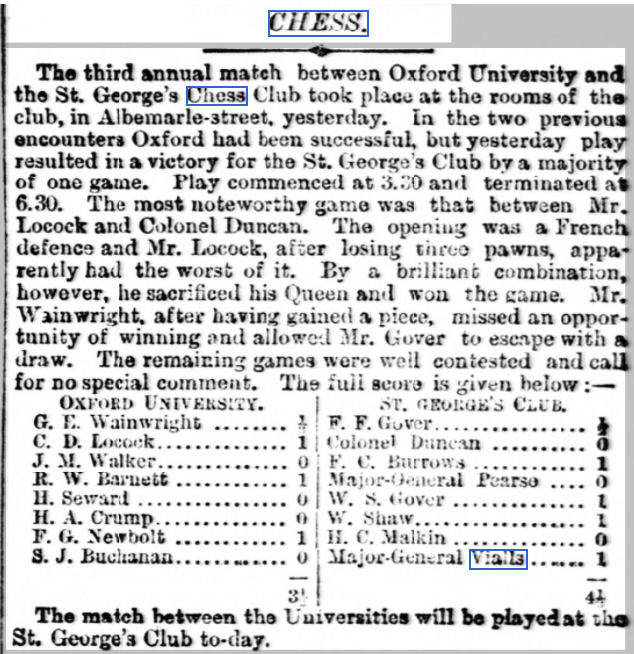
Last time I left you in 1980, when Mike Fox had moved to Birmingham, leaving me in charge of Richmond Junior Club, whose membership included a growing number of very strong and talented young players, inspired by Mike’s teaching and charismatic personality to excel at chess.
I had been the backroom worker to Mike’s front man, but now, reluctantly, I was the front man as well.
My forte was organising rather than teaching, and, wanting to provide experience of serious competitive chess, I ran regular training tournaments for our strongest players.
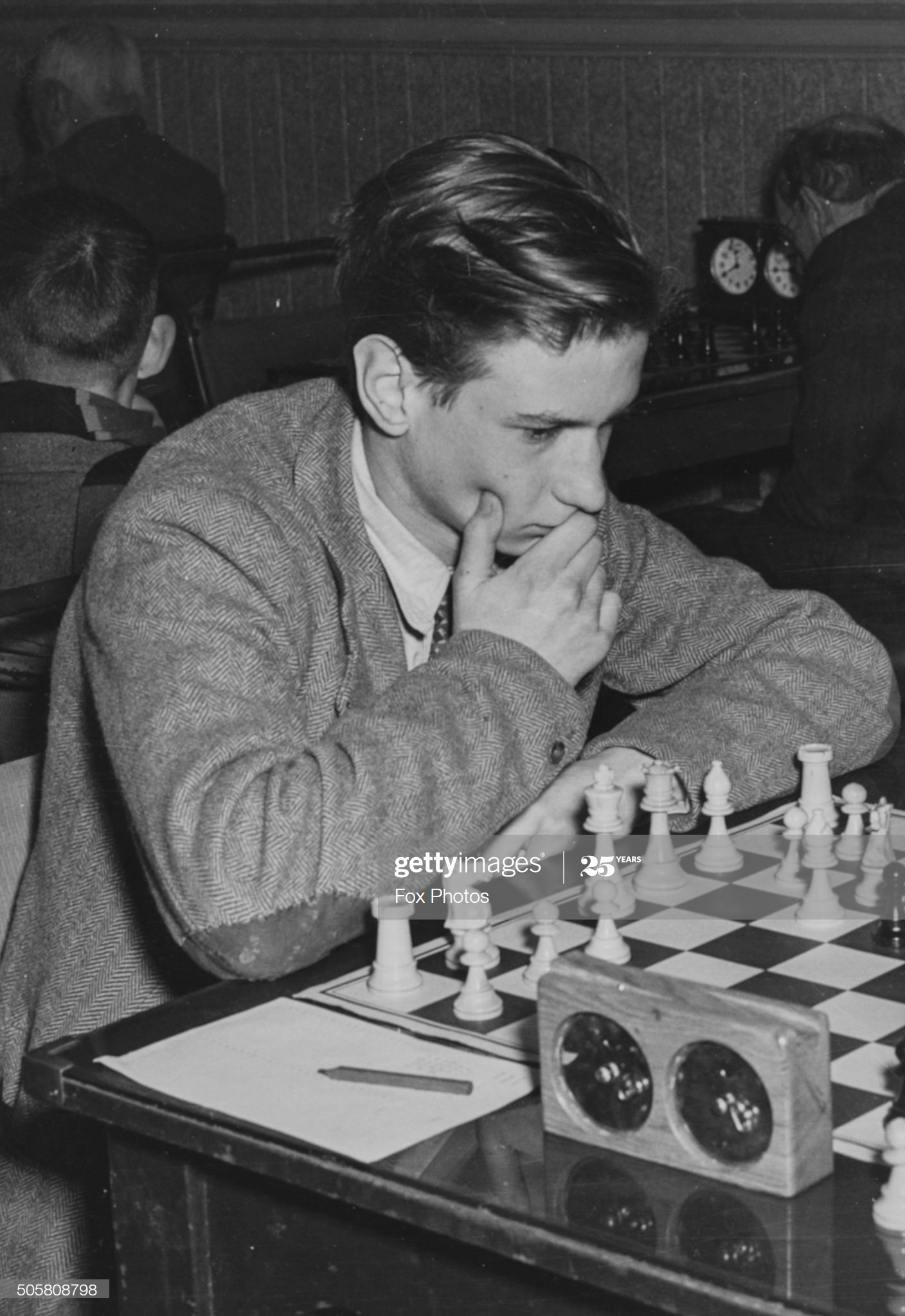
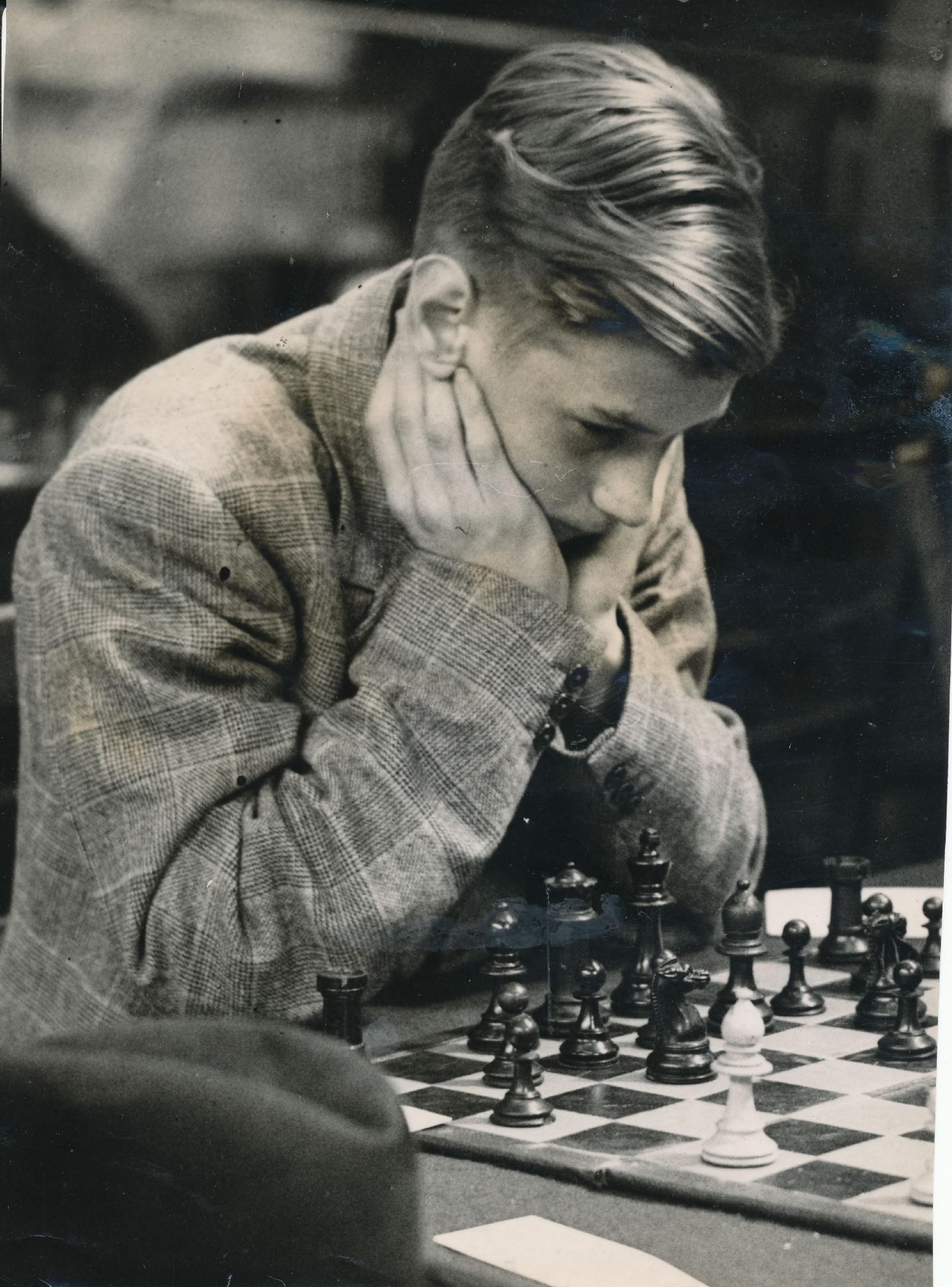
Here, for instance, is a game from a 1981 training tournament. Aaron Summerscale is now a grandmaster and chess teacher. Nick von Schlippe is now an actor, director and writer, but maintains his interest in chess. Nick was one of a quartet of outstanding players from Colet Court/St Paul’s along with Harry Dixon (now playing chess in South East London), Michael Arundale and Michael Ross.
Click on any move of any game in this article for a pop-up window.
To give you some idea of our strength four decades ago, the leading scores in the 1982 Richmond U14 Championship were:
Nick von Schlippe 5/6
Demetrios Agnos (now a GM) 4½/6
Michael Ross 4/6
Philip Hughes 3½/5
Gavin Wall (now an IM and, for many years Richmond London League captain), Ben Beake, Harry Dixon, Sampson Low (currently secretary of Richmond & Twickenham Chess Club) 3½/6
Ali Mortazavi (now an IM) 3/5
Mark Josse (now a CM), Rajeev Thacker 3/6
and 6 other players, including Chris Briscoe (now a CM).
Here’s a game from that event for your enjoyment.
The results of our 1983 Under 14 Championship told a fairly similar story.
Scores out of games played (there are either two missing scoresheets or two players took byes in Round 4 and two didn’t play in Round 6) were:
Gavin Wall 6/6
Demetrios Agnos 4½/6
Philip Hughes 4/6
Harry Dixon, Ben Beake, Chris Briscoe 3½/6
Aaron Summerscale 3/5
Michael Ross, James Cavendish, Rajeev Thacker, Mark Josse, Bertie Barlow 3/6
Ali Mortazavi 2½/5
Leslie Faizi 2½/6
Grant Woodhams 2/6
Alan Philips, Chris Bynoe 1/5
Daniel Falush 0/6
At some point I’d acquired a copy of Chess Life and discovered that the members of our small suburban junior chess club were, over the top few boards and applying the conversion factor in use at the time, stronger than the juniors in the whole of the USA.
The significant factor in all this is, for me, not just the strength of the players, but how many are still playing, or at least keeping up with the chess world, and, even more so, how many I’m still in touch with, or have spoken to on social media, almost 40 years on. Talking to them now, they always have very fond memories of their time at Richmond Junior Club.
What we were doing, although I wasn’t aware of it then, was building a lifelong chess community. Producing future GMs and IMs was merely a by-product of the actual purpose.
But it was clear that, as the younger players coming into the club were less strong and less interested than their predecessors, changes had to be made. Perhaps I needed someone who was a much better chess teacher than me and, like Mike Fox, had the charisma to attract strong new members into the club. There was no doubt who the best chess teacher was in my part of the world: Mike Basman. He agreed to help and, for a time in 1983-84 we worked together.
Of course, Mike was, and still is, brilliant, but he’s also a maverick, someone who, like me, prefers to do things in his own way. There were a couple of issues, in particular, where we disagreed.
Mike has always been known for his love of eccentric openings, and he’d sometimes give lessons on these. My view was different: children should, in the first instance, be given a thorough grounding in all the major openings. If they decide later that they want to experiment, that’s fine, but understand the basics first.
My second point was that we were inviting near beginners to training tournaments where clocks and scoresheets were used. My view was, and still is, that children should be able to play a reasonably proficient game without giving away pieces before clocks and scoresheets are used. Clocks and scoresheets add to the game’s already bewildering complexity and, if children are not used to them, they will concentrate too much on remembering to press their clock and working out how to write their moves down and forget about how to play good chess.
This is still one of my big problems with junior chess today: we’re putting children who barely know how the pieces move into tournaments with all the accoutrements of proper grown-up chess: clocks, arbiters, strictly observed silence, touch and move. My view is that this is totally wrong, but, even more so today than 40 years ago, I appear to be in a small minority. Very often, these days, parents are insisting that their children should take part in serious external competitions before they’re ready in terms of both chess and emotional development.
You’ll find out next time how I addressed these two issues over the following years. I had to find my own methods of doing exactly what I wanted. If anyone else wanted to come in with me, that was fine, but I was never going to compromise on doing it someone else’s way rather than mine.
Meanwhile, in April 1984 we were offered the chance of a simul given by Hungarian GM Zoltan Ribli, who at that time was ranked 13th in the world with a rating of 2610. Although we had to pay quite a lot for the privilege, this was too good an offer to turn down. According to the scoresheets that were handed in he scored +13 =4 -2: again, a pretty good performance for a suburban junior chess club! Here’s one of his losses.
At that time, we were constitutionally part of Richmond & Twickenham Chess Club, and our accounts were incorporated in theirs. Up to that point we’d made a reasonably healthy profit each year, but in 1983-84 we had only just broken even. At the 1984 AGM the RTCC treasurer wasn’t impressed, thinking we might jeopardise the club’s finances in future, and uttering the immortal words ‘What’s a Ribli Simul?’. (Strangely enough, the other day I chanced upon a record of him playing in a simul some 35 years or so earlier!)
Our turnover was also much larger than that of RTCC so it seemed sensible that we should declare financial independence. I would remain on the committee as the officer responsible for junior chess, providing a link to RJCC. (I still hold that post today, but without the RJCC link.) We already had a parent, Derek Beake, serving as our Treasurer, a role he’d occupy for 22 years, long after his son Ben had given up competitive play.
In 1985 we were again offered the chance of a simul given by a world class player, in this case by local GM John Nunn, who, at the time, was ranked joint 11th in the world (one place behind Ribli) with a rating of 2600. This time we invited a few of our friends from Richmond & Twickenham Chess Club to join us.
Out of 23 games, John scored 14 wins, 6 draws and 3 losses, to RTCC’s Paul Johnstone, a slightly pre-RJCC Richmond Junior (someone suggested the other day I should write something about the pre-RJCC Richmond Juniors, which perhaps I should), to future GM Demetrios Agnos and to the unheralded Leslie Faizi, who had also drawn with Ribli the year before.
Even our lesser lights from that generation could play pretty good chess. Here’s a draw against Alan Phillips, who had beaten Ribli the year before (and who contacted me on Twitter a few years ago).
Yes, many of our stronger players from a few years earlier still kept their association with the club, and with chess in Richmond in general (and some of them still keep that association in the 2020s), although they had now outgrown our Saturday morning sessions. We were also no longer successful in attracting strong players into the club. (I suspect, looking back, they just weren’t around in our area: these things come and go.)
I knew I needed to make changes, and that I had to find my own way of running the club rather than trying to work with anyone else.
I wanted to separate the club in order to differentiate between the players who were able to play a proficient game, and who needed experience playing under more serious conditions using clocks and scoresheets, and those younger and less experienced players who were not yet able to play fluently without making regular oversights.
By now home PCs had become available. I was able to use my (admittedly limited) programming skills to write a grading program in BASIC for my BBC Micro into which I entered all our internal club results. I used a pseudo-BCF system with a crude but reasonably effective iterative process providing anti-deflation factor which would take into account my assumption that our members were either improving or remaining stationary at any point.
This gave me the information to decide, by monitoring all the internal results of all our members, which players should be in which group. The decision was made – and my intuition again turned out to be correct (although it’s not how things work today) – that players of primary school age would move up to the higher group when they reached a grade of 50 (equivalent to 1000 Elo). I’ll write a lot more about this, either here or elsewhere, later.
By the start of the 1986-87 season the club had become something totally different. Two things had also happened which would have an enormous impact on the club’s further development.
You’ll find out what they were, and a lot more besides next time.