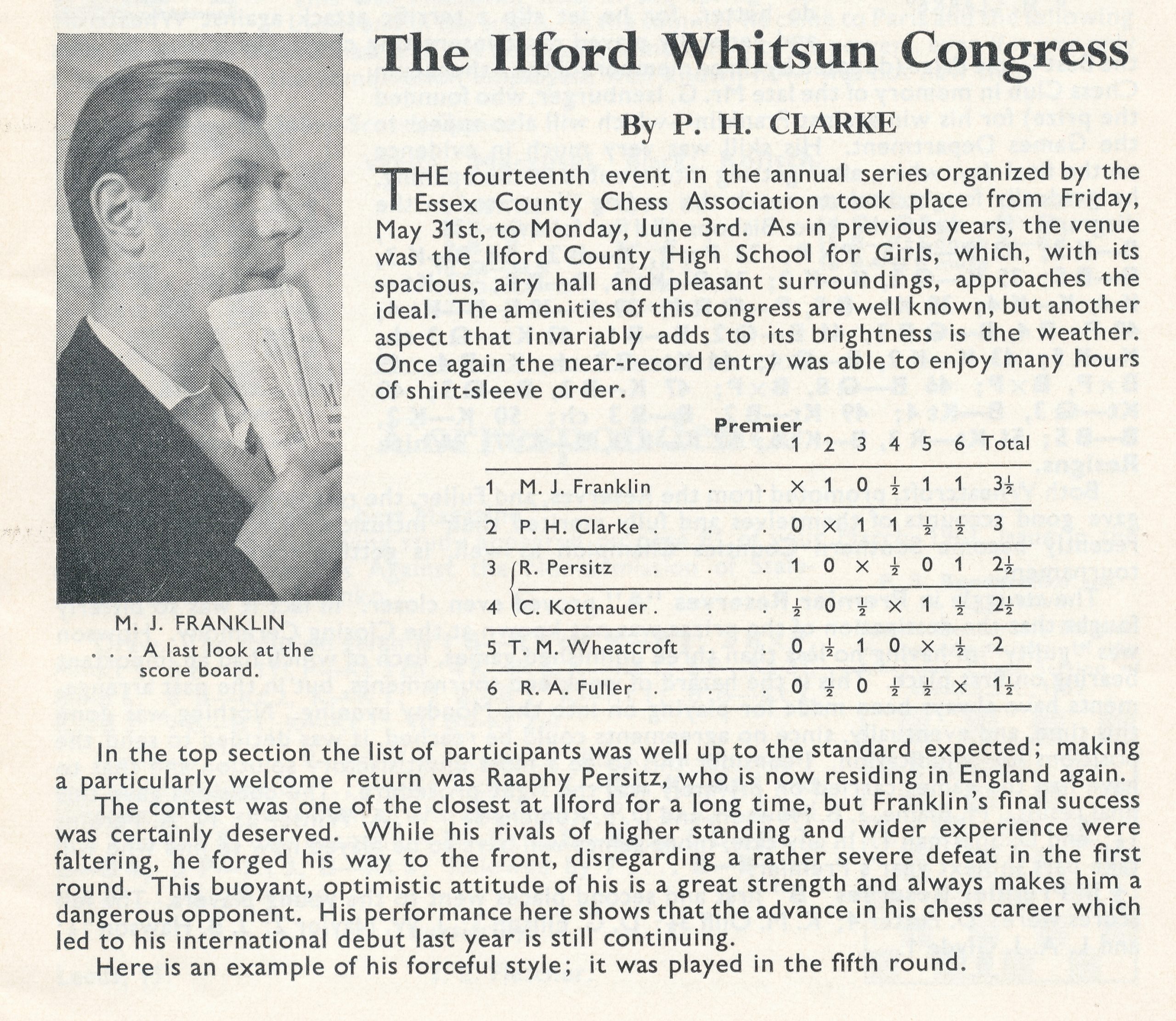
The 1932-33 Hastings Tournament provided some local interest with the emergence of another Leicester Lady Player: Miss Elsie Reid.

Elsie finished in 4th place, as you see: a highly commendable result for such an inexperienced player.
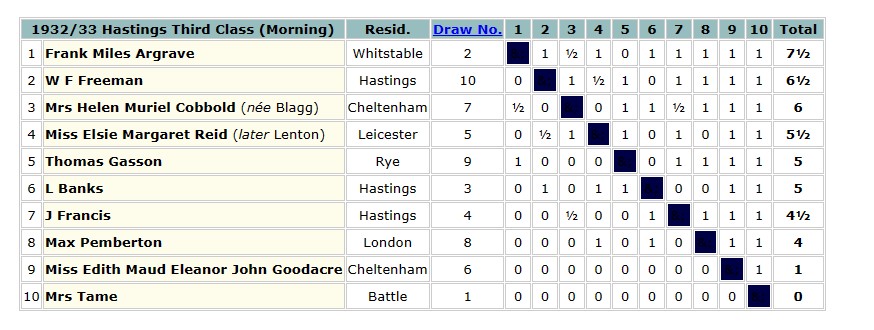
Elsie Margaret Reid was born in Leicester on 20 May 1909, so she was 23 years old at this point. Her father had been born Frederick Neale in East Leake, near Loughborough, in the fourth quarter of 1876, but when his mother married a widower and framework knitter named Isaac Reid, he took on his stepfather’s surname.
By 1901, Frederick had joined the Royal Marines, and, on returning to civilian life, he married Clara Elizabeth Guillain in Leicester in 1908. The 1911 census found them living about 1½ miles east of the city centre, with Frederick working as an engineer’s driller. Another daughter, named Clara Elizabeth after her mother, was born in 1912. On the outbreak of war, Frederick rejoined the Royal Marines, serving in the Light Infantry division. Tragically, he lost his life on 21 May 1915, perhaps in the Gallipoli campaign. He was buried at sea, but his heroism is commemorated on the Portsmouth Naval Memorial.
Clara, then, was left a widow with two young daughters, and, as it happened, her family were around to help out.
Her background was rather more exotic than that of her husband. Her paternal grandfather had been born in France, but, at some point in the mid 19th century, moved to London where he seems to have been working for the French government, perhaps in some sort of diplomatic role. His son, Adolphe, became a chef and confectioner, and, in the mid 1890s, moved with his family to Leicester. One wonders if he had any business connections with Victor Hextall Lovall.
After her husband’s death, Clara had to find a job to make ends meet. The 1921 census records her as a despatch clerk working for Gimson’s shoe machinery company. You might recall the Gimson family from Sydney’s association with chess at Desford Approved School. His father was also, briefly, a member of Leicestershire Chess Club. The two girls were at school, while Clara’s mother was there to carry out home duties, and one of her brothers, another Adolphe, who worked as a shoe clicker, was also living there.
How, one wonders, did Elsie learn chess? Perhaps the Guillain family were players. From 1935 onwards, one of the solvers in Alfred Lenton’s chess column was M Guillain. The only M Guillain around at the time was Elsie’s cousin Margaret, born in Leicester in 1920. Was Margaret a teenage chess problem devotee? I’d like to think she was.
Returning to Elsie’s chess career, she was also playing for Leicester Victoria, alongside Alfred Lenton, in the top division of the league. In this match she lost to reformed juvenile delinquent Phillip Rimmington.

The following year she was back at Hastings, having been promoted from the Third Class to the First Class.
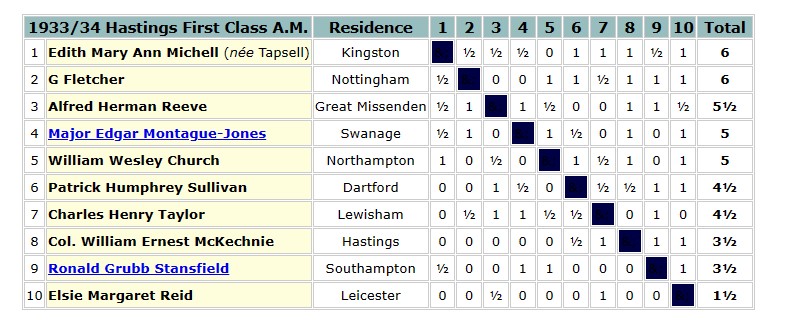
It looks from the results as if she was rather overmatched here, and would have been much better off in one of the Second Class sections.
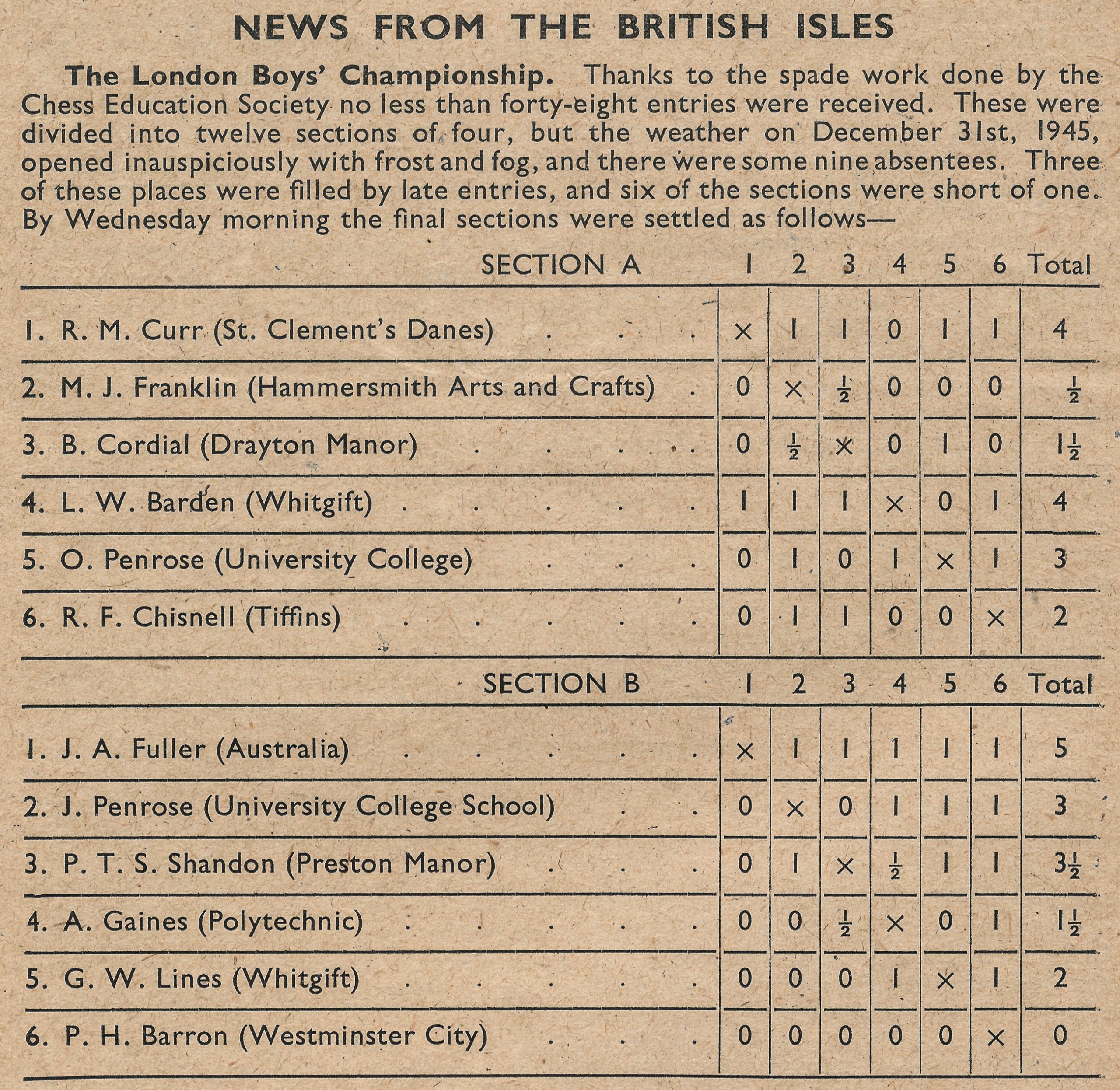
That summer, she was selected to play in the British Ladies’ Championship in Chester. The appearance of a young woman from a working class background must have come as something of a shock to the other players, mostly ladies of a certain age and class. (Not so much of a shock, though, as that provided by Miss Fatima, who had won the title the previous year, also taking part in 1931.
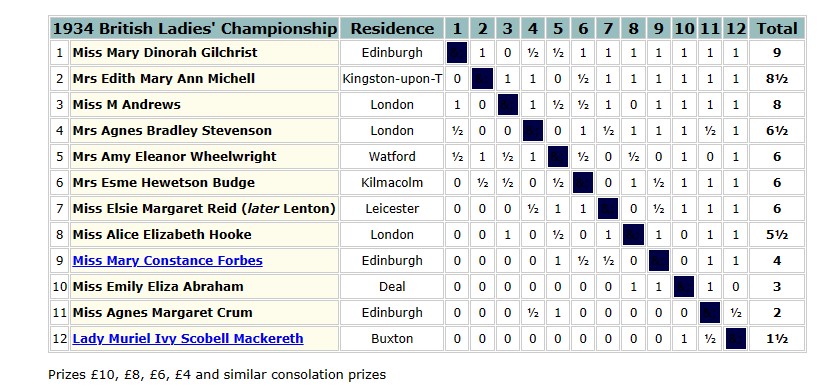
You’ll see she performed very well, with a score of +1. Alfred was clearly impressed.

Here’s the game extract, in which Elsie shows exemplary endgame technique, trading off queens to win the pawn ending. Always good to see!
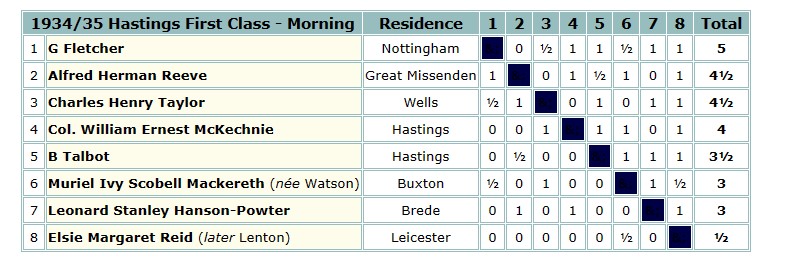
Back at Hastings for the third time that December, she was again placed in one of the First Class sections, meeting several of the same opponents as the previous year, and again rather out off her depth.
 The 1935 British Championships took place in Great Yarmouth. Elsie was rather less successful this time round, only scoring 3½ points.
The 1935 British Championships took place in Great Yarmouth. Elsie was rather less successful this time round, only scoring 3½ points.
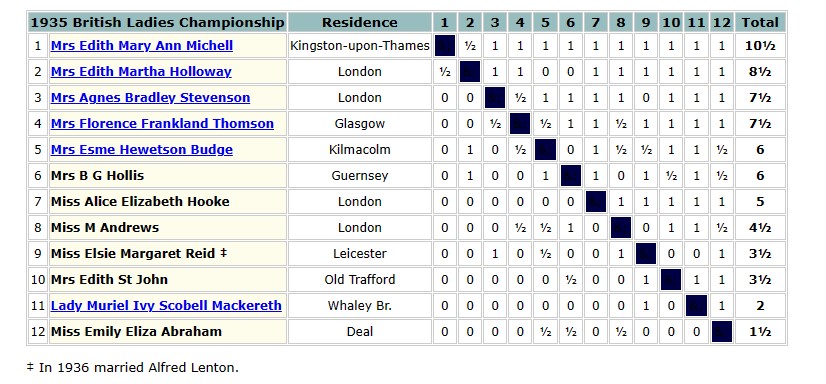
Thanks to Brian Denman for contributing her loss to the tournament winner, whom you’ll meet in a future Minor Piece.
In 1936, Elsie Reid was otherwise engaged, in more ways than one. Her marriage to Alfred Lenton was registered in Leicester in the 4th quarter of 1936.
Now a married woman, she returned to action in Blackpool the following year, this time recording a 50% score.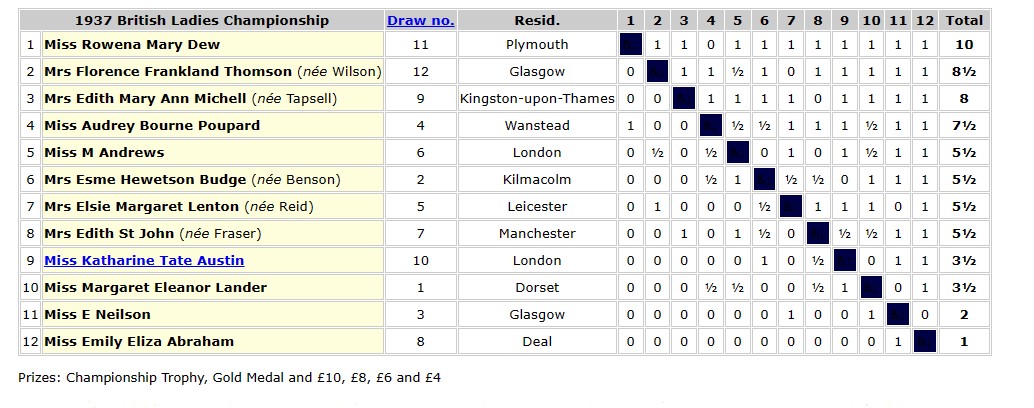
That was to be her last tournament appearance, although she continued to play club and county chess up to 1939.
The 1939 Register records Alfred and Elsie living next door to Alfred’s parents and brothers at 65 Copdale Road Leicester. Her occupation is given as Hosiery Terrot Machinist. A Terrot Machine, since you asked, is a circular knitting machine made by a company of that name in Germany. They’re still making them now, although they had some financial problems earlier this year.
Although she had long since given up competitive play, she maintained her interest in the game for the rest of her life.
In the mid 1970s, Leicester was a hotbed of junior chess. The local papers were full of the exploits of teenage stars such as Mark Hebden, Glenn Flear and Geoffrey Lawton, not to mention a certain Keith Arkell from nearby Warwickshire. I wonder what happened to them. Elsie Lenton was still following the game, and was mentioned here in 1975.

Edwin Breckon Chapman (Dick to his friends) (1906-2001) had been involved in local chess journalism since the 1930s, and was clearly still keeping in touch with Elsie.
Unfortunately, the snippet and game above are the only examples I’ve been able to find of Elsie’s play. Her husband published quite a lot of local games in his column, but none of hers.
Alfred and Elsie’s only child, a son named Philip, was born in 1942. His parents naturally taught him chess, and, as it happens, I played him twice during my time running a Leicester Polytechnic team in the Leicestershire League, when he was representing his parents’ old club. I had no idea at that time he was Alfred’s son.
Anyone familiar with my play won’t be surprised by the results. The first one was undoubtedly drawn in the final position.
In this game, though, I appear to have been winning in the final position. I don’t recall whether we agreed a draw or whether the game was adjudicated.
Elsie Margaret Lenton died in the third quarter of 1991, at the age of 82. Alfred outlived her by 13 years. There will be a lot more to write about him in future Minor Pieces. Don’t you dare miss them!
Sources and Acknowledgements:
ancestry.co.uk
findmypast.co.uk/British Newspaper Archive
Wikipedia
BritBase (John Saunders)
chessgames.com
Brian Denman
Streatham & Brixton Chess Club Blog (Martin Smith)