If you’ve been following these articles you’ll have met quite a lot of Twickenham Chess Club members from the 1880s and 1890s. You might have noticed they all had several things in common.
They were all male, and, although they followed a wide variety of occupations, they were all from well-off upper middle class backgrounds. There was a bit of social mobility, it’s true: Wallace Britten came from relatively humble origins, while on the other hand, Arthur Sabin Coward’s family had some problems caused perhaps by his fondness for the demon drink.
For several years the club advertised in the Surrey Comet at the start of the season. This is from 1889 when timber merchant’s clerk John May Gwyn (1860-1930) had just taken over as club secretary from Wallace Britten.

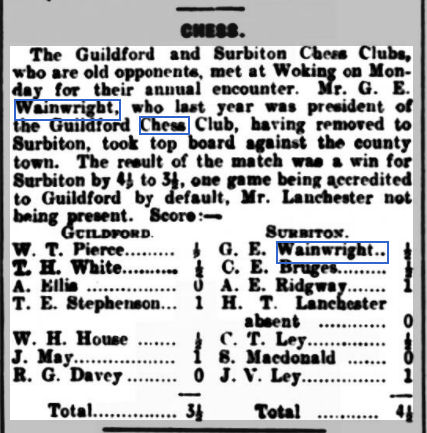
Note that it welcomes ‘gentlemen’ – not ladies and certainly not working class plebs. (The annual Gentlemen v Players cricket matches, the first of which were played in 1806, were very important at the time, and would continue until 1962.) Following our investigation into the life and career of George Edward Wainwright we have one more gentleman to meet.
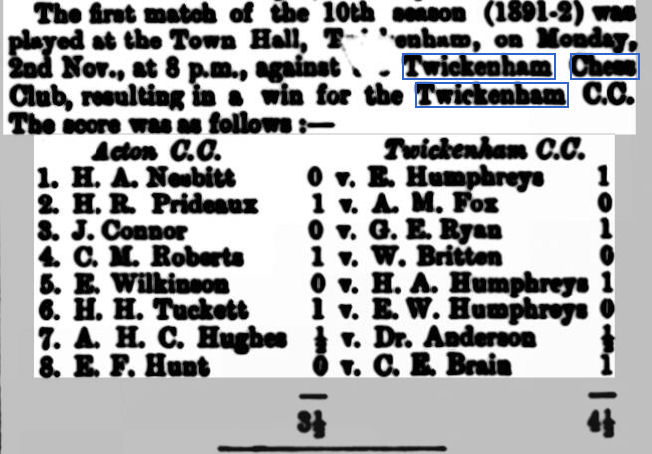
In March 1896 Twickenham scored a notable success against the powerful Metropolitan Chess Club (still going strong today). You’ll see some familiar names there: members of the Humphreys and Ryan families, for example, but with a new name on top board: T E Harper won his game against James Mortimer, a regular competitor in international tournaments.
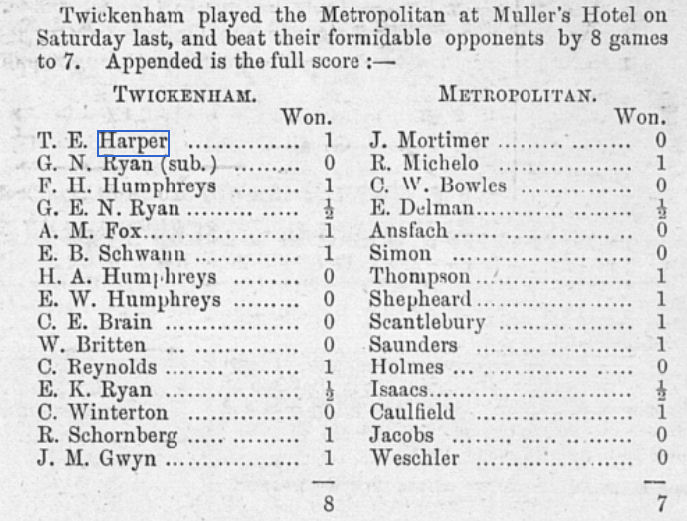
He also won the 1895-6 Handicap Tournament of Twickenham Chess Club with a perfect score, so he was clearly a strong player.

Was he a promising youngster? No – he was a much older player who had just moved into the area.
Thomas Etheridge Harper, a solicitor by profession, had been born in Suffolk village of Hitcham: his birth was registered in the second quarter of 1839. He married Mary Jane Cousins in Dorking, Surrey in 1866, and, in between having 11 children, moved around quite a bit, spending time in North London, Hertfordshire and Essex before moving to Richmond, presumably round about 1894.
The 1901 census found Thomas and Mary Jane at 100 Sheen Park, Richmond, just off Sheen Road very near the Red Cow, where Richmond & Twickenham Chess Club met in the 1960s, along with their two youngest children.
It seems like he may have had previous form: there are records of a T Harper playing in handicap tournaments in London in 1869 and 1871, giving odds to the likes of Augustus Mongredien Junior and the artist Wyke Bayliss, both pretty strong amateurs, playing the wonderfully named problemist Edward Nathan Frankenstein, and only taking odds from Cecil de Vere. It seems quite likely this is the same player.
(Just as an aside, there’s more about Wyke Bayliss in this highly recommended book.)
Rod Edwards also asks: A ‘Harper’ played against Janssens in 1859 (see Chess Player’s Chronicle, 1860, p.60) and in a consultation game with Zytogorski against Harrwitz and Healey in 1863 (see Chess Note 4783). Is this the same ‘Harper’? I guess it’s possible. Especially when you come across this problem, composed by T E Harper of London.
White to play and mate in 4 moves (Norfolk News 5 January 1861)
Why not have a go at solving it yourself? The solution is at the end of the article.
This was presumably the same T E Harper, who was the secretary of the Sussex Hall Chess Club, which seems to have met in Sussex Hall, Leadenhall Street, London, the livery hall of the Bricklayers’ Company. Was it our man? The chances are it was, but I don’t know for certain.
So it seems he was briefly active around 1860, again around 1870, but then, as it does, life got in the way, and he was only able to return to the game once his children had grown up and his work commitments, perhaps, lessened. Moving into an area not far from a strong chess club would also have helped.
A few months after Thomas Etheridge Harper’s success the club had an important announcement to make.

There you have it: Twickenham Chess Club changed its name when it moved down the road to Teddington, to the Clarence Hotel, now the Park, right by the station a couple of minutes from the Adelaide.
(Further articles will reveal how the Thames Valley Chess Club eventually merged with Kingston Chess Club. So the players you’ve been reading about over the past few months have, in effect, not been my great predecessors at Richmond & Twickenham Chess Club, but the great predecessors of my friends at Kingston Chess Club.)
I guess it made sense: most of the club administrators, then as now, lived in the Twickenham and Teddington area. The move would have not been such good news for those who, like Thomas Etheridge Harper, lived the other side of the river.
But no matter: there was a new kid on the block, a new club which really was the predecessor of the current Richmond & Twickenham Chess Club, and Harper was already a member.
Here’s the Morning Post in 1894.

The Castle, right by the river and opposite the Town Hall, where Richmond & Twickenham Chess Club would meet for a few years in the early 1970s, would, in 1912, be the venue for the British Championship, and whose proprietor back in 1851, Benjamin Bull, was the grandfather of future Twickenham and Durban Chess Club champion Cecil Alfred Lucas Bull.
When the Richmond & Twickenham Times is finally digitised I’ll be able to find out more, but perhaps Mr H L Pring was the new club’s prime mover. Horace Lyddon Pring (1870-1938) seems to have been an ambitious young man. (His name appears in various sources as ‘Mr Bruin’ and ‘Mr Priory’: perhaps his handwriting wasn’t especially legible.)

Sadly, the local library refused to display an advertisement for the new club, but Horace can only be praised for making the effort. Some 70 years later, when my mother asked in the local library about chess clubs, they were only too happy to point her in the direction of what had only fairly recently become Richmond & Twickenham Chess Club.
He was soon arranging matches, but at this point they were only strong enough to take on Twickenham’s 2nd team.

By now, chess leagues providing competitions between clubs were in full sway, and Richmond started to take part in leagues run by the Surrey County Chess Association. The Surrey Trophy was first played for in the 1883-4 season, and in 1895-96 a second division, the Beaumont Cup was added. Both these competitions – with a number of lower divisions as well – are still popular and successful today.
Richmond entered the Beaumont Cup and, in 1896-97 were successful in winning the trophy.

Twickenham/Thames Valley, being north of the Thames, were presumably not eligible for Surrey competitions, although an unsuccessful attempt had been made to play in the London League, founded in 1888, in 1893. Twickenham entered the second division but had to withdraw as they were unable to field enough players.
For now, let’s return to our protagonist, Thomas Etheridge Harper. He soon found himself playing on top board for the young and upwardly mobile Richmond Chess Club with considerable success.
At that point there were close connections between Richmond and Windsor Chess Clubs, and two friendly matches, one at each club’s venue were arranged every year. The Windsor and Eton Express, with great excitement, published colourfully breathless reports of these encounters.
This, perhaps, was the first.

You’ll notice a few points of interest. The Richmond Chess Club had moved from the Castle Hotel to the Station Hotel, and, only 2½ years after its foundation, with no assistance from social media, or even notices in libraries, already had 40 active members. Pretty good going, I think, from the enterprising young Mr Pring and his colleagues. You’ll also see that Windsor had a celebrity top board in Sir Walter Parratt, Master of the Queen’s Musick, who was paired against our protagonist Thomas Etheridge Harper.
After winning the Beaumont Cup, Richmond ambitiously decided to enter the Surrey Trophy, the competition to discover the strongest club in the county. In this 1899 match, against a powerful South Norwood team (they’re still active in Surrey today) they found the going rather too tough.
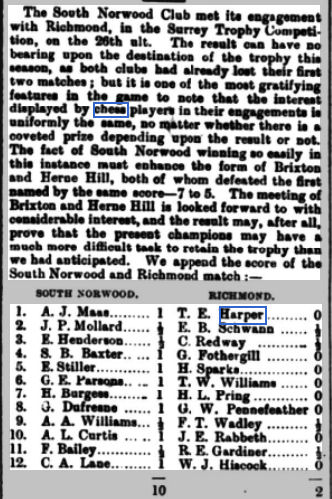
Here, the only specimen of Harper’s play I’ve been able to find (if you come across any more do let me know) is his loss on top board against Arthur James Maas (1857-1933). Maas is certainly worth a future Minor Piece: he showed considerable promise in chess as a teenager, but preferred to focus on his work with the Anglo-Swiss Milk Company (now part of Nestlé) where he claimed to have been the first to suggest selling milk in tins.
It’s clear from the way the Norwood News introduced the game that Harper had a big reputation as a solid player.

Thomas Etheridge Harper’s last match for Richmond I’ve been able to find so far was in 1902. At some point he moved from Richmond to Surbiton: the 1911 census recorded Thomas, still working as a solicitor, his wife and a domestic servant at 323 Ewell Road. He died there on 6 January 1915 at the age of 76 (according to official records, but by my calculations, unless his birth was registered very late he was 75), leaving £632 9s 2d to his wife. His probate record also gives an address in the City of London, presumably the address of his legal practice.
It appears he was a strong player who, due to demands of work and family, played very little chess over the years. He should be remembered for his part played in developing Richmond Chess Club in the early years of its existence.
Join me again very soon as I introduce you to some more members of Richmond Chess Club in the 1890s.
Problem solution: 1. Ra5+! Kxa5 2. Rb5+ Ka4 3. Ra5+! Kxa5 4. Bc3#
Sources/credits:
ancestry.co.uk
findmypast.co.uk
EdoChess.ca
Wikipedia
Annotations using Stockfish 14/ChessBase
Various other sources: links above.