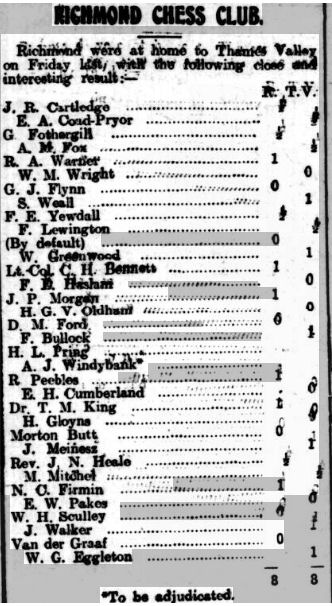
From the publisher:
“The rivalry between William Steinitz and Johannes Zukertort, the world’s strongest chess players in the late nineteenth century, became so fierce that it was eventually named The Ink War. They fought their battle on the chessboard and in various chess magazines and columns. It was not only about who was the strongest player but also about who had the best ideas on how to play the game. In 1872, Johannes Zukertort moved from Berlin to London to continue his chess career.
Ten years earlier, William Steinitz had moved from Vienna to London for the same purpose; meanwhile, he had become the uncrowned champion of the chess world. Their verbal war culminated in the first match for the World Championship in 1886. Zukertort is certainly the tragic protagonist of this book, but is he also a romantic hero? He has often been depicted as a representative of romantic chess, solely focusing on attacking the king. Steinitz is said to have put an end to this lopsided chess style with his modern scientific school. This compelling story shakes up the traditional version of chess history and answers the question which of them can claim to be the captain of the modern school. With his first book, Move First, Think Later, International Master Willy Hendriks caused a minor revolution in the general view on chess improvement.
His second book, On the Origin of Good Moves, presented a refreshing new outlook on chess history. In The Ink War, Hendriks once again offers his unique perspective in a well-researched story that continues to captivate until the tragic outcome. It gives a wonderful impression of the 19th-century chess world and the birth of modern chess. Hendriks invites the reader to actively think along with the beautiful, instructive and entertaining chess fragments with many chess exercises.”
“Willy Hendriks (1966) is an International Master who has been working as a chess trainer for over thirty years. His bestseller Move First, Think Later won the English Chess Federation Book of the Year Award in 2012. In his much-acclaimed second book, On the Origin of Good Moves, he presented a provocative new view on chess history.”
There are always dichotomies, aren’t there? You only have to look at any news website or paper to see them playing out before your eyes. Passionate people on either side of an argument taking extreme views and unwilling to listen to the other side.
In the world of education, for example, there’s the dichotomy between ‘trad’ and ‘prog’, traditional or progressive values, which has been going on, in one form or another, since the days of Rousseau. (Sensible teachers, of course, know that you need some of both.) The same terms are also used in music: perhaps you’re a fan of prog rock, or a devotee of trad jazz.
Let me take you back now to the musical world of the 1850s and 1860s, specifically to central Europe and, in particular, Germany. There were two groups of composers in opposition in what would later become known as the War of the Romantics. Both groups, in very different ways, saw themselves as heirs to Beethoven. The conservative, traditionalist camp was led by the likes of Brahms and Clara Schumann, while, in the opposite corner, were the progressive modernists such as Wagner and Liszt. Nowadays we have no problems listening to the music of both groups with equal pleasure.
Moving forward a couple of decades we come to a very similar war, which, although the camps were led by Central Europeans, took place mostly in London. The Ink War: Romanticism and Modernity in Chess, the subject of Dutch IM Willy Hendriks’ latest book, features Johannes Zukertort flying the romantic flag while William Steinitz sports the colours of Modernity. Two men with, at least if you believe their writings, very different views about how chess should best be played.
This is a successor to the author’s previous book which I reviewed enthusiastically here. Whereas the previous book took a wide-ranging view of 19th century chess history, here we look in more detail at a period of fourteen years: between Zukertort’s arrival in London in 1872 and the first official world championship match, between Steinitz and Zukertort, in 1886.
In the course of 468 pages we meet not just our two protagonists, but a whole host of colourful characters who enlivened the 19th century London chess scene. While we’re given an in depth look at the games of Steinitz and Zukertort, there are many other games included to put their moves in context. A lot of fascinating history, and also a lot of fascinating chess.
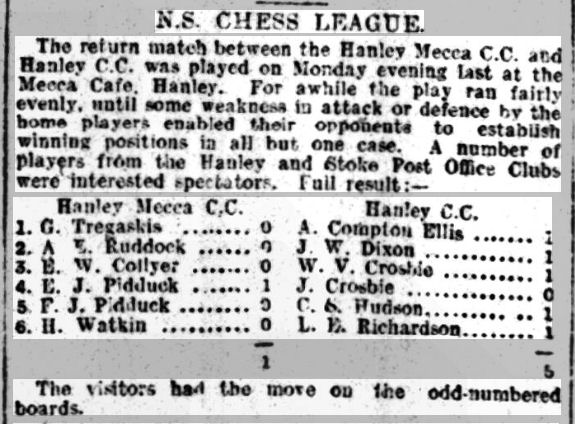
At the time there were very few players making a living out of chess, and, if you wanted to be a professional player, the place to go was London. Steinitz had moved there in 1862, and, not the most likeable of men, soon made enemies. The British Chess Association wanted to put him in his place, and, invited Zukertort, who had just won a match against Anderssen, to London.
As Hendriks relates in his prologue:
This book tells the story of this struggle, which was fought on the chessboard, but also, to a significant extent, in chess magazines and in columns in newspapers. First and foremost, this battle was about who was the strongest, and who could eventually call himself the first World Champion. But there was more at stake. Chess and chess theory were in full development and the ideas about how the game should be played were quite divergent. Steinitz had a very outspoken position and saw himself as the foreman of a scientific modern school. For our story it would be nice if Zukertort represented the other pole, the romantic attacking school, but things are not that simple. The larger public, however, understood the rivalry between the two for the greater part along these lines. Thus, the struggle on and around the chessboard was closely linked to the societal developments of the time, such as the rise of science and technology and the romantic resistance to them.
After introductions to Steinitz and Zukertort, in Chapter 3 Hendriks tackles the question of chess style. This ‘primitive dichotomy’, between tactics and strategy, ‘plays a major role in (traditional) chess history writing.’ ‘The danger of this is that it can easily lead to caricatures’.
Of course these caricatures can be seen in later rivalries as well: Alekhine v Capablanca, Tal v Petrosian, Kasparov v Karpov. The tactician against the strategist.
But, in reality, we’re all just trying to find the best moves.
As you’ll know if you’ve read his previous book, Hendriks takes a different approach, looking at ‘the quantitative changes that led to an increase in chess knowledge and to a higher level of skill’. He’s contextualising the games he demonstrates by looking at what the players would have known from previous experience about the positions on the board.
Here, for example, is Zukertort, just having arrived in London in 1872, playing White against the archetypal tragic/romantic hero Cecil de Vere.
You’ll recognise this as a Sicilian Taimanov, which, almost a century later, would become very popular, but this would have been virgin territory to both players. It’s quite understandable, given what he would have known at the time, that de Vere now blundered with 7… Nge7? (you can play this in similar positions but not here), and likewise impressive that Zukertort found the refutation, Ndb5!, over the board.
In the same event Steinitz and Zukertort met for the first time. Steinitz, playing White, essayed his favourite gambit, based on his belief that the king was a strong piece which could take care of itself.
Here’s the game. Click on any move for a pop-up window.
A strong defensive performance by Steinitz, according to Hendriks, who, understandably, only gives us the first 24 moves. A triumph for materialism over romanticism, you might think. Or equally that Zukertort’s second piece sacrifice on move 12 was tempting but unsound.
Hendriks is at his best discussing the development of both positional and tactical ideas. His contextualisation is both informative and instructive.
In those days the French Defence was considered a dull and even cowardly opening, an opinion which continued well into the 20th century. The justification at the time was that the lines where White plays e5 were considered favourable for Black, so the first player usually chose the Exchange Variation.
In 1875 Zukertort played a match against (the very interesting) William Norwood Potter. In the 10th game they reached this position.
A stark contrast to the Steinitz game above. Zukertort, playing White, saw nothing wrong with winning a pawn: 9. Bxf6 Qxf6 10. Nxd5, but after 10… Qh6 11. h3? Nxd4! he was losing material. The Nxd4 idea is very familiar to most club players today, but back in 1875 it would have been unknown: they would have had to discover it for themselves.
Another idea in this sort of position was for one player to swing the queen’s knight over to the kingside, allowing doubled pawns after a trade on f6. In exchange you get the two bishops and a possible attack down the g-file.
It didn’t work in this game from Paris 1878.
You’ll observe that by no means all the games in this book feature Steinitz or Zukertort.
Chapter 11 is intriguingly titled The discovery of the queenside. In his 1880 match against Samuel Rosenthal, Zukertort switched from his usual Ruy Lopez to the Queen’s Gambit. This was by no means a new opening: it dates back to Greco and de Labourdonnais played it on many occasions against McDonnell. In those days the Queen’s Gambit, like the King’s Gambit was usually accepted: after all accepting gambits was the chivalrous thing to do. Rosenthal preferred to decline Zukertort’s gambit, and, in the 9th match game White was able to carry out his favourite plan of a queenside pawn roller, playing an early c5 followed by advancing his a- and b-pawns.
In the 9th game of the match he reached this position, with White to play.
Any strong player will start by considering Rb6, having seen the idea many times before in games played by the likes of Botvinnik and Petrosian. Stockfish agrees that it’s the best move here. Zukertort saw it but, not having had the advantages we have, mistakenly rejected it, eventually drawing a favourable ending. As Hendriks demonstrates, 12 years later, in a very similar position against Chigorin, Steinitz, who had learnt from this example, did indeed play Rb6 with success.
Again and again, throughout the book, we see examples of ideas which are familiar to us now, but would have been new at the time.
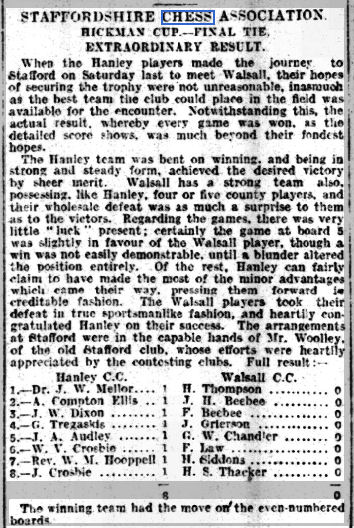
By 1881, as Hendriks relates, Steinitz and Zukertort were engaged in a war of words over the analysis of recent chess games: the Ink War. The war was not just about the rights and wrongs of particular moves, but about how games should be annotated: a debate which is still continuing today. Zukertort tended to publish long variations while Steinitz took a more scientific approach.
It was generally understood that Steinitz was, following Morphy’s retirement, the strongest player in the world (EdoChess ranks him top from 1868 onwards) but he hadn’t been active since his 1876 match against Blackburne, and his last tournament had been Vienna 1873. Questions were now being asked as to whether Zukertort was now stronger, so Steinitz decided to return to the fray in 1882, again in Vienna.
This was the strongest tournament yet held, and resulted in a very exciting finish. Steinitz and Winawer shared first place, a point ahead of Mason, with Zukertort and Mackenzie another half point behind, but Zukertort scored 1½/2 against his arch rival.
Another strong tournament took place in London in 1883, and again Steinitz and Zukertort took part.
Here’s Zukertort’s exciting Round 3 encounter with Mason.
White had the draw in hand before blundering on move 57. Curiously, Mason lost the return encounter with Zukertort through a very similar oversight.
Hendriks comments: Such small tactics were often missed in those days, as back then the possibilities for training your tactics were minimal. Today’s diligent student solves more tactical puzzles in a day than the old masters did in their entire lives.
This is one of the themes of both this and his previous book. We might assume that the 19th century greats didn’t have today’s opening knowledge but were equally good at tactics. Hendriks’ view, reinforced by many examples here, is that they weren’t – and unsurprisingly so, as they didn’t have the opportunities for practice and training. Zukertort himself was particularly prone to blunders which would have shamed your club’s third team players.
It was in Round 6 of this game when Zukertort played his Most Famous Game, to which Hendriks develops a whole chapter.
With three rounds to go, Zukertort had reached the extraordinary score of 22/23, losing only to Steinitz in the first cycle, but he then lost his last three games, two of them to the tournament tail-enders. Was this due to problems with his health, or with the medication he was using to treat his health problems, or just a random occurrence? Hendriks considers the evidence here.
Finally, we move onto the 1886 World Championship match. By that point Steinitz had moved to America, and Zukertort was also spending time there, so the contest took place in New York, St Louis and New Orleans. Most of the twenty games are full of interest, and Hendriks contextualises and analyses them in depth.
Ironically, the ‘modernist’ Steinitz opened with the king’s pawn in all his white games, while the ‘tactical’ Zukertort, in all but one of his white games, chose the supposedly more modern and positional Queen’s Gambit. This demonstrates, I suppose, that the dichotomy between them was more about a personality clash than anything else, although, by this point, the two men seemed to have been on tolerably friendly terms.
Several of Zukertort’s white games reached IQP positions, which were, at the time, very little understood, so are of some historical interest.
Here’s the 9th game.
Hendriks has some interesting things to say about the hanging pawns position after Black’s 22nd move, which will give you some idea of his annotation style.
The exchange of pieces in the past few moves did not help White, but Zukertort apparently had a lot of confidence in his attacking chances in this position. However the beautiful knight on e5 can be chased away, and White does not have that many pieces to strengthen his attack either, so he no longer has the better chances. Therefore, this was a good moment for the quiet move 23. h3. Many contemporary players would play this way, but in those days such a prophylactic move was not a matter of course. The idea of prophylaxis would only be introduced a quarter of a century later by Aron Nimzowitsch. This strategy consists of improving one’s position and protected potential weaknesses even before they are threatened.
Steinitz won the first game in brilliant style, but Zukertort then won four in a row. After that, with Zukertort’s health problems worsening, it was mostly one-way traffic, with Steinitz emerging a convincing winner by 12½ to 7½, becoming the first official world champion.
The end of the story is rather sad: Zukertort’s standard of play and health both declined rapidly, and he died in London two years later.
I thoroughly enjoyed this book, just as I did its predecessor. Willy Hendriks is a born storyteller: the book is grippingly written. You’ll always want to turn over the page to see what happens next. If you thought chess history was boring this book may persuade you to think again. It’s beautifully produced and copiously illustrated. I suppose more serious chess historians than me might regret that it’s not as fully referenced as you’d expect from an academic history book, but it’s quite understandable that the author and publisher would take the approach they chose. The English is fluent and highly readable, if not always totally idiomatic. I found one or two minor mistakes, but they didn’t interfere with my enjoyment. If you’re interested in improving your rating, the book is there to help you as well. As with many books from this publisher, most chapters are preceded by puzzles based on games discussed within: if you feel inclined you can attempt to solve them before reading on. If you love, as I do, 19th century chess history, you won’t want to miss this book. You don’t just get the games: there’s a lot of engrossing information about the leading personalities of the day and the way top level chess was organised as well.
You might want to start, if you haven’t read it already, with On the Origin of Good Moves, which is more general and wide-ranging, before continuing with this book. You may not agree with all the author’s opinions and conclusions, but you’ll find something thought-provoking on every page. This is the ideal chess book for me and goes straight into my list of all-time favourites. I can’t wait to see what Willy Hendriks writes about next.
Richard James, Twickenham 5th June 2023

Book Details:
- Softcover: 468 pages
- Publisher: New in Chess (30 Nov. 2022)
- Language: English
- ISBN-10:9493257649
- ISBN-13: 978-9493257641
- Product Dimensions: 17.22 x 1.52 x 23.65 cm
Official web site of New in Chess.
You can read some sample pages here.





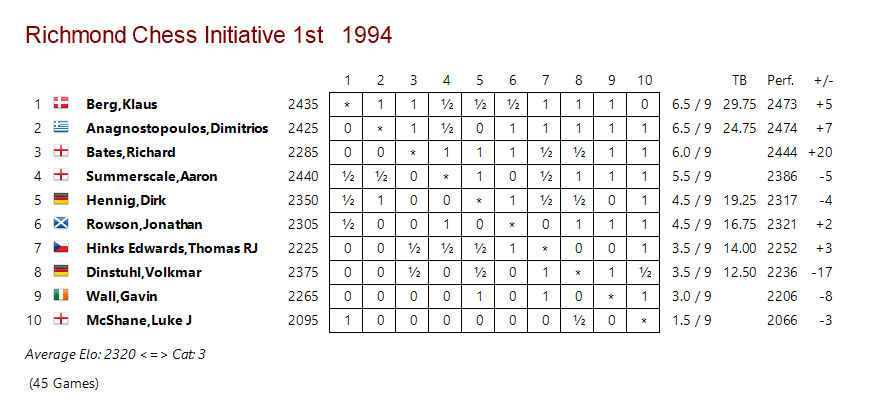



















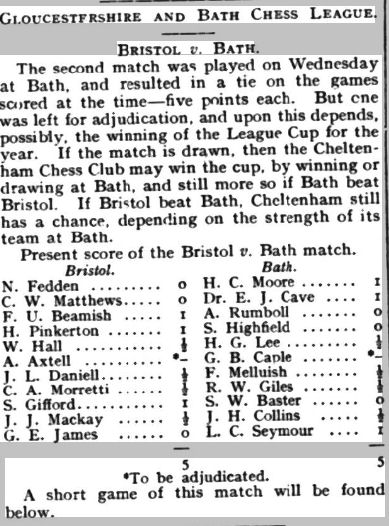
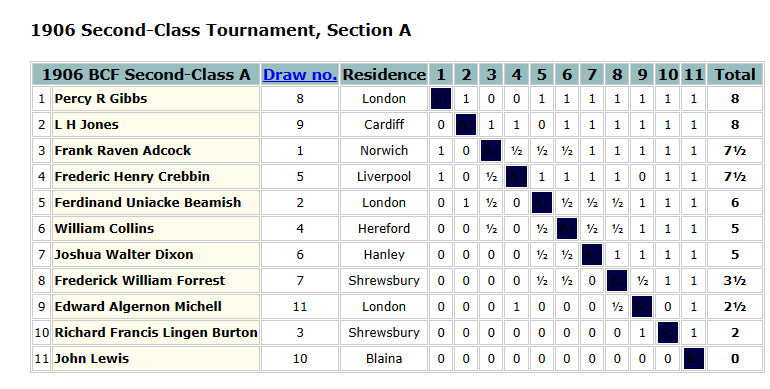



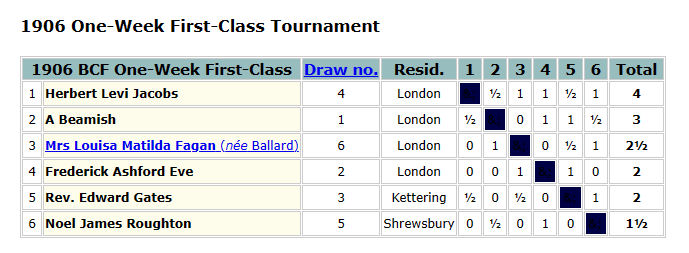
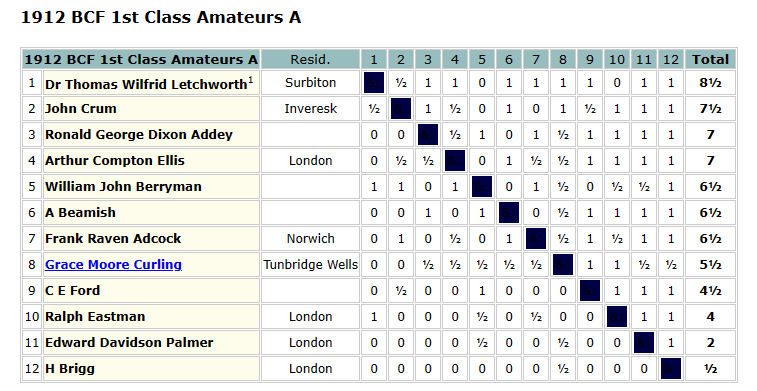
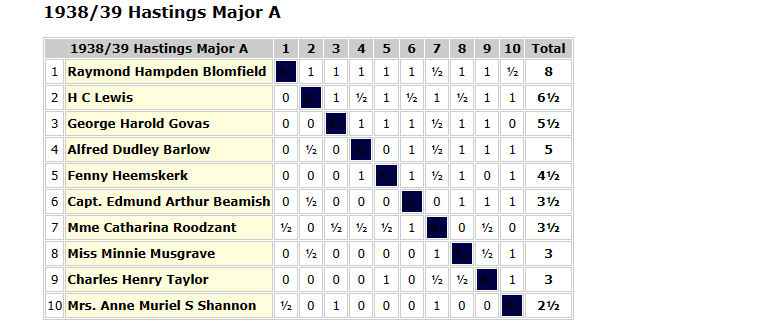








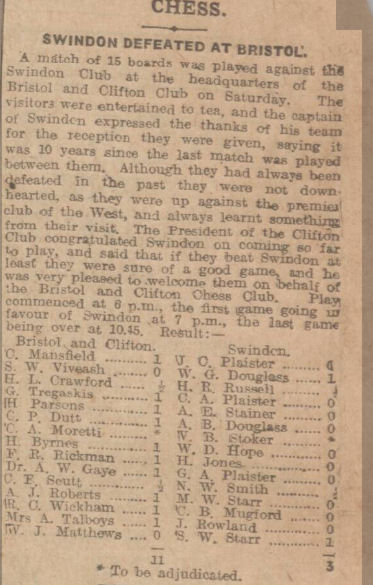
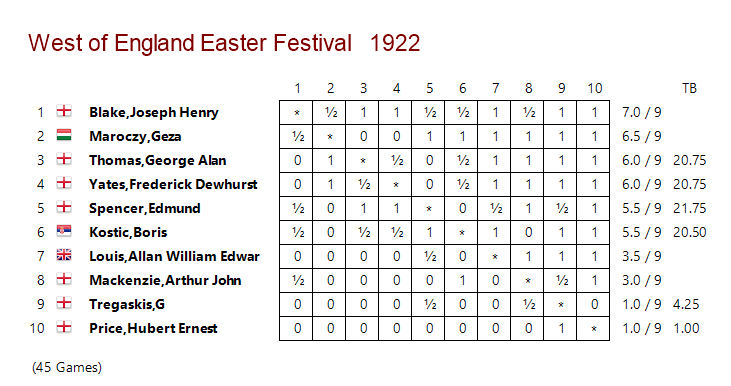





 With a score of 10½/11, it was clear that he was improving fast, and should have been in at least the 2nd Class division. The prizes were presented by none other than
With a score of 10½/11, it was clear that he was improving fast, and should have been in at least the 2nd Class division. The prizes were presented by none other than